Quiz Summary
0 of 99 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 99 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), 0
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Audio(s)/Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- Anatomic Distribution 0%
- Arrhythmia 0%
- Bundle Branch Blocks 0%
- Chamber Enlargement 0%
- Conduction Disturbances 0%
- Electrolyte Derangements 0%
- Environmental/Toxicologic Emergencies 0%
- Ischemia 0%
- Ischemia Mimics 0%
- Left Axis Deviation 0%
- Left Ventricular Aneurysm 0%
- Low Voltage 0%
- Narrow Complex Tachycardia 0%
- Normal 0%
- Pacemakers 0%
- Right Heart Strain 0%
- Standard Interpretation 0%
- STEMI 0%
- Ventricular Preexcitation 0%
- Wide Complex Tachycardia 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 99
1. Question
According to the ACCF/AHA guidelines, thrombolytics should be given if a STEMI transfer is expected to take more than how many minutes?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 99
2. Question
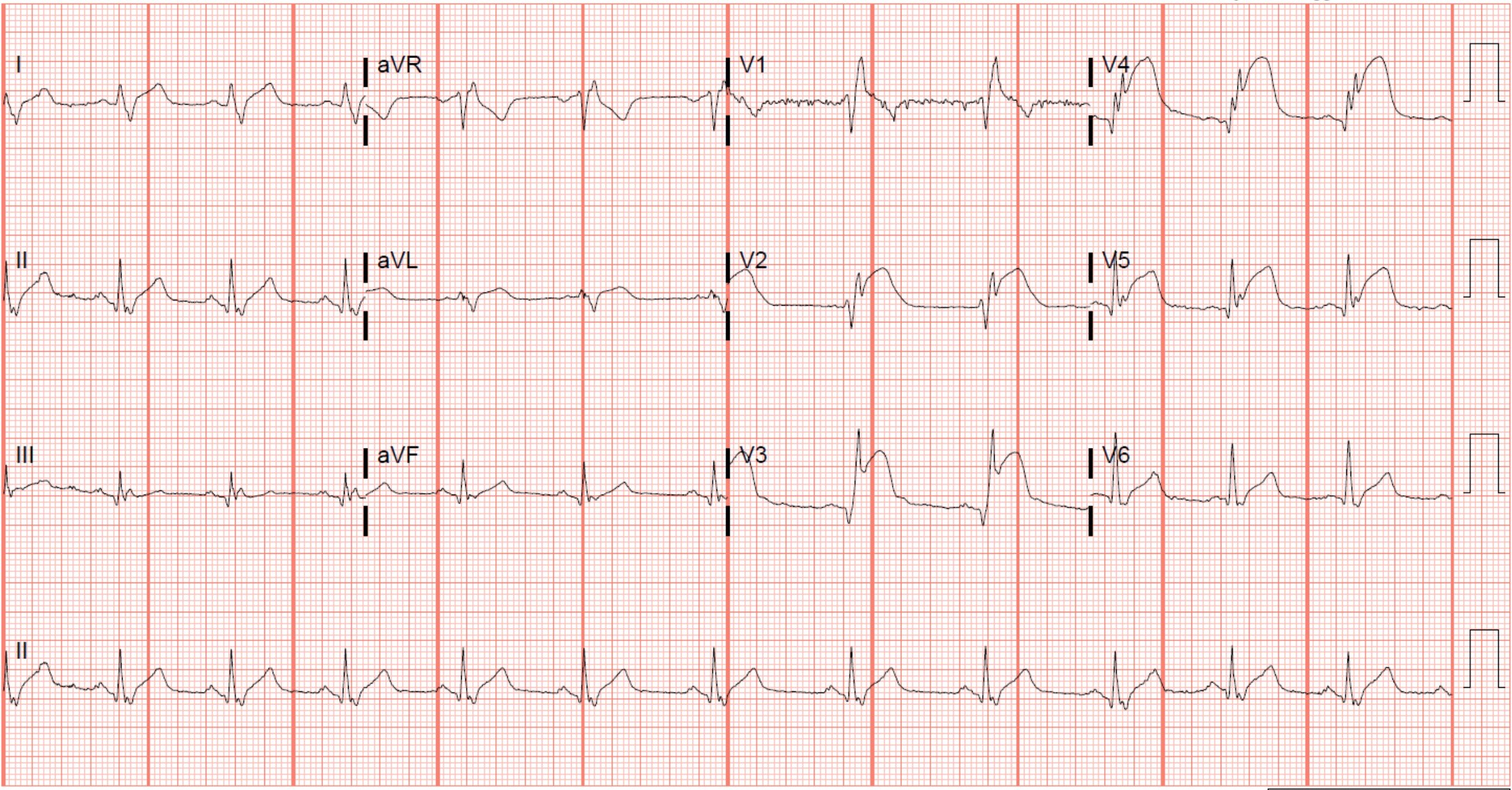
What complications are expected in a patient with this ECG? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 99
3. Question
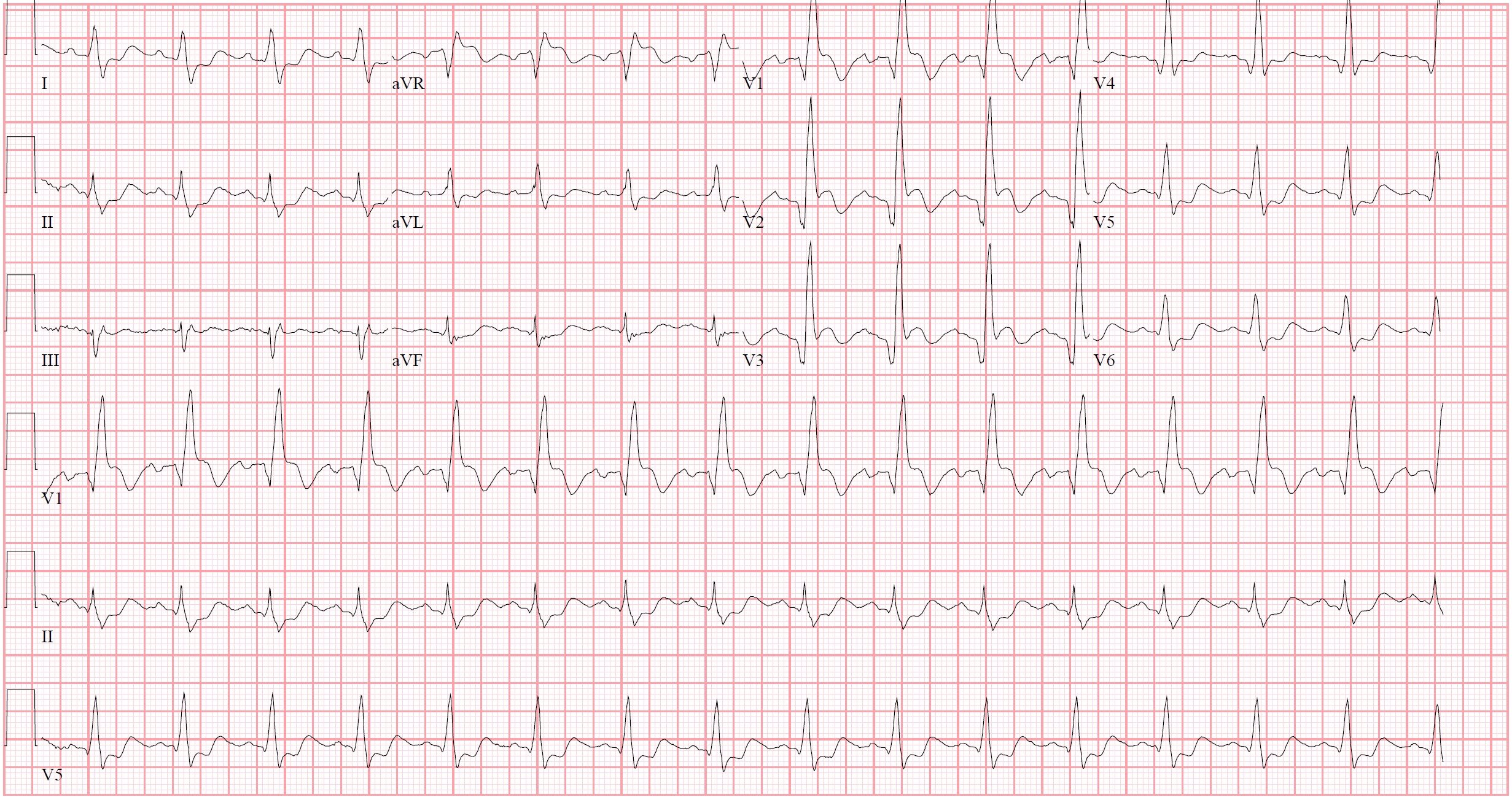
Which coronary artery is likely occluded?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 99
4. Question
Which of the following are seen with left bundle branch block? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 99
5. Question
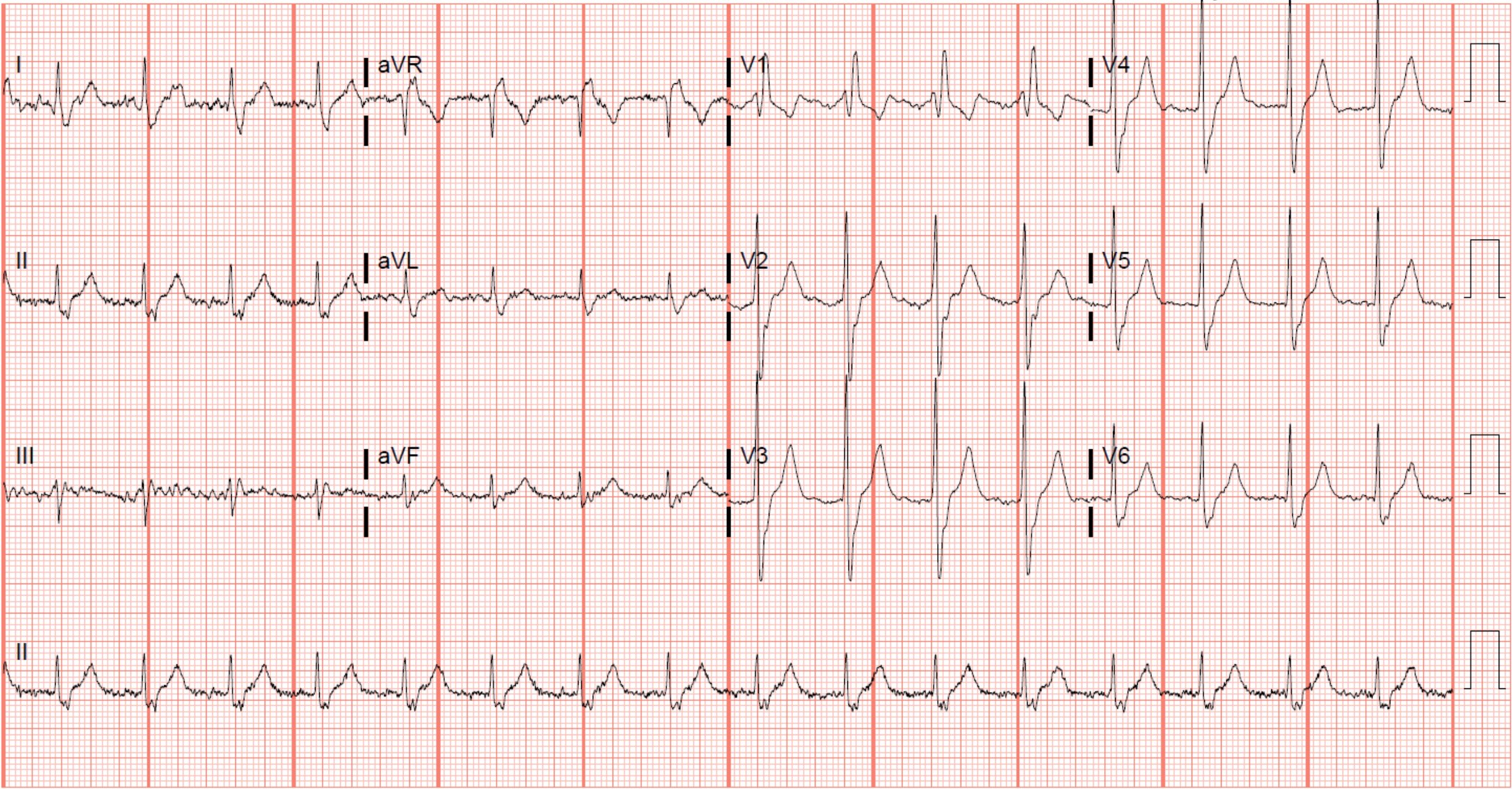
Which of the following is seen on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 99
6. Question
What ST/T changes are expected with right bundle branch block?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 99
7. Question
Which of the following are included in the differential diagnosis for wide complex tachycardia? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 99
8. Question
Which electrocardiographic abnormality is present in pre-excitation syndromes?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 99
9. Question
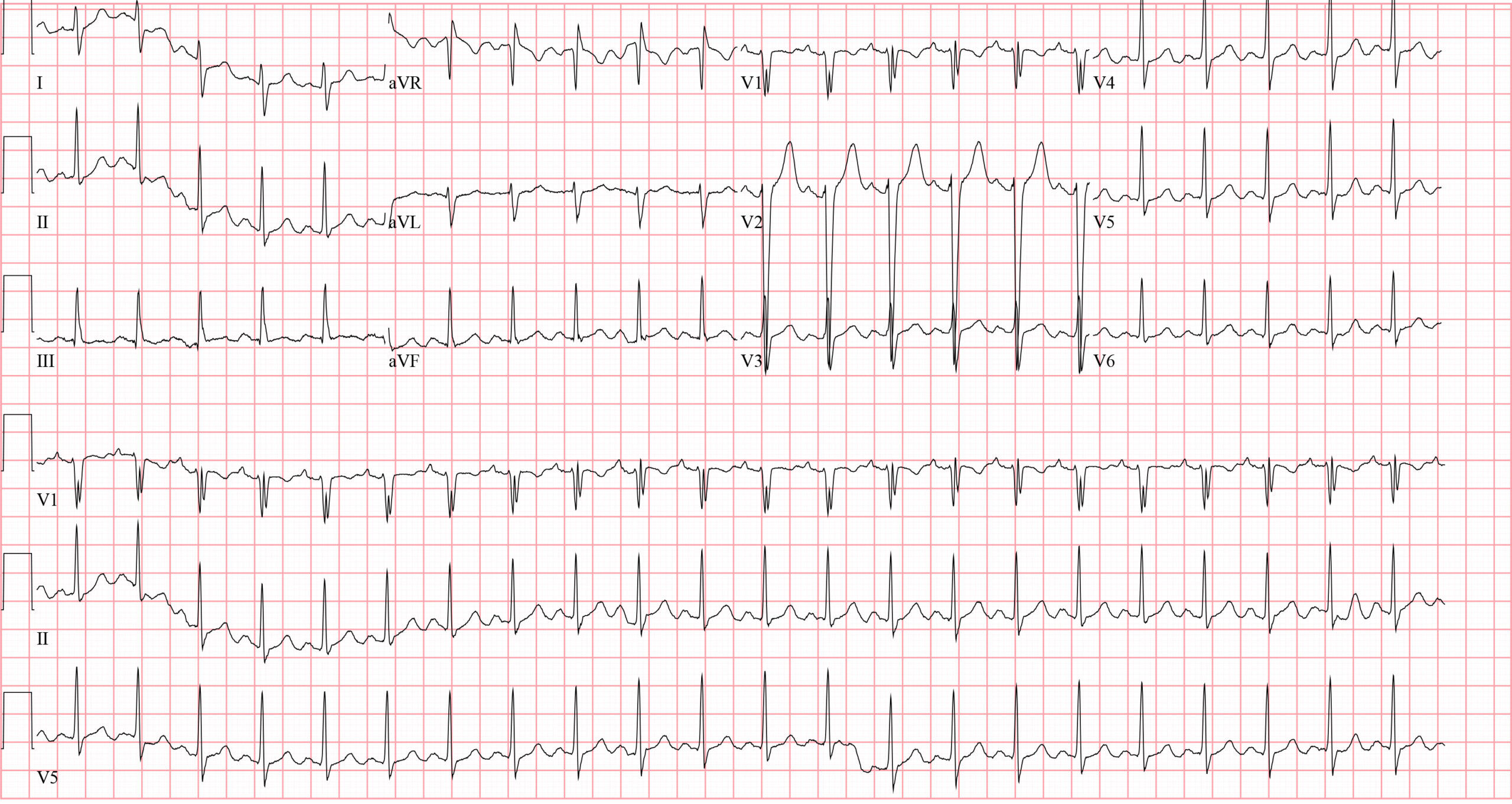
Select the correct standardized interpretation of this ECG.CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 99
10. Question
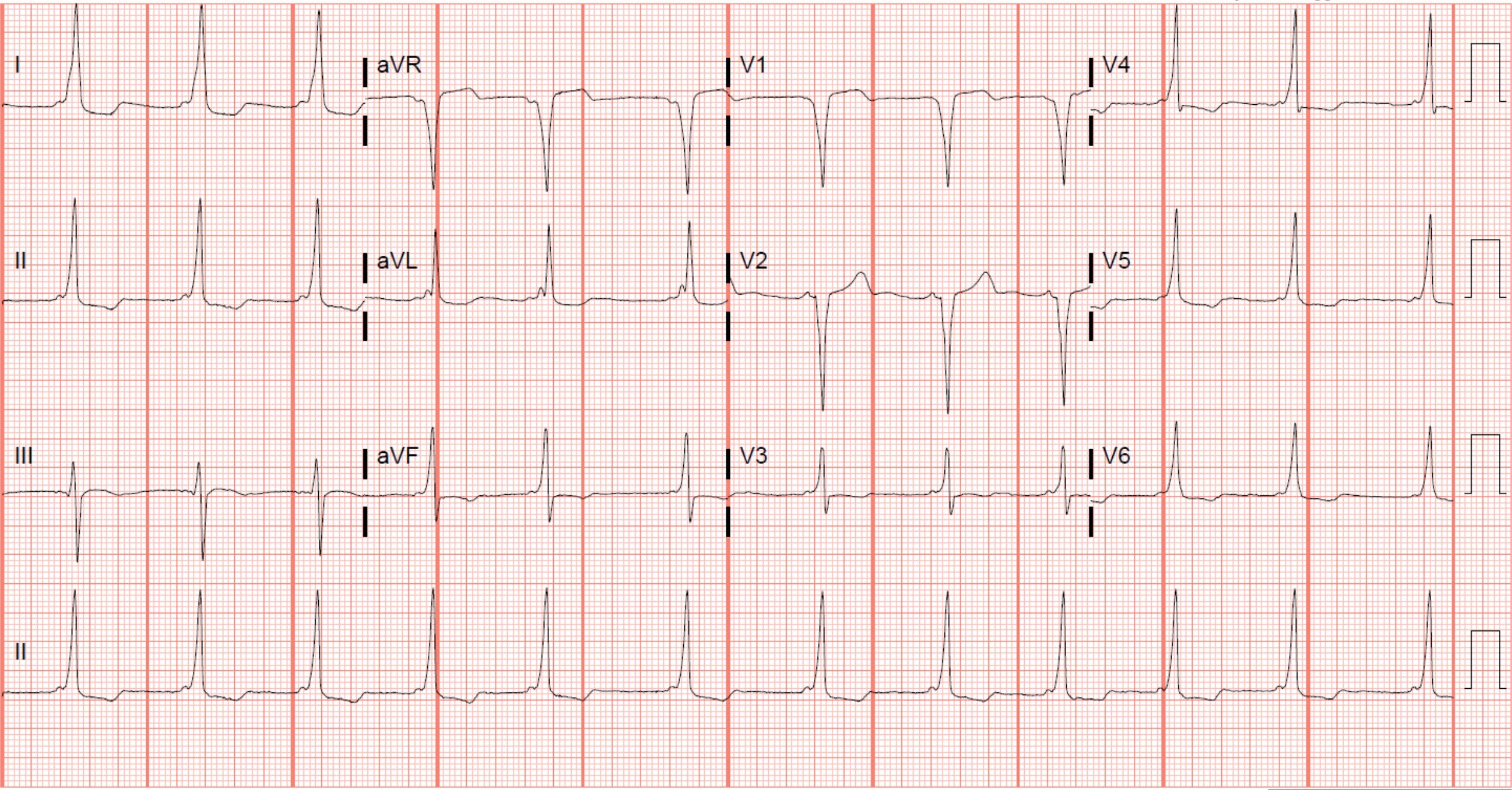
What is the most likely explanation for the widened QRS on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 99
11. Question
What ST/T wave changes are expected with left bundle branch block?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 99
12. Question
Which of the following is expected for posterior STEMI?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 99
13. Question
What are the original Sgarbossa criteria?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 99
14. Question
Which of the following are causes of left axis deviation? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 99
15. Question
Which of the following are considered bifascicular blocks? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 99
16. Question
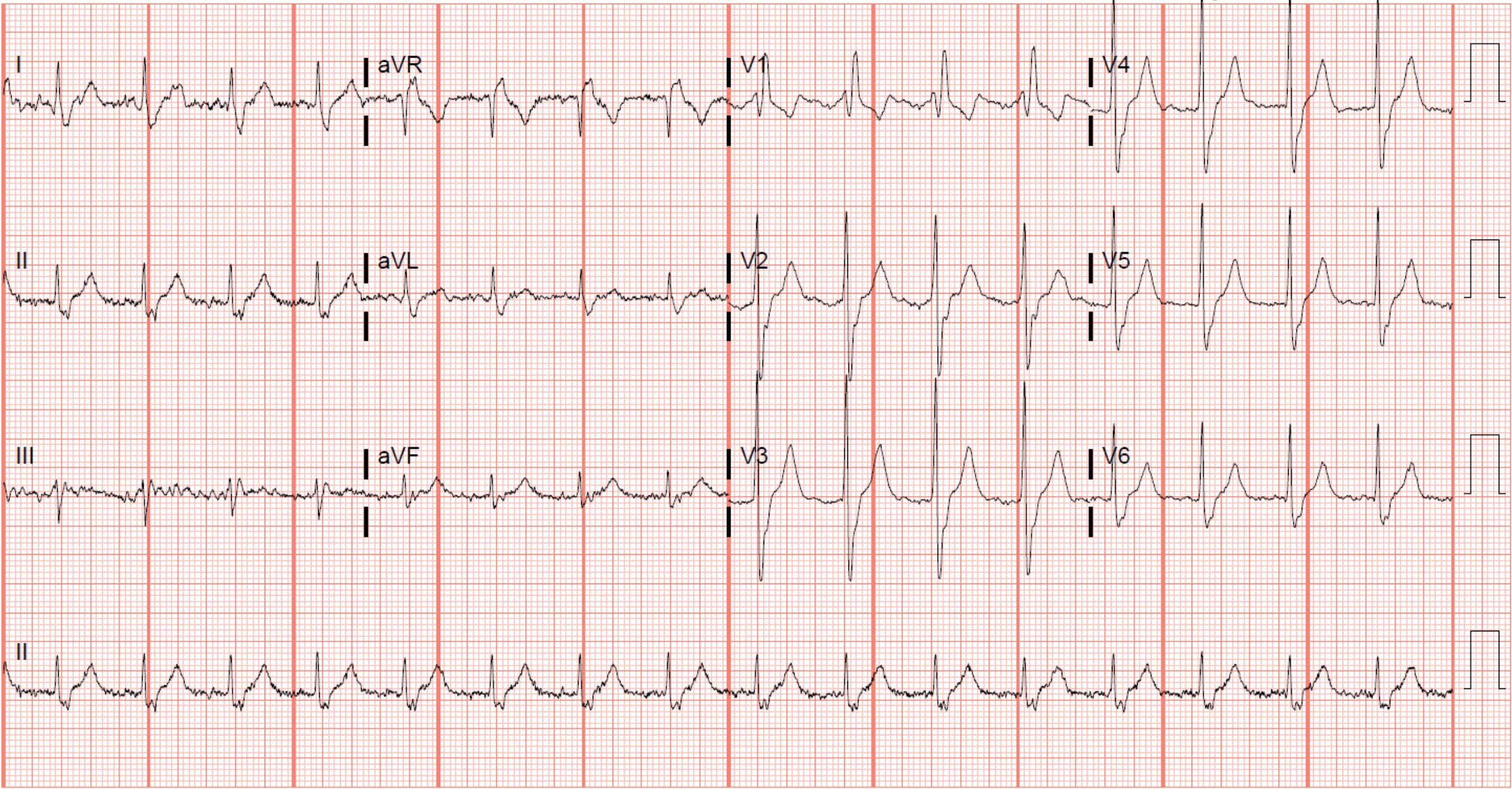
Which of the following are common causes of the conduction disturbance seen in this ECG? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 99
17. Question
What condition causes greater than 45 degrees of leftward axis deviation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 99
18. Question
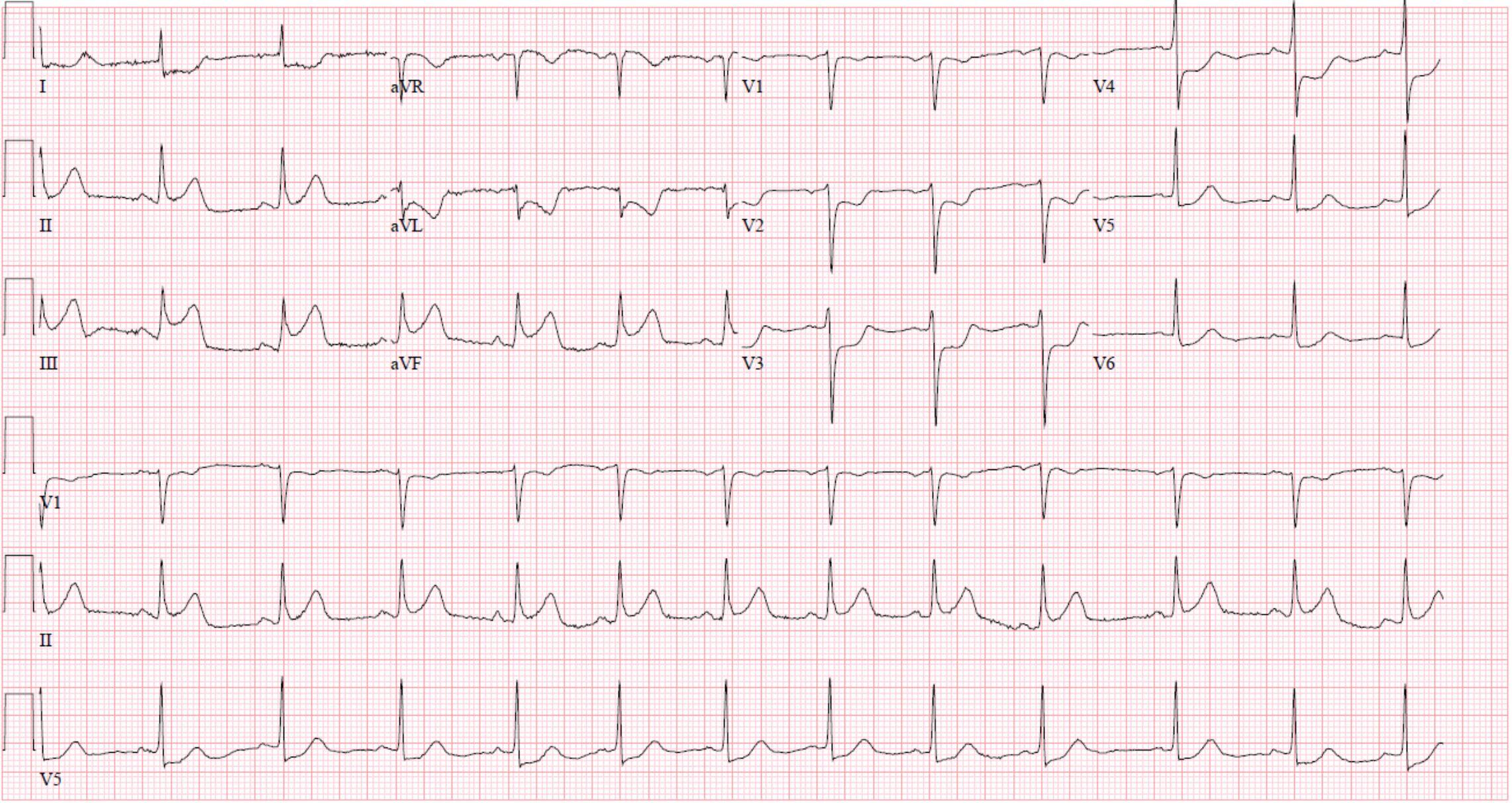
What is the diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 99
19. Question
Which of the following are causes of right axis deviation? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 99
20. Question
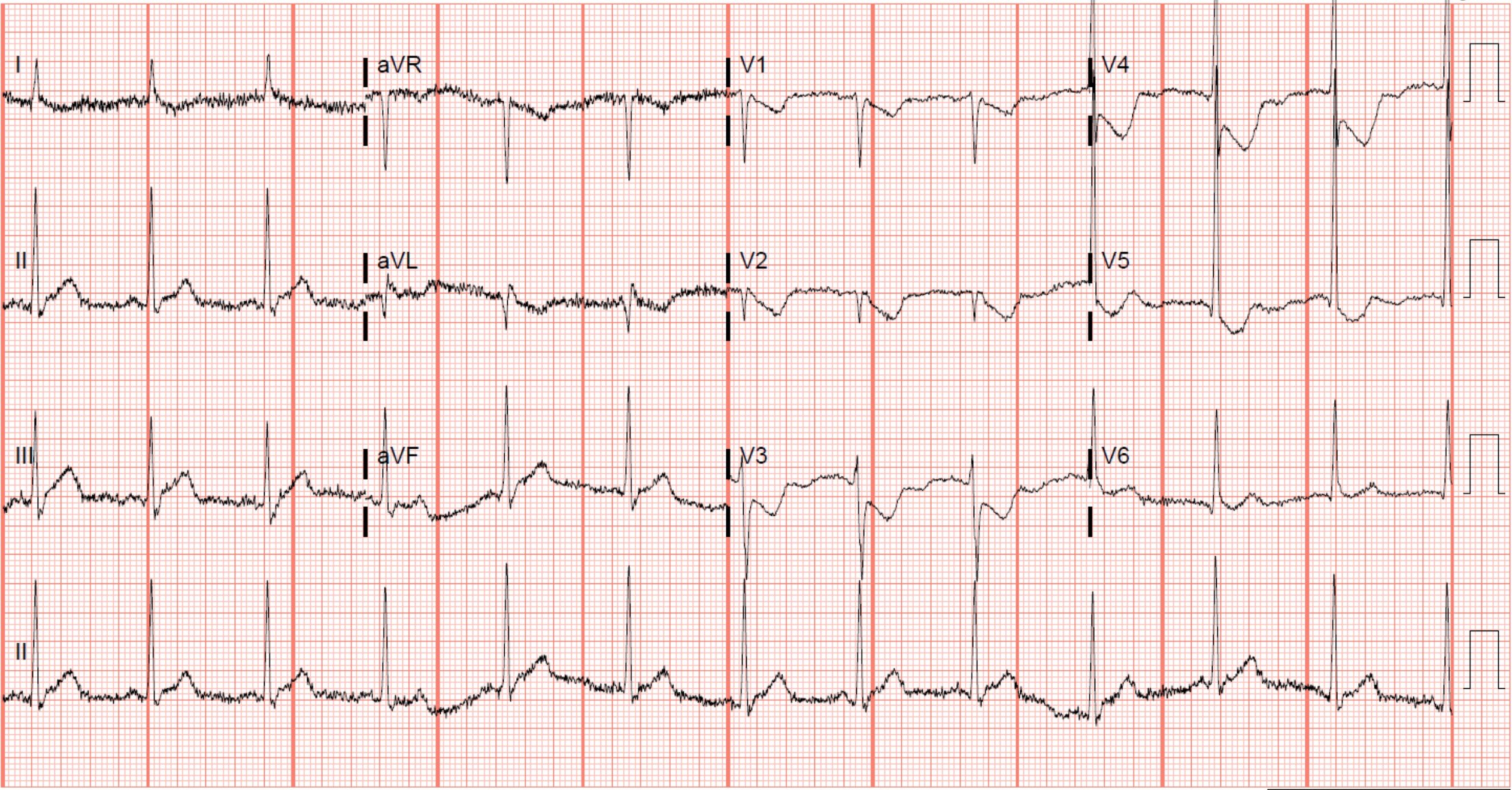
The patient with this ECG presented with chest pain. What additional leads could secure the diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 99
21. Question
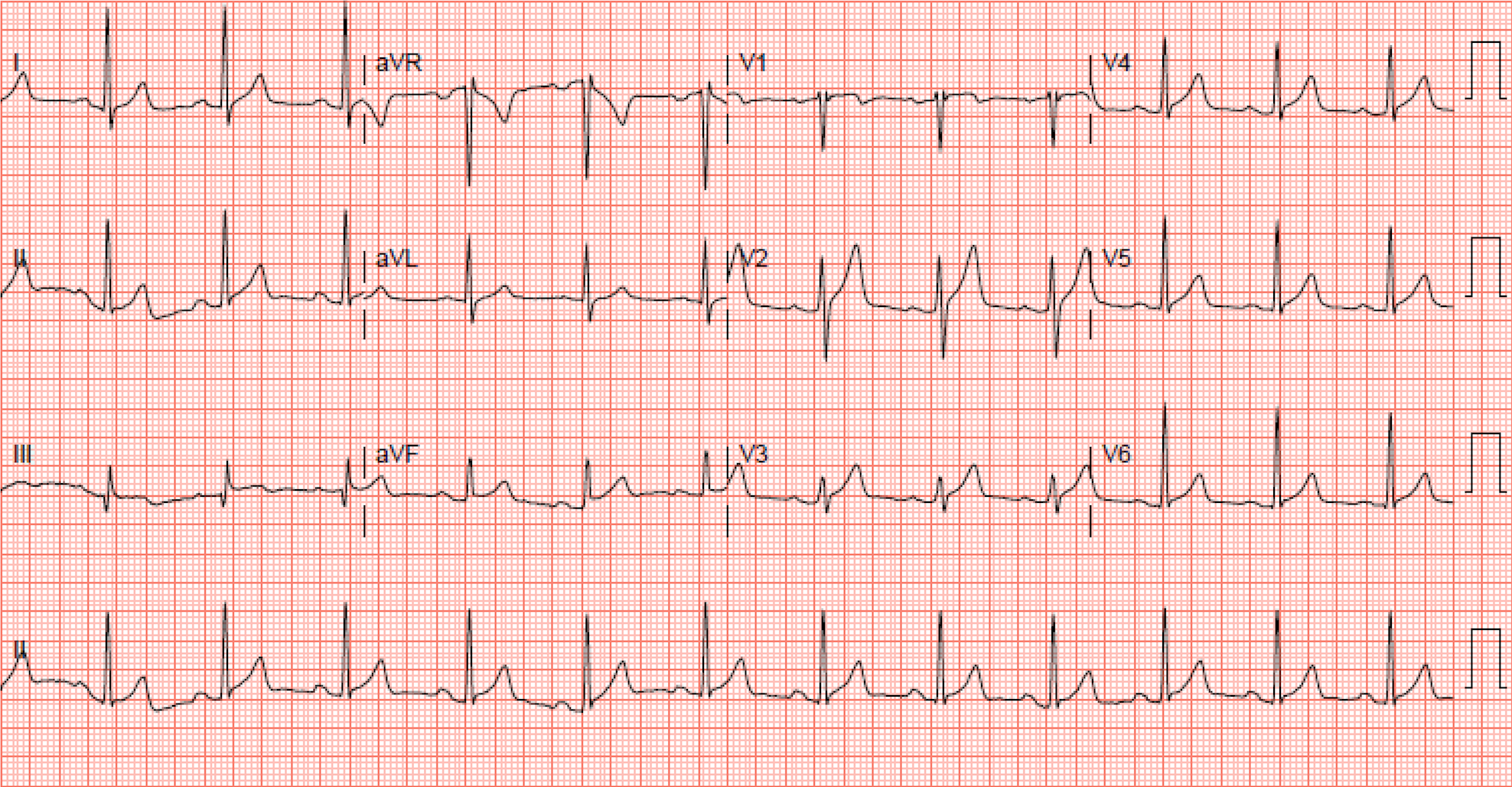
A healthy 25 year old male patient presents with this ECG after a motor vehicle collision. What’s the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 99
22. Question
Which of the following is a description of early repolarization or the J wave pattern?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 99
23. Question
What ECG features suggest the diagnosis of left ventricular aneurysm?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 99
24. Question
Which of the following findings is consistent with left main or triple vessel disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 99
25. Question
Which of the following is an UNLIKELY cause of an ECG with multilead ST depressions with ST elevation in aVR (≥1mm)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 99
26. Question
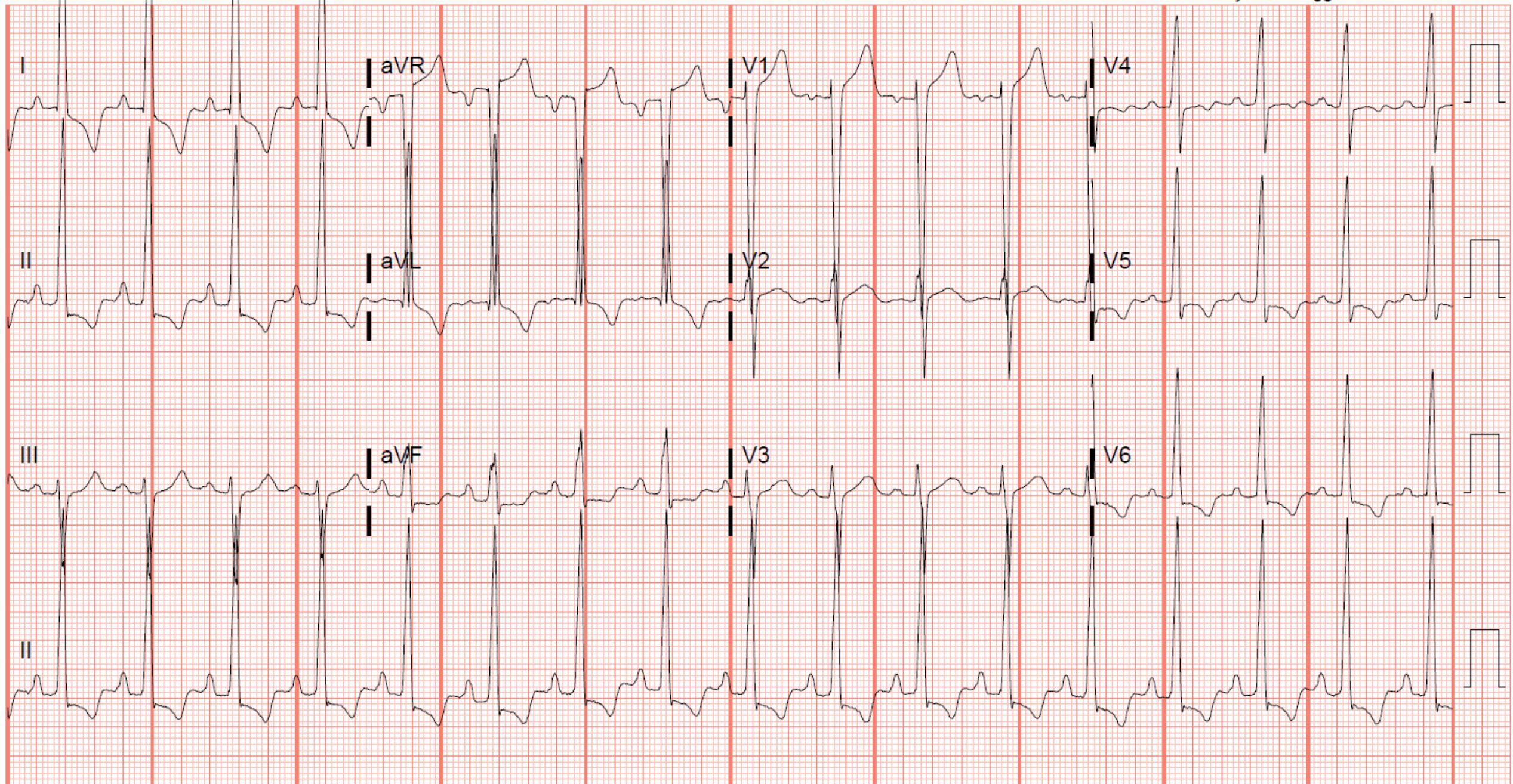
What is the most likely explanation for the repolarization abnormalities seen on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 99
27. Question
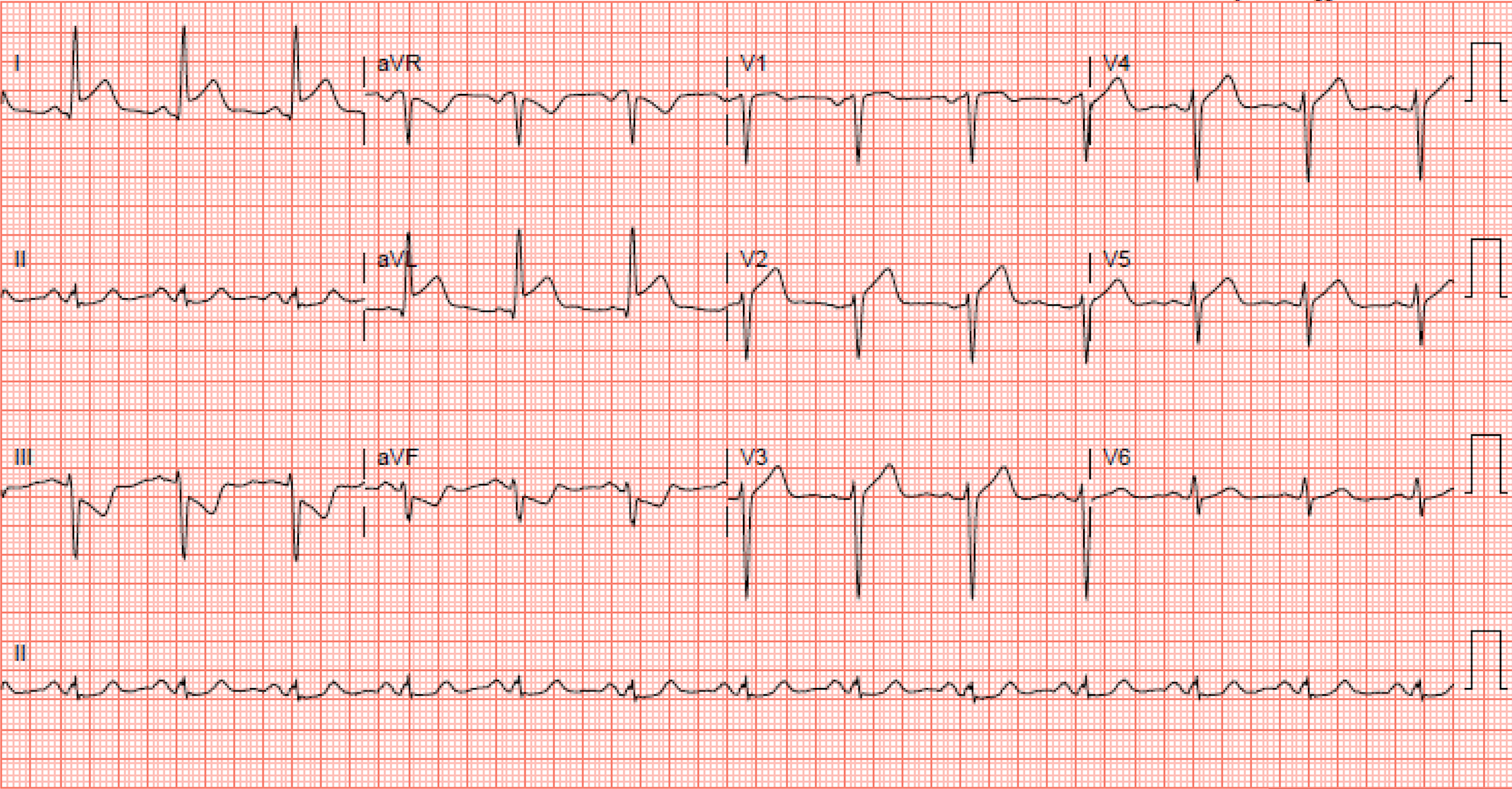
What artery is most likely occluded?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 99
28. Question
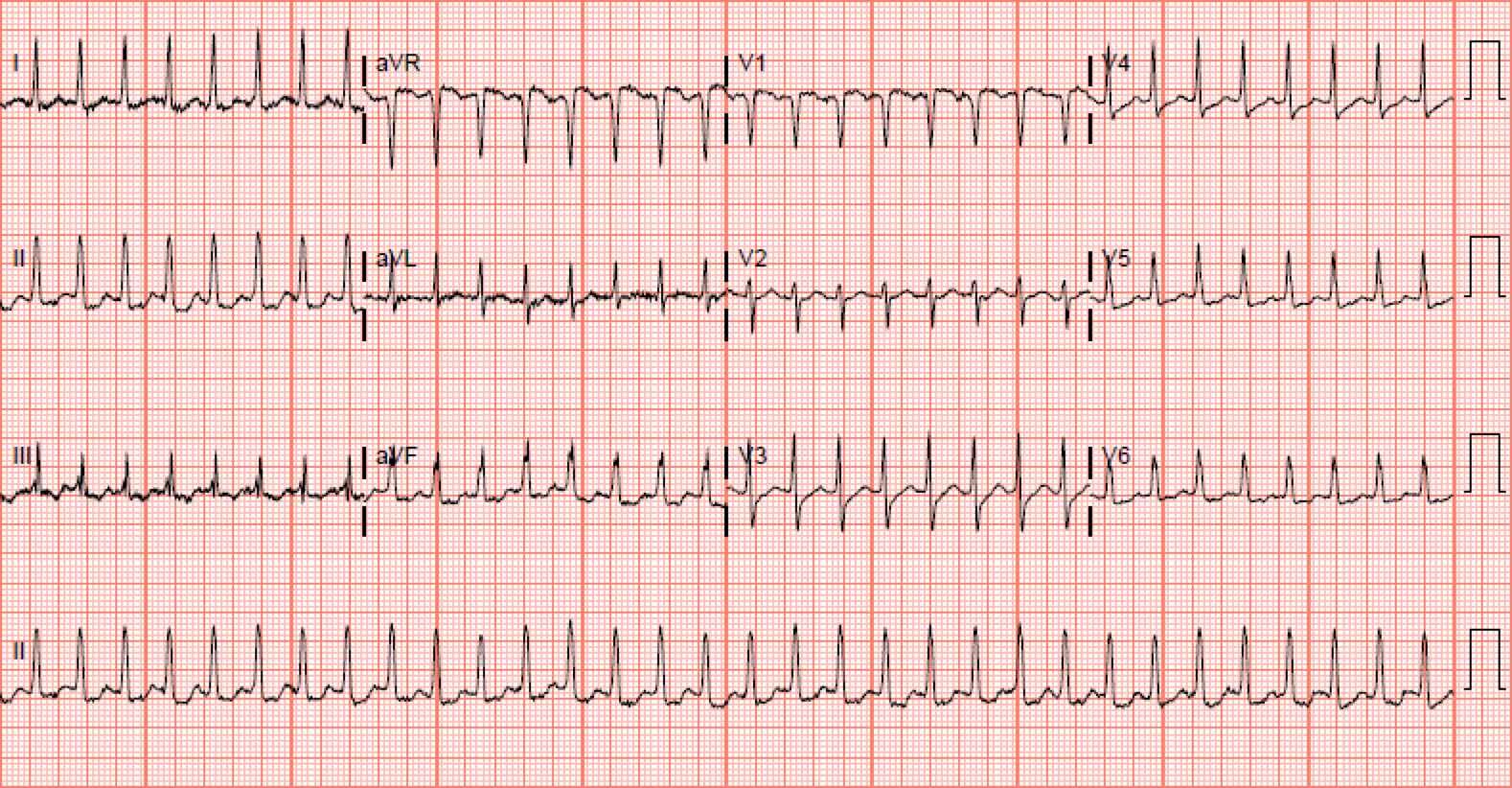
What is the most likely cause of aVR ST elevation in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 99
29. Question
Which of the following are common electrocardiographic criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 99
30. Question
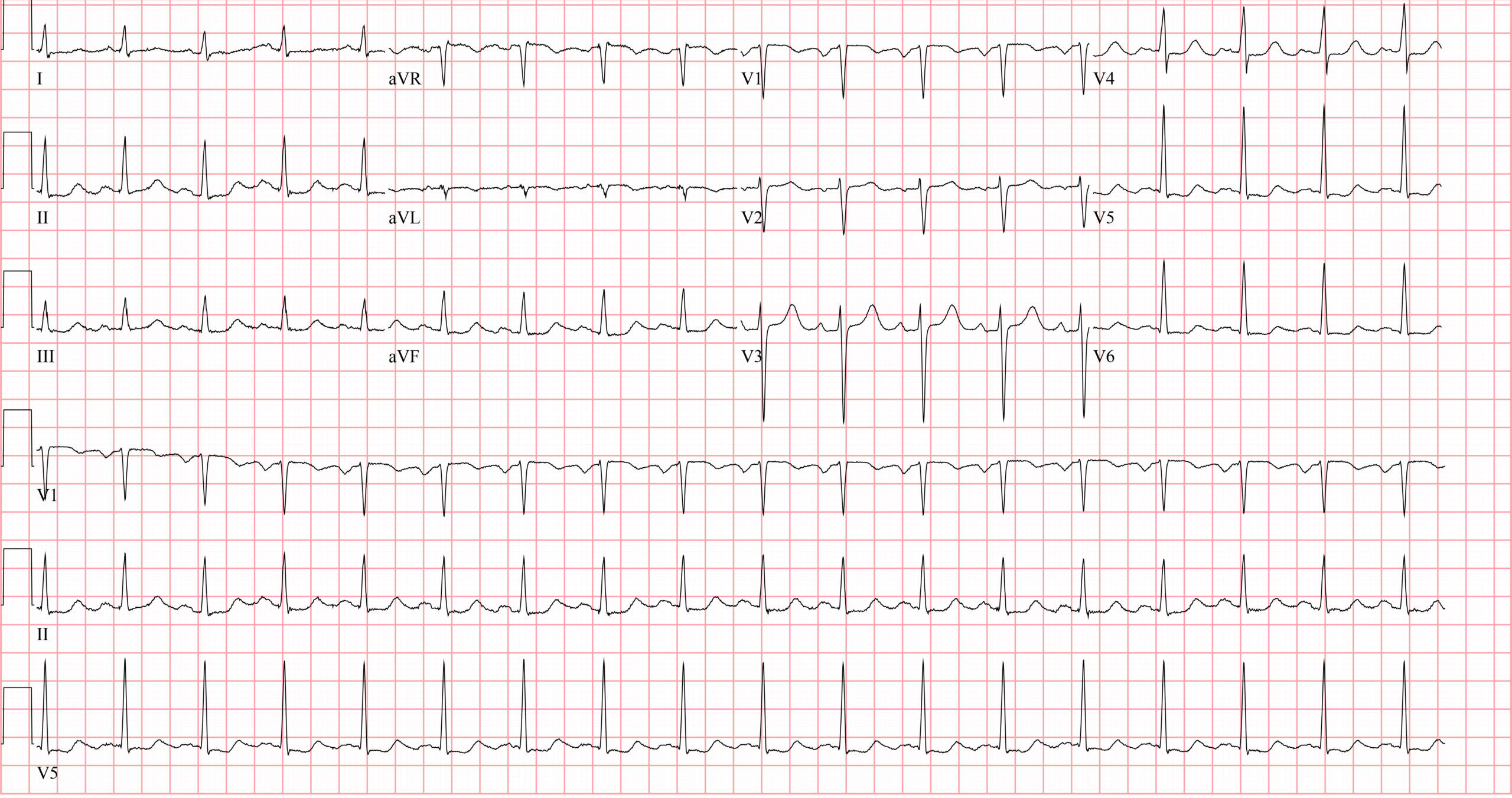
There are subtle signs of ischemia in this ECG of a patient that presented with dyspnea on exertion. Which of the following are possible explanations for these findings? (Select all that apply)CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 99
31. Question
Which of the following findings are seen in pericarditis? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 99
32. Question
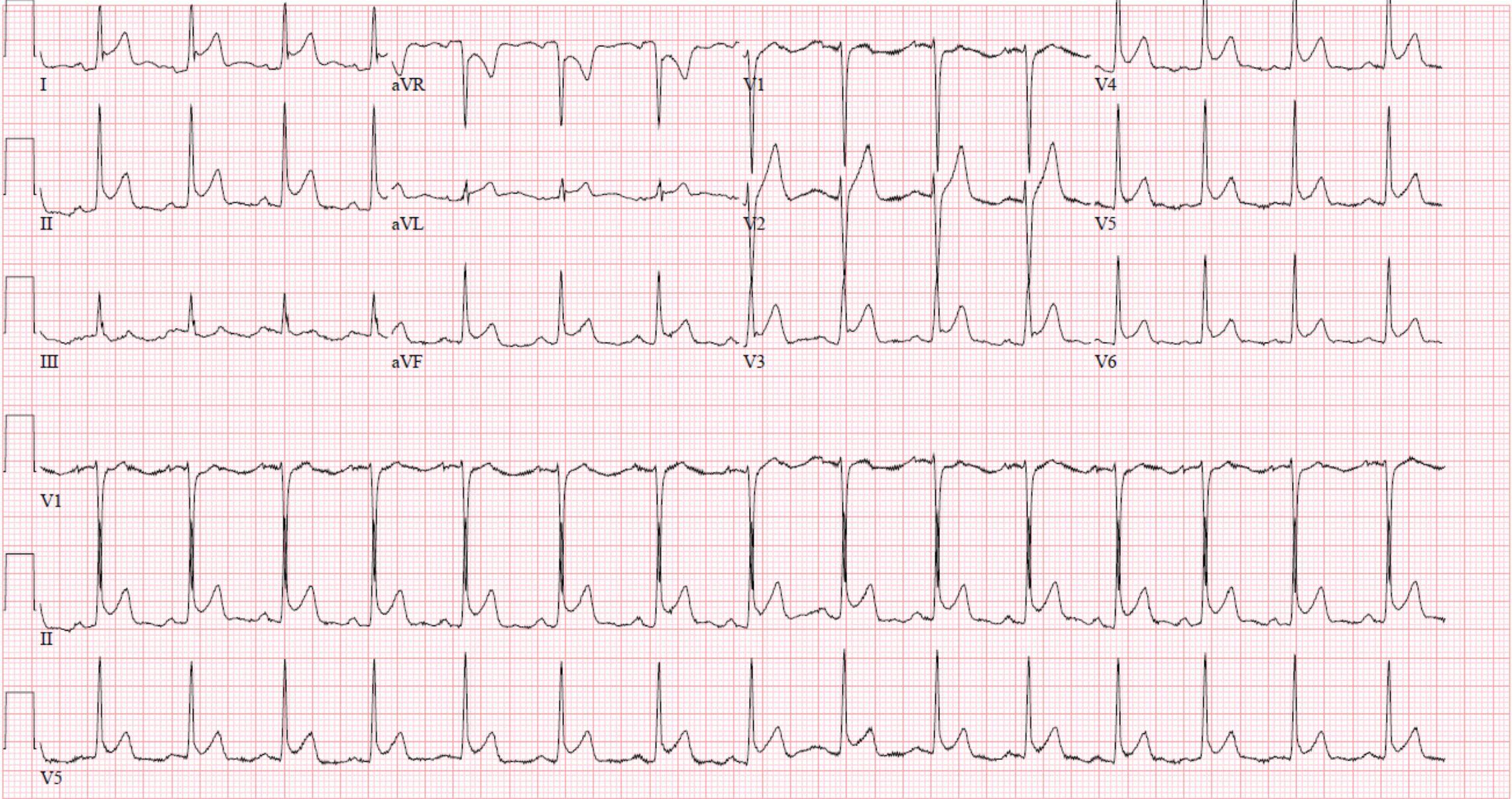
What is a first line treatment for a patient complaining of pleuritic chest pain with this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 99
33. Question
Which of the following is used for membrane stabilization in the setting of hyperkalemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 99
34. Question
In the setting of hyperkalemia, which of the following predict adverse outcomes? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 99
35. Question
Which of the following complications are associated with right ventricular infarction? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 99
36. Question
Which of the following best describes the ECG findings in right ventricular infarction?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 99
37. Question
About 2% of ECGs in acute LAD occlusions have tall, prominent, symmetric T waves in the precordial leads. What are these T waves commonly called?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 99
38. Question
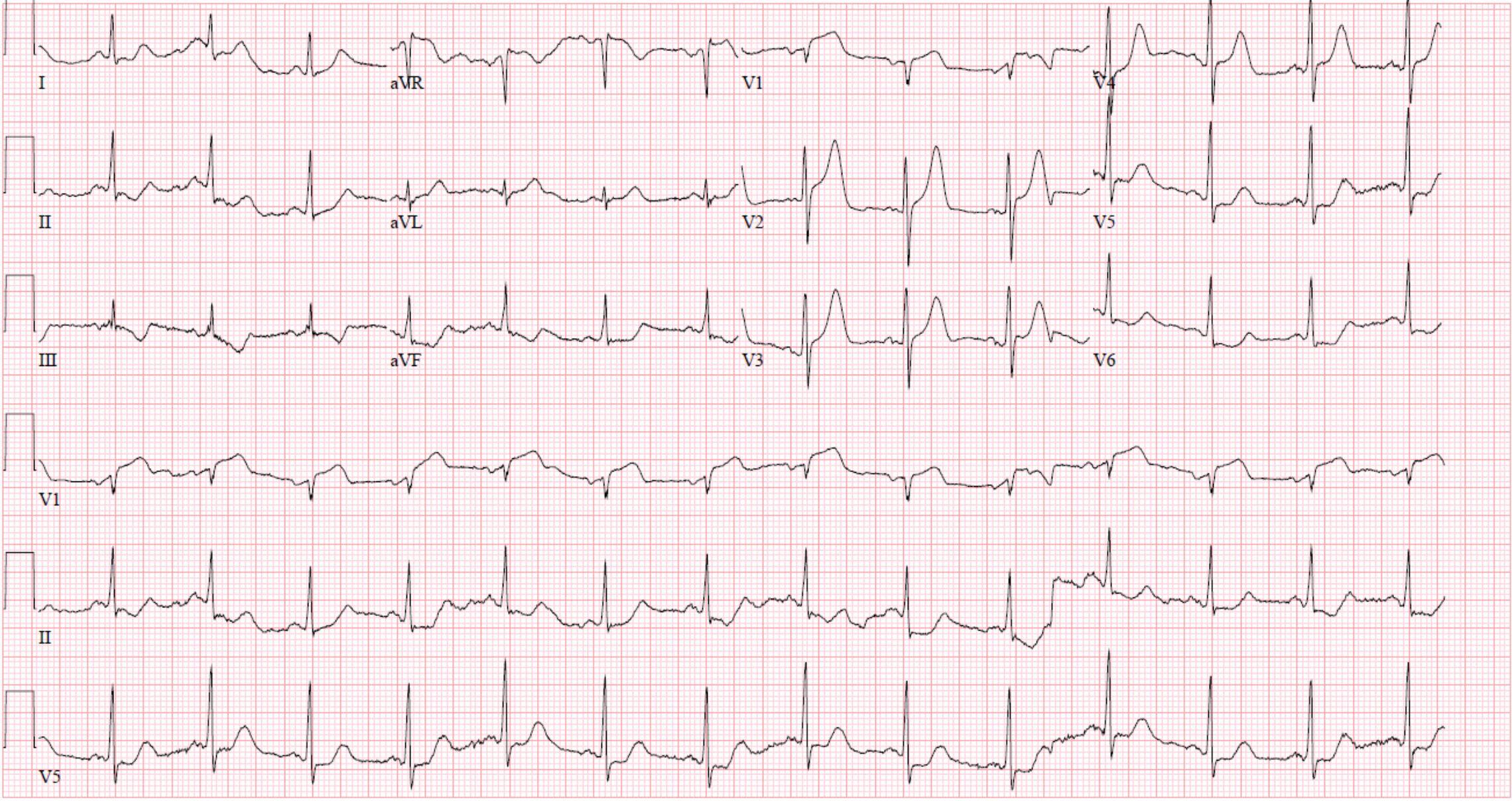
What condition likely explains the findings on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 99
39. Question
Which electrocardiographic feature is best at predicting acute myocardial infarction over acute pericarditis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 99
40. Question
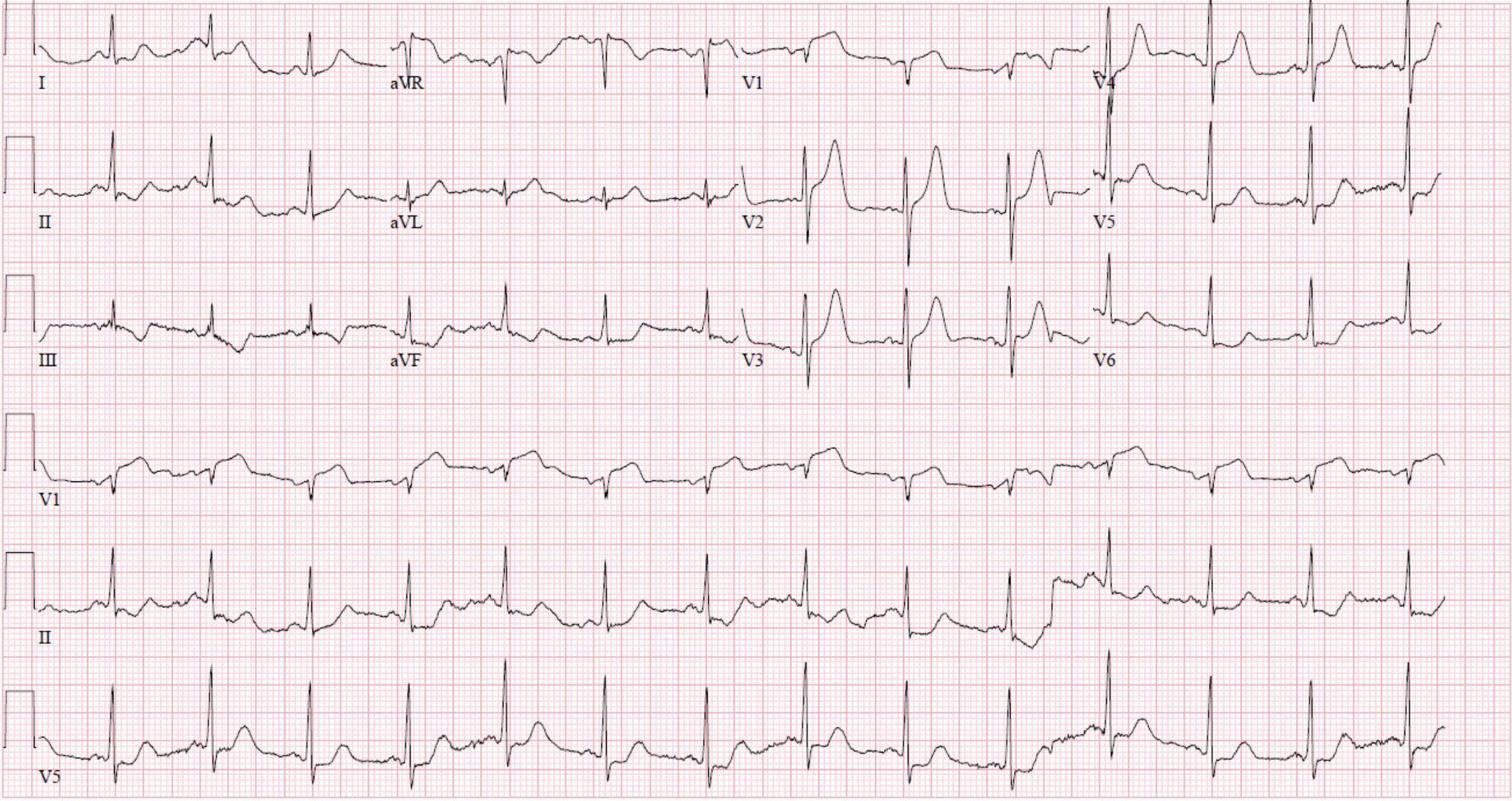 The T waves in V2 and V3 of this ECG are clear examples of:CorrectIncorrect
The T waves in V2 and V3 of this ECG are clear examples of:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 99
41. Question
Which of the following ECG findings is most consistent with the coved-type Brugada pattern?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 99
42. Question
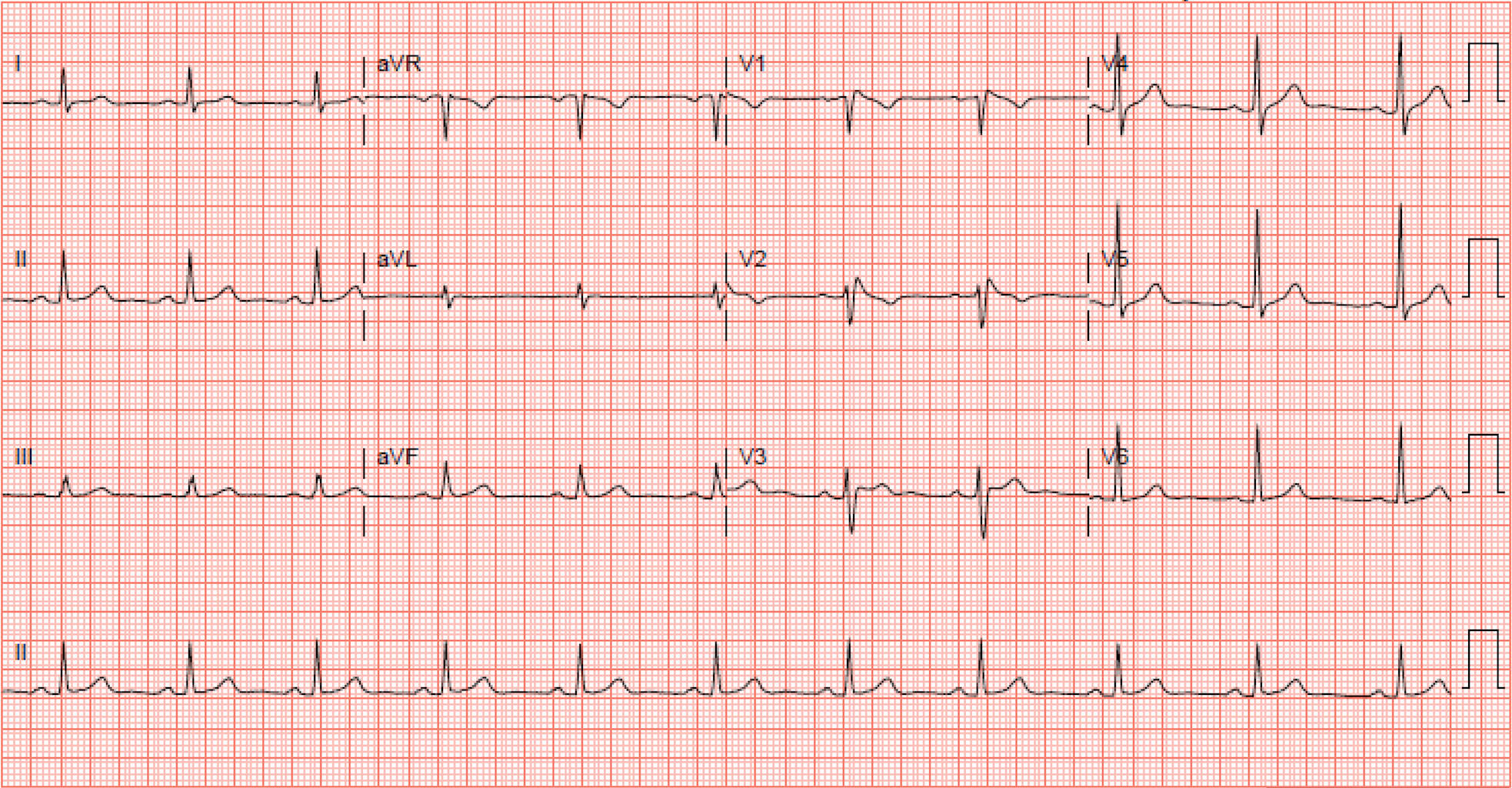
What is the next step in management for a patient who presents with syncope and this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 99
43. Question
Which of the following ECG findings can be seen in acute pulmonary embolism? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 99
44. Question
A patient with prolonged QT is at risk for what dysrhythmia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 99
45. Question
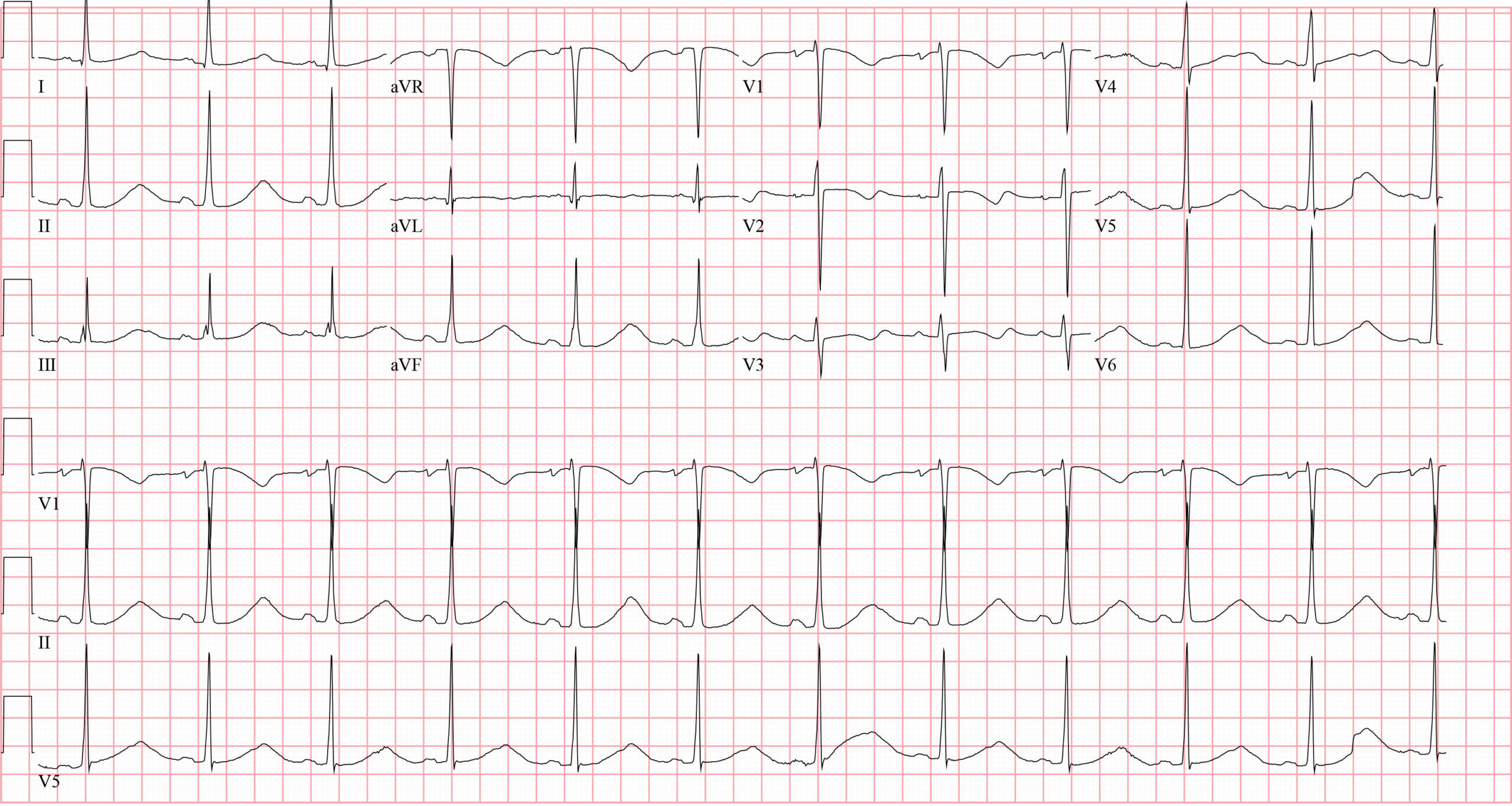
Which of the following is NOT a cause of the QT interval changes seen on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 99
46. Question
Which of the following are appropriate treatments for a decompensating patient with a long QT interval? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 99
47. Question
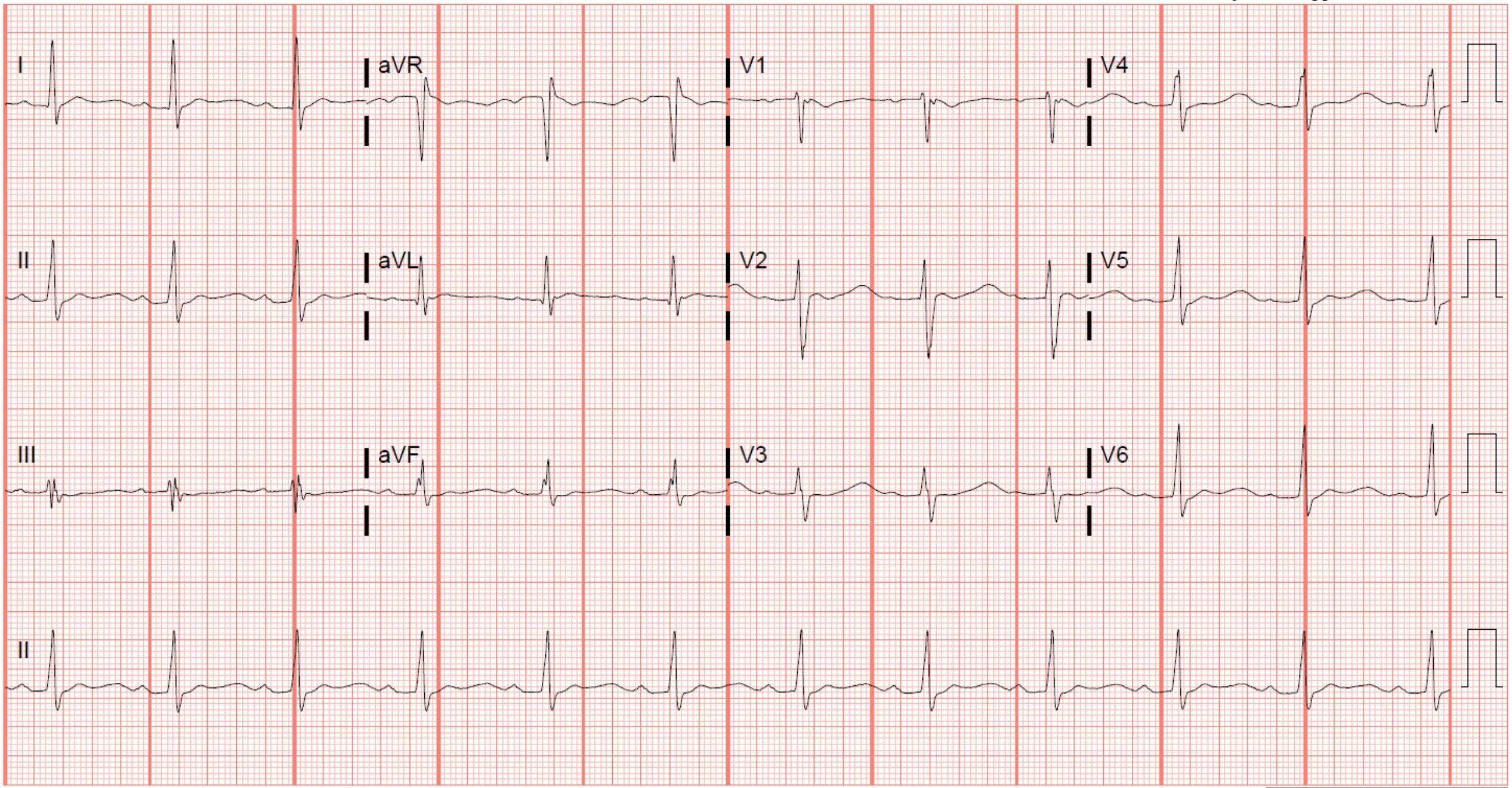
Which of the following electrolyte abnormalities is most likely to cause the findings in this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 99
48. Question
Which of the following ECG findings is associated with hypothermia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 99
49. Question
Which of the following are features of right ventricular strain? (select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 99
50. Question
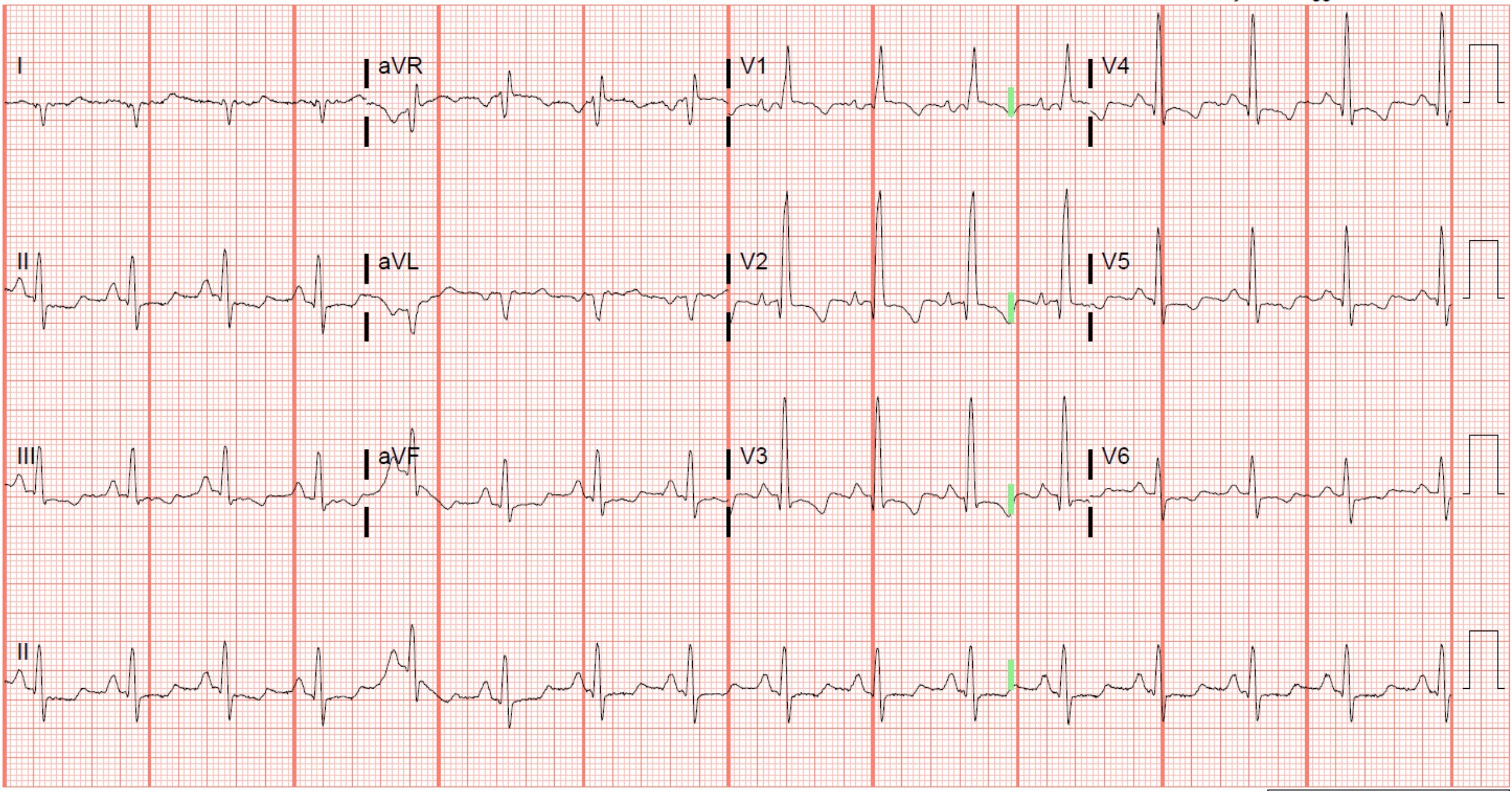
An unstable patient with chest pain, shortness of breath and this ECG is most likely to benefit from what immediate treatment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 99
51. Question
What medication should be given to a stable patient with Wolf-Parkinson-White in atrial fibrillation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 99
52. Question
Which of the following are expected electrocardiographic changes in Wolf-Parkinson-White? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 99
53. Question
Which of the following ECG findings are expected with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 99
54. Question
Which of the following is a potential treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 99
55. Question
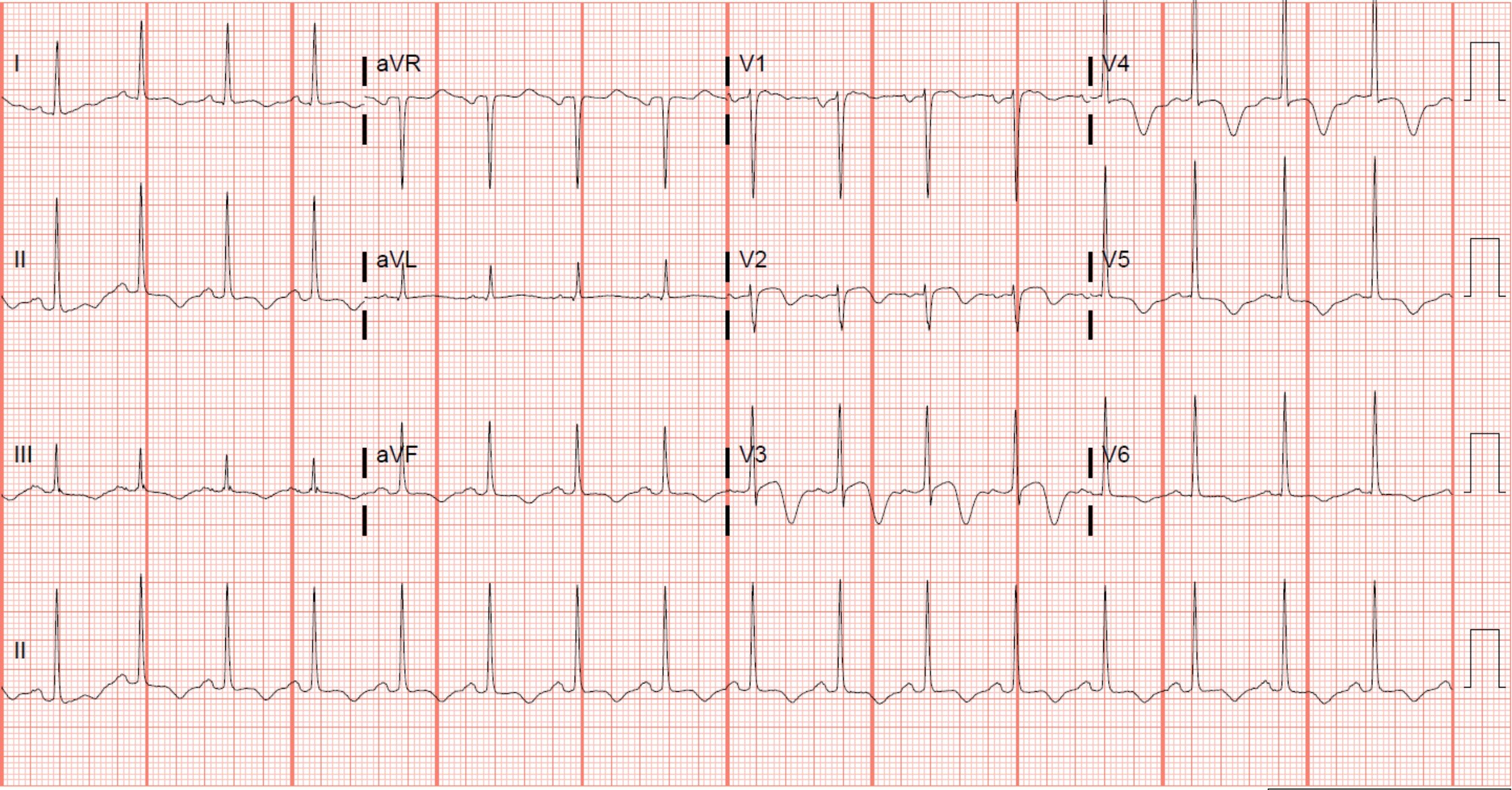
A patient with this ECG who previously had chest pain, but is now chest pain free may have what condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 99
56. Question
What are the ECG findings associated with Wellens syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 99
57. Question
A patient with Wellens syndrome develops chest pain. What early ECG findings are expected?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 99
58. Question
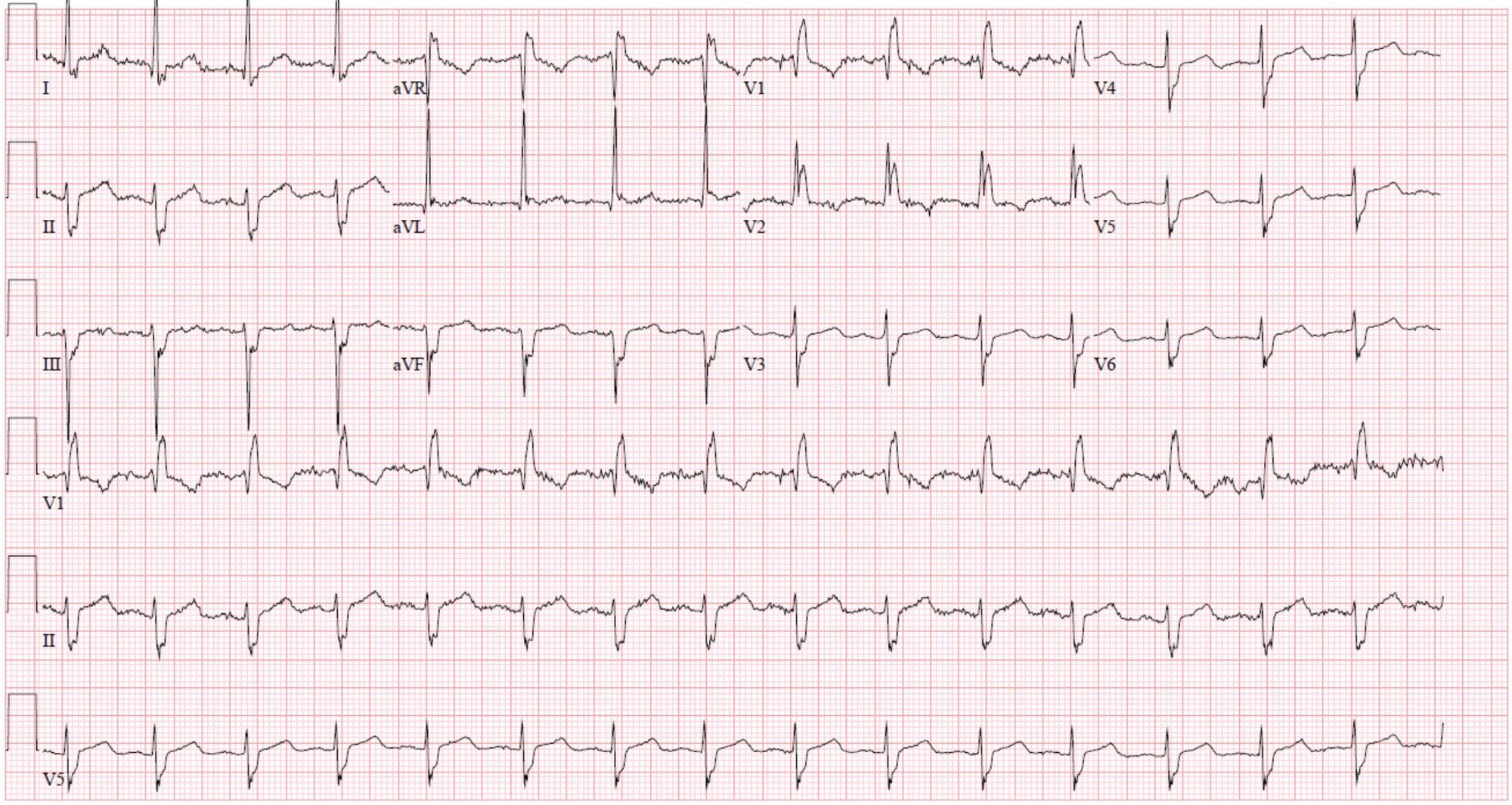
Which block is seen in this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 99
59. Question
Which of the following are criteria for low voltage (select all that apply)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 99
60. Question
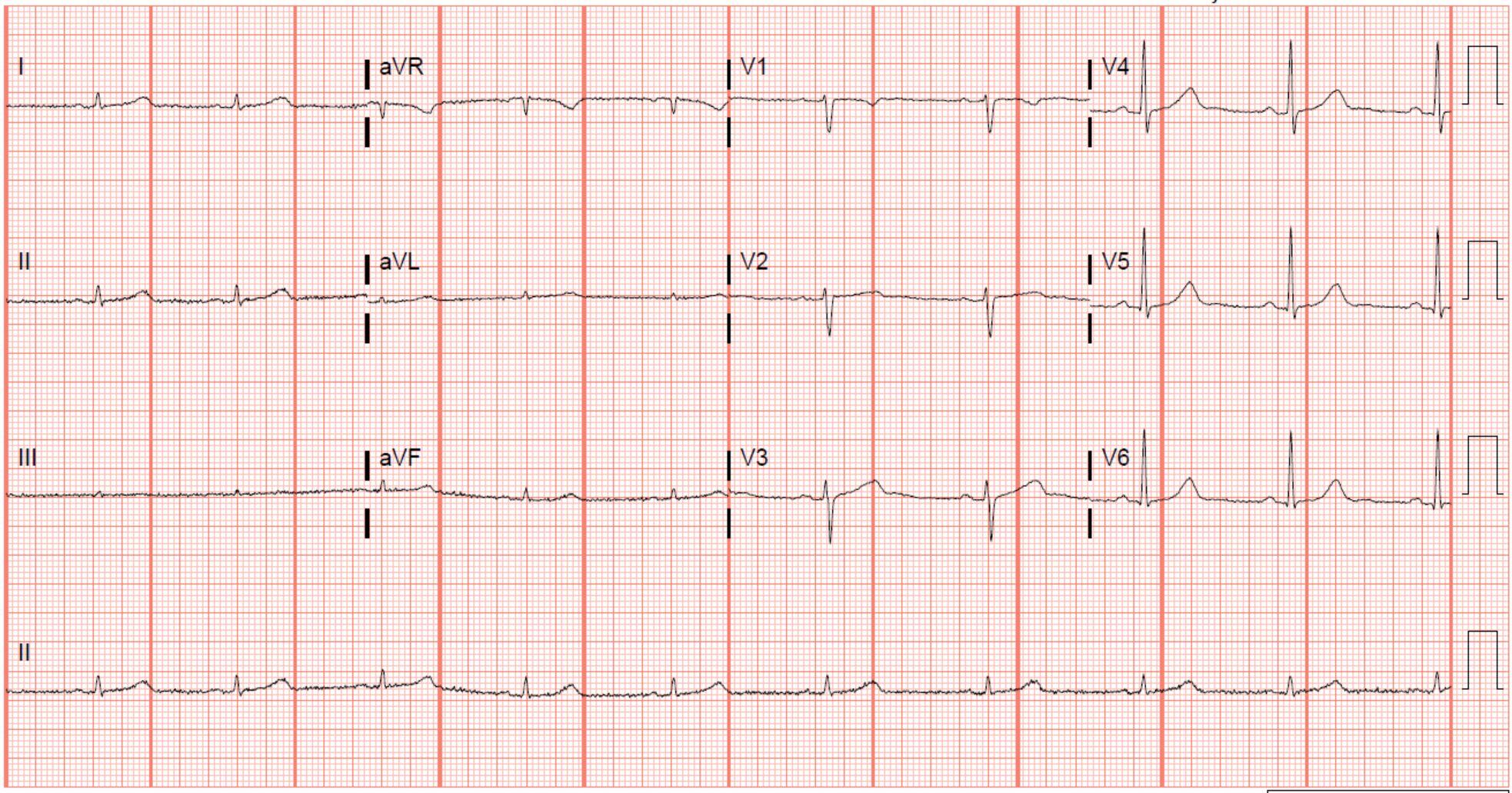 A patient with this ECG presents with dyspnea, your bedside ultrasound shows ventricular hypertrophy and no pericardial effusion, which causes are you considering?CorrectIncorrect
A patient with this ECG presents with dyspnea, your bedside ultrasound shows ventricular hypertrophy and no pericardial effusion, which causes are you considering?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 99
61. Question
Which of these abnormalities is most likely to degrade into a complete heart block?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 99
62. Question
Which of the following may cause a second degree atrioventricular block, Mobitz II?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 99
63. Question
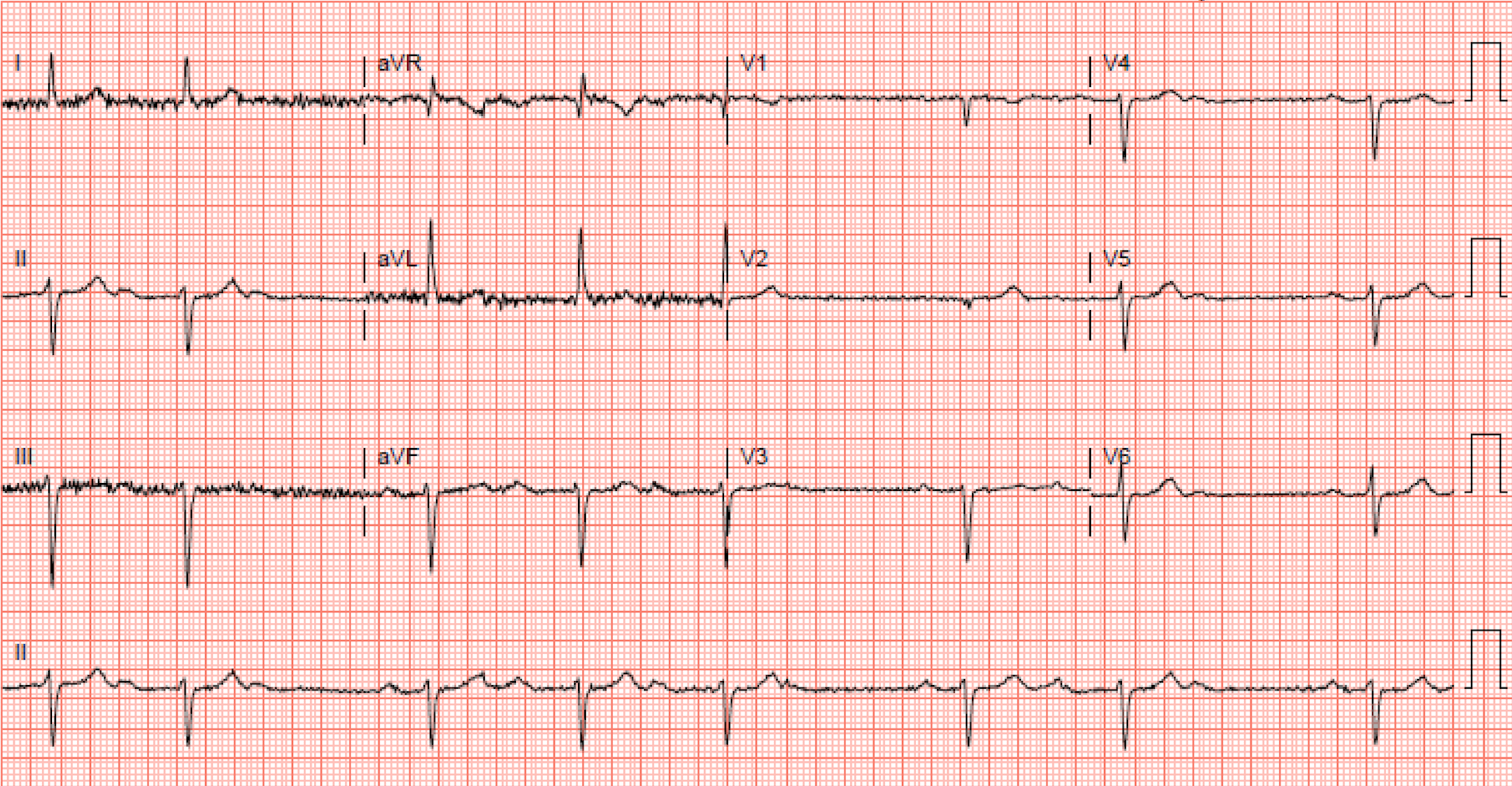
What is the most likely location of this conduction block?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 99
64. Question
What acutely occluded artery is most likely to cause a second degree, Mobitz I rhythm?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 99
65. Question
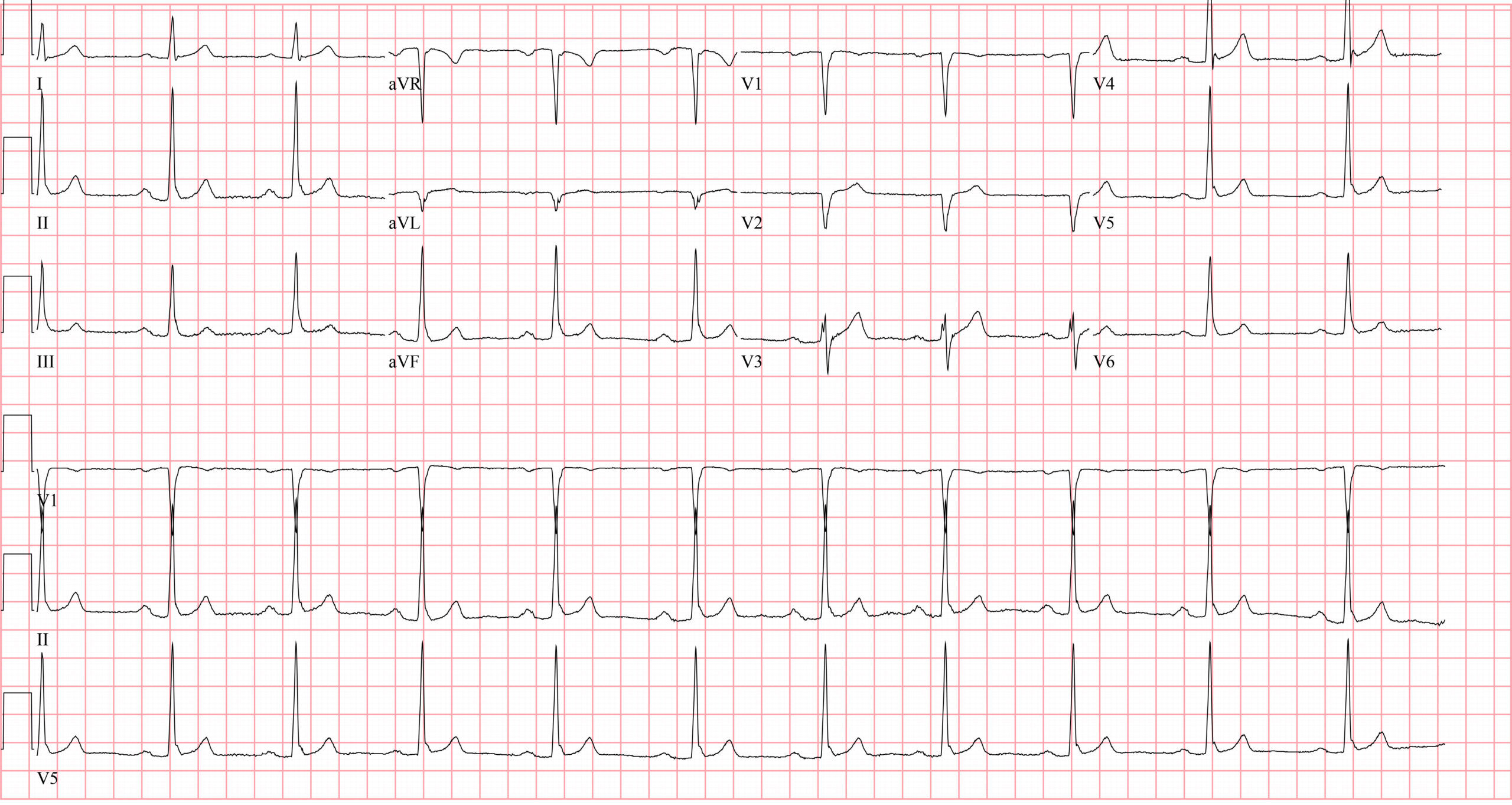
Which of the following can cause the interval abnormality in this ECG? (Select all that apply)CorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 99
66. Question
Which of the following findings is typically seen in a patient with hypokalemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 99
67. Question
In the setting of hyperkalemia, which of the following predict adverse outcomes? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 99
68. Question
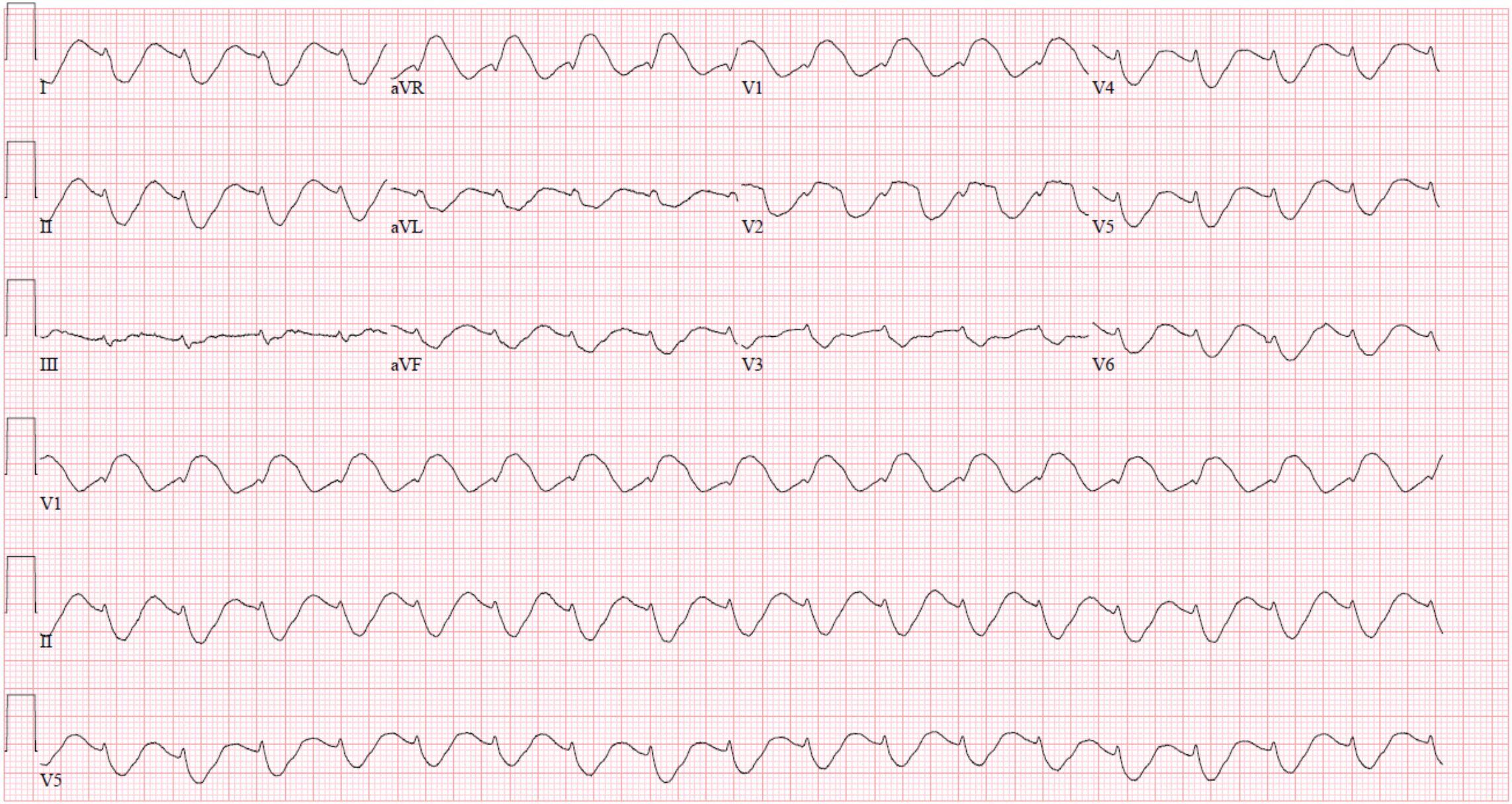
What is the most likely electrolyte disturbance causing the pattern seen on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 99
69. Question
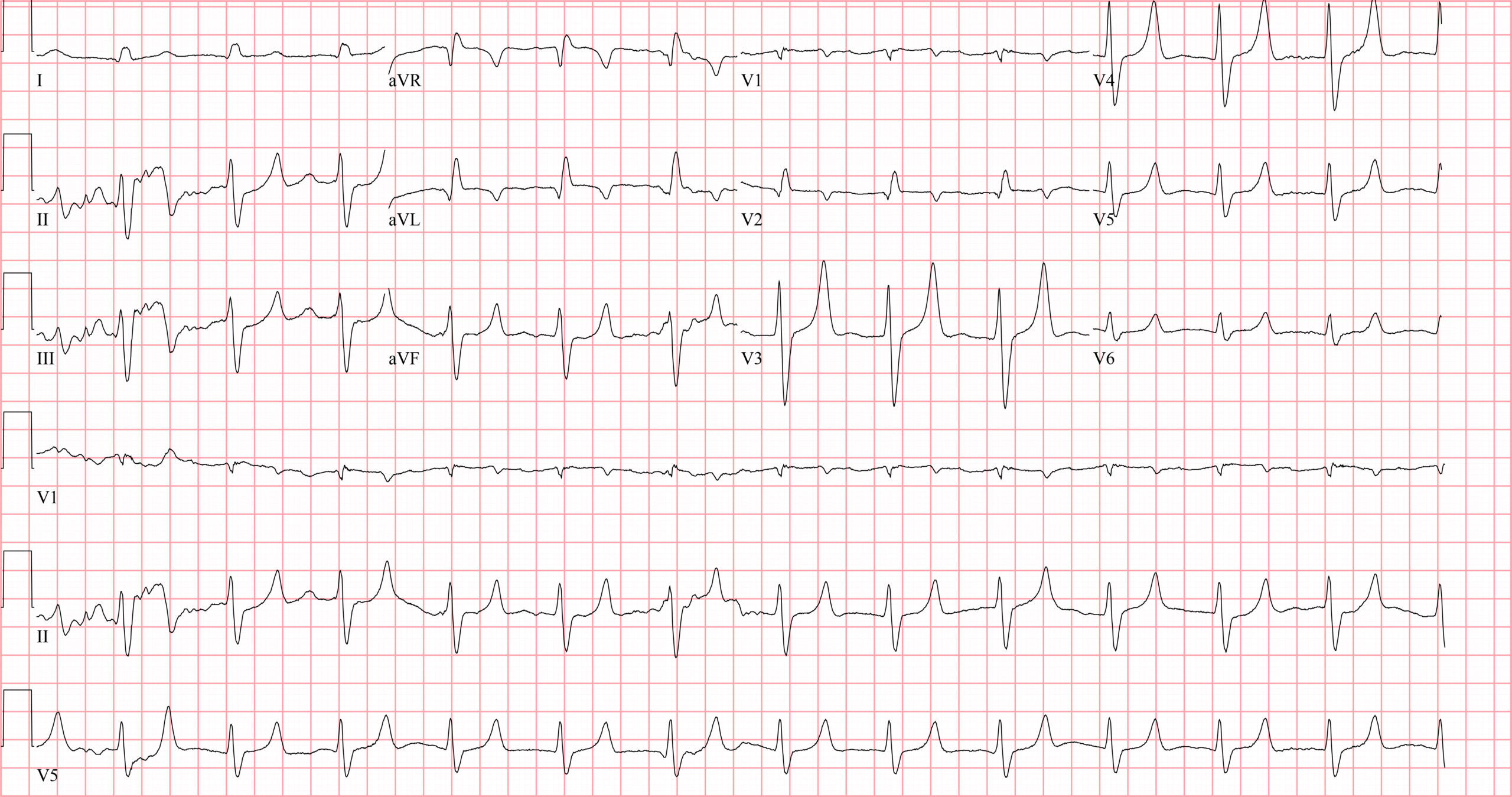
What is the most likely electrolyte disturbance causing the changes in this ECG?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 99
70. Question
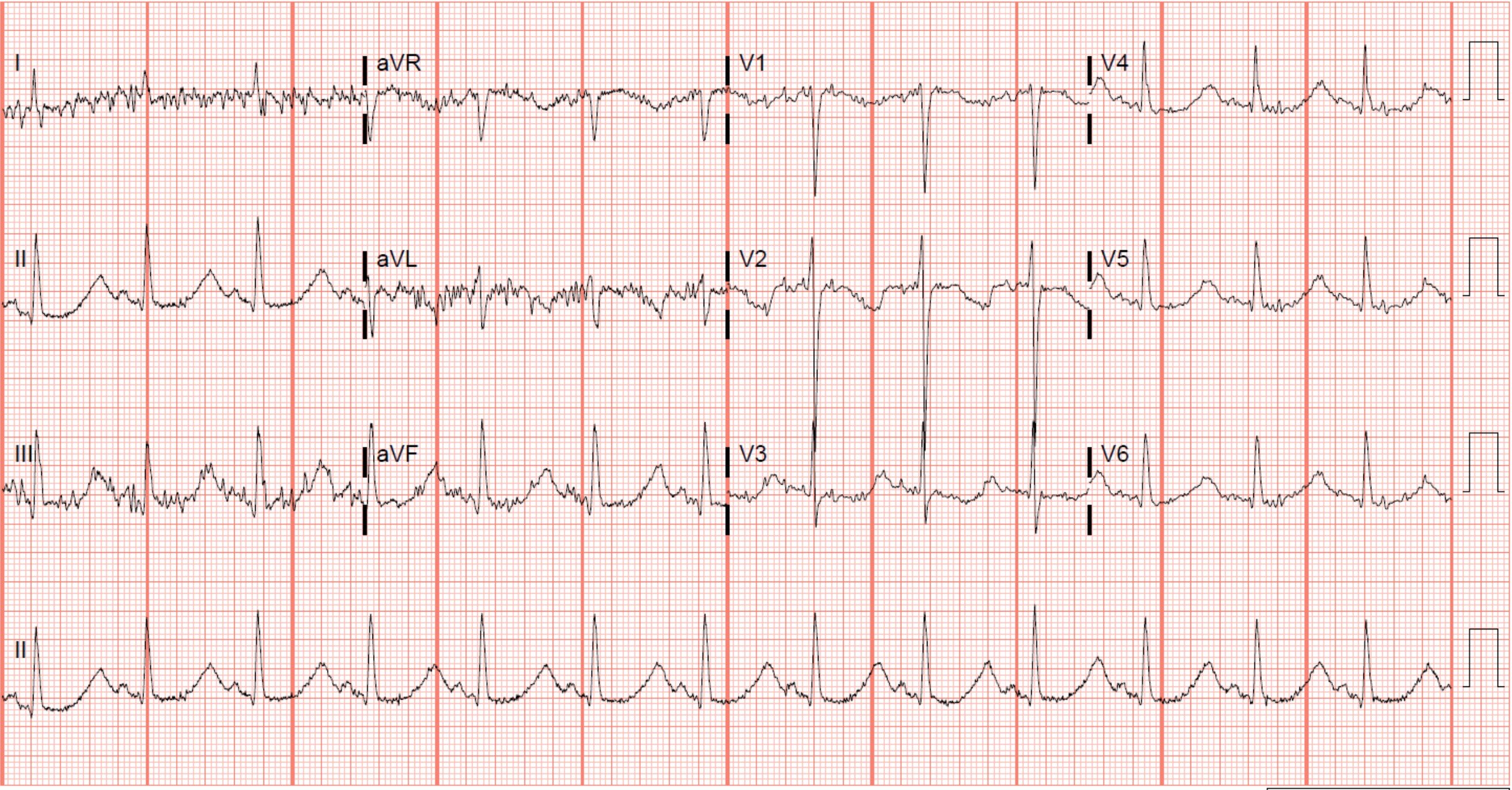
What is the most likely electrolyte disturbance causing the changes in this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 99
71. Question
In a patient with complete heart block and a narrow QRS, where is the block located?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 99
72. Question
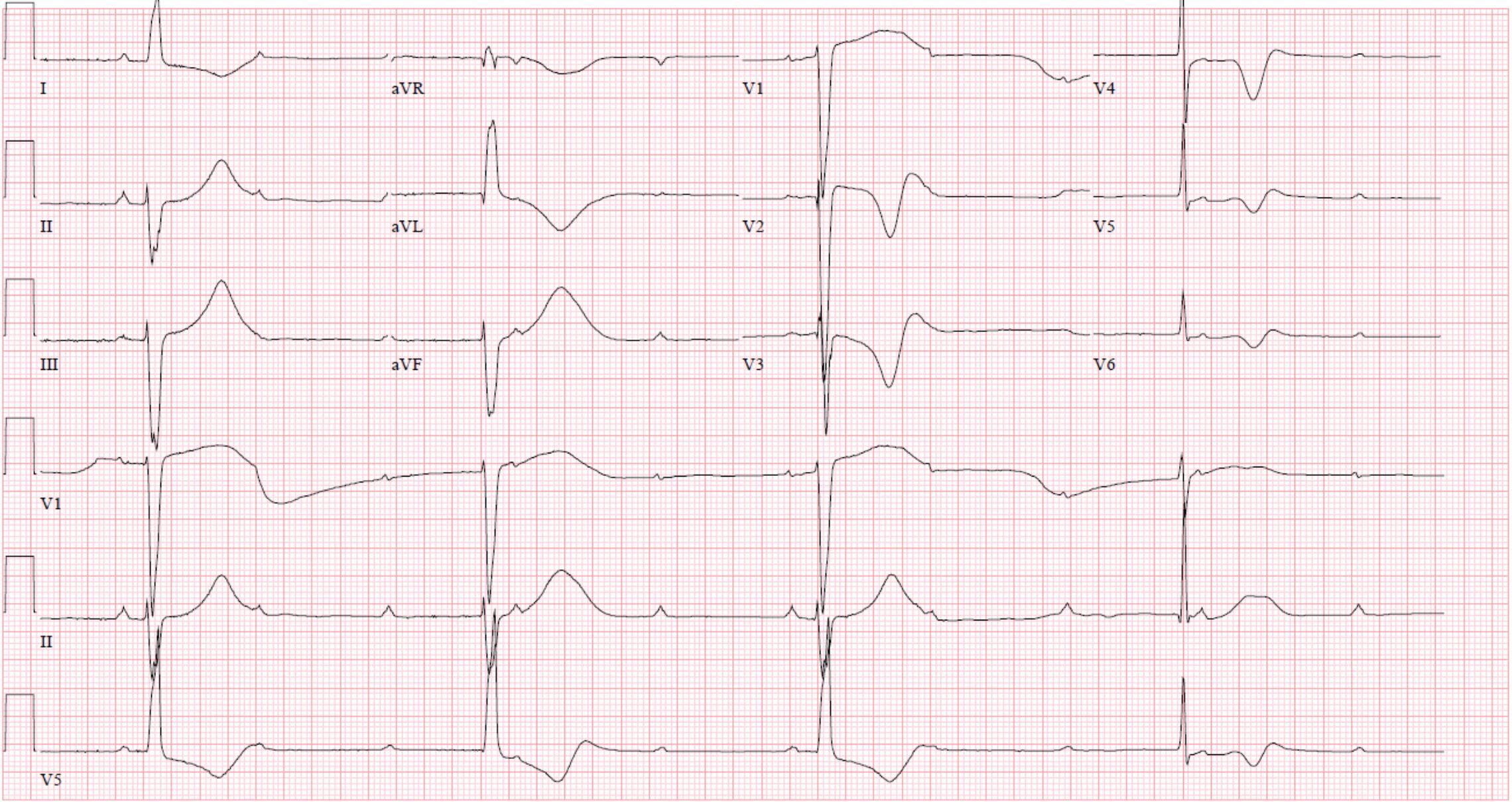
An unstable patient with this ECG requires what immediate treatment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 99
73. Question
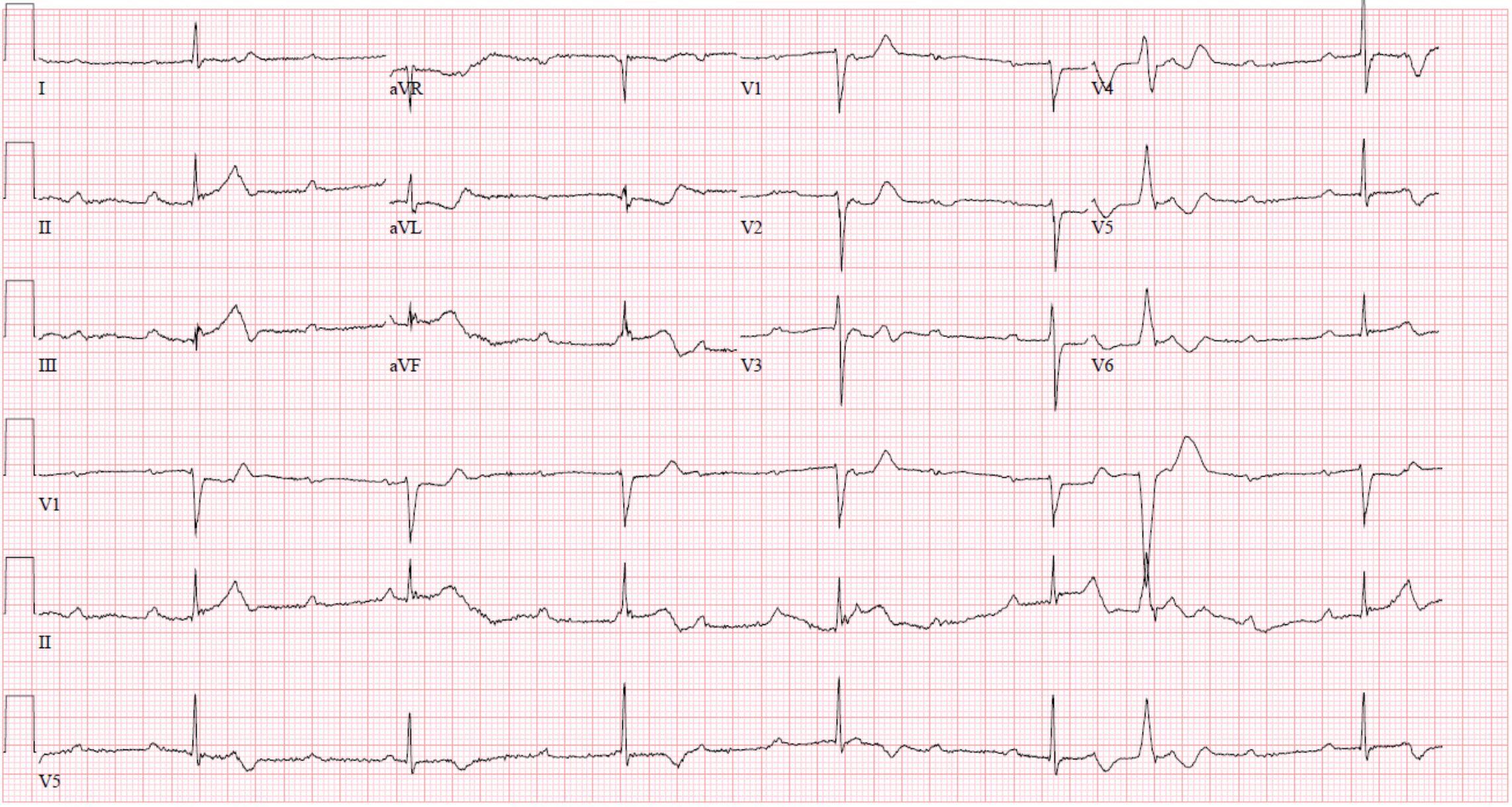
What conduction deficit is seen here?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 99
74. Question
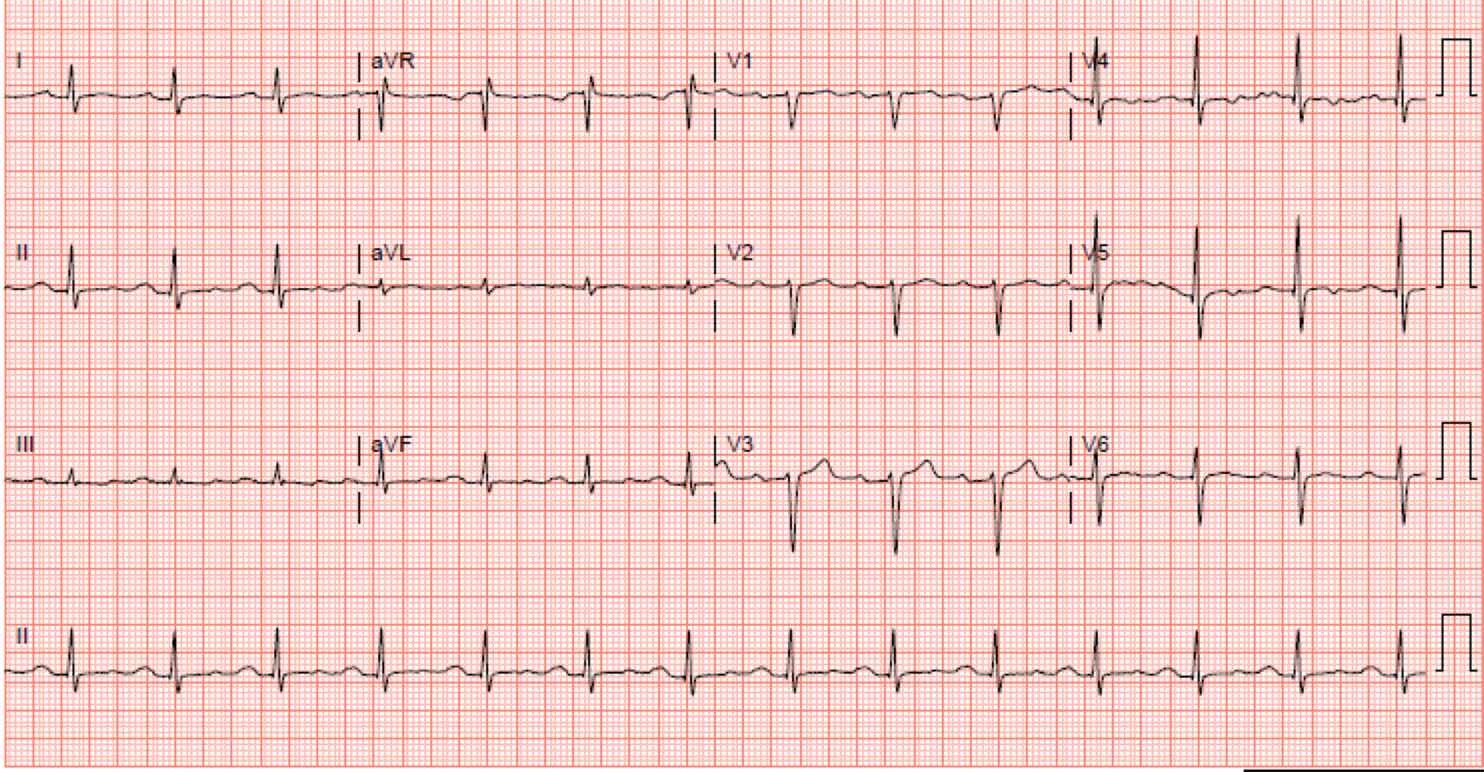
What conduction disturbance is seen here?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 99
75. Question
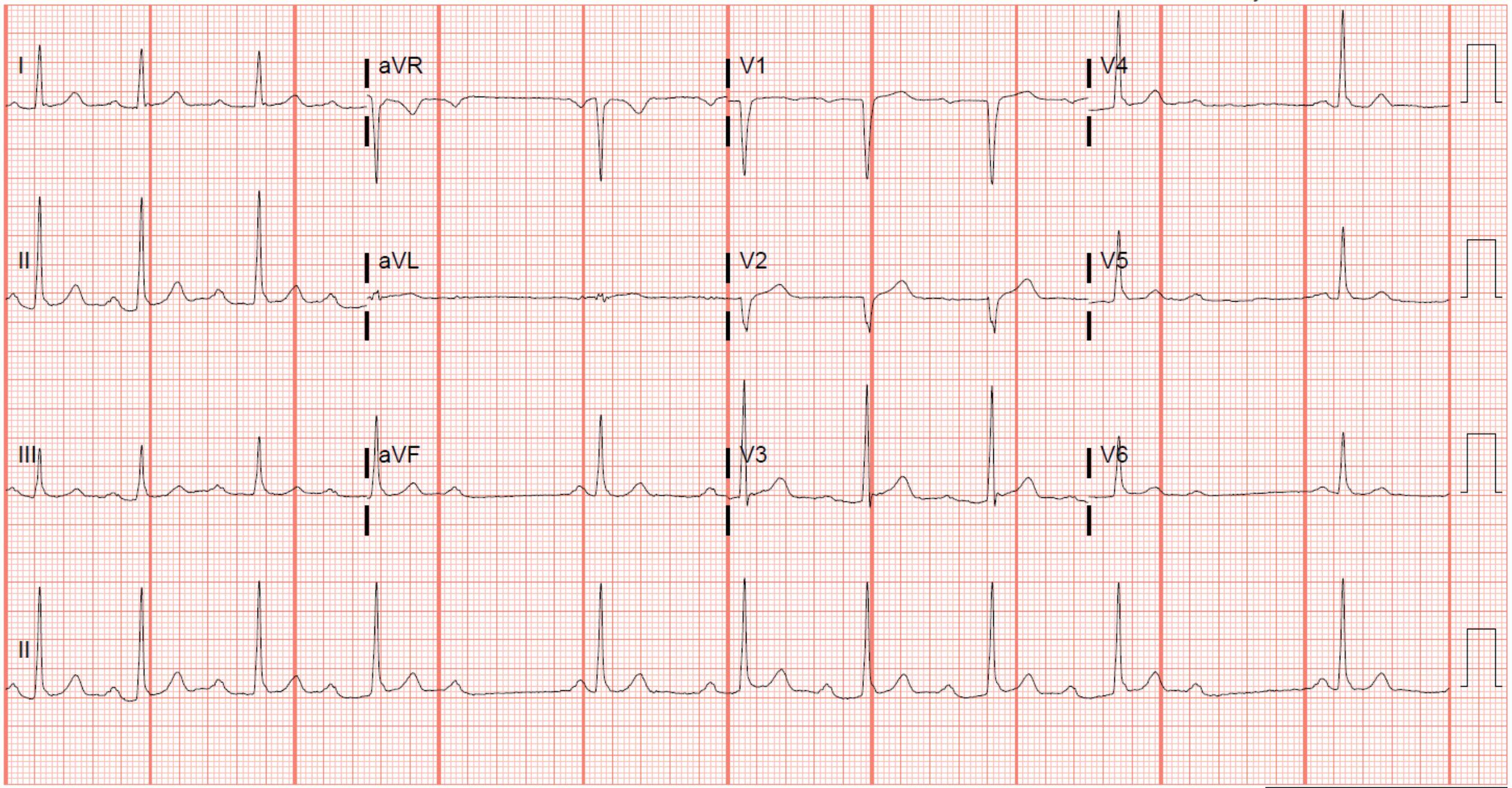
A young healthy male has the following ECG. What is the appropriate treatment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 99
76. Question
Which of the following ECG findings is hyperkalemia expected to cause? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 99
77. Question
Which of the following are intracellular potassium shifters used in hyperkalemia? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 99
78. Question
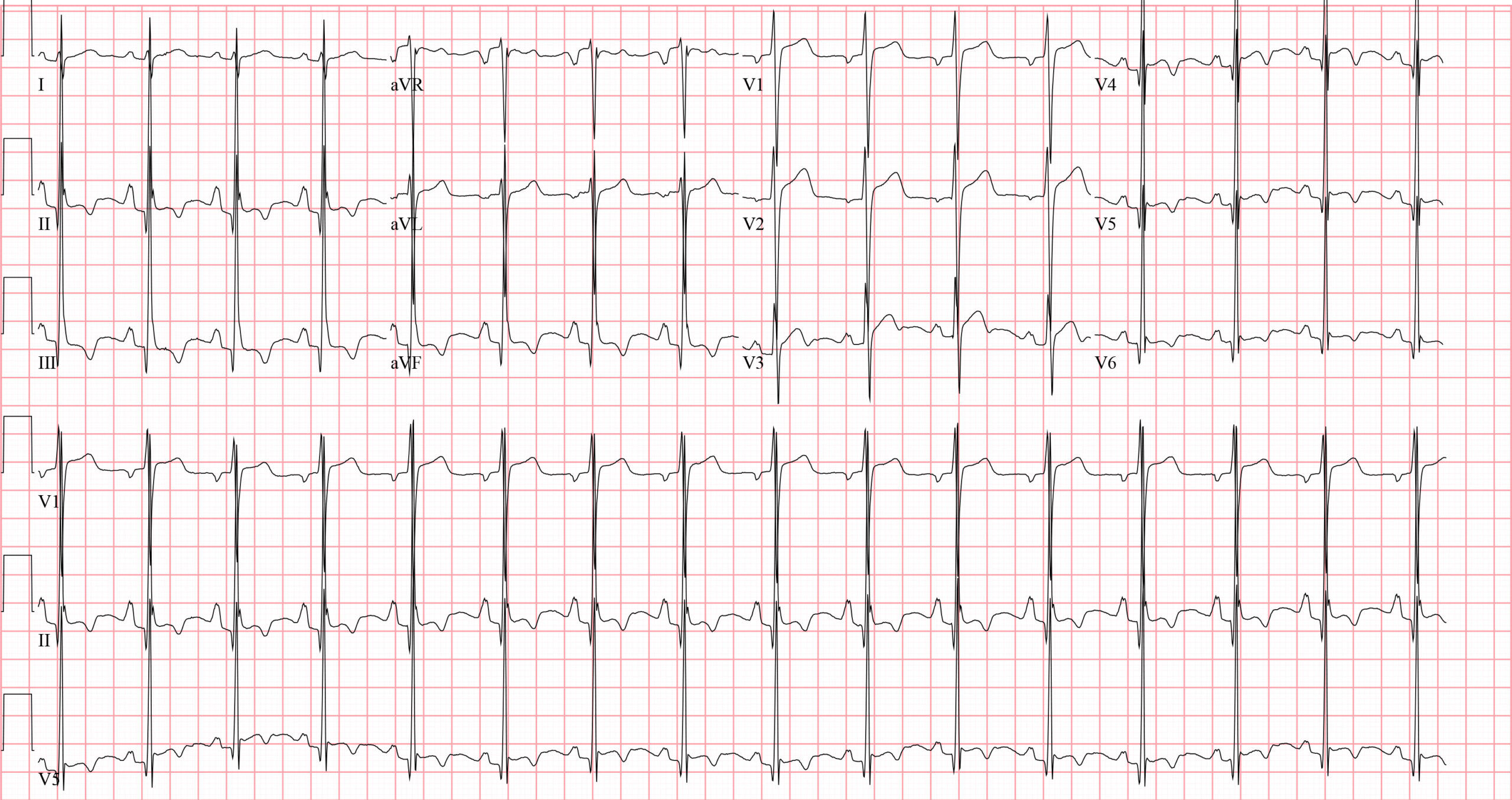
Which of the following is demonstrated in this ECG?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 99
79. Question
Escape rhythms from which structures are incapable of producing a narrow QRS complex? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 80 of 99
80. Question
Which chamber abnormality produces a “p mitrale” appearance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 81 of 99
81. Question
Which least invasive measure can be taken in order to better visualize atrial activity?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 82 of 99
82. Question
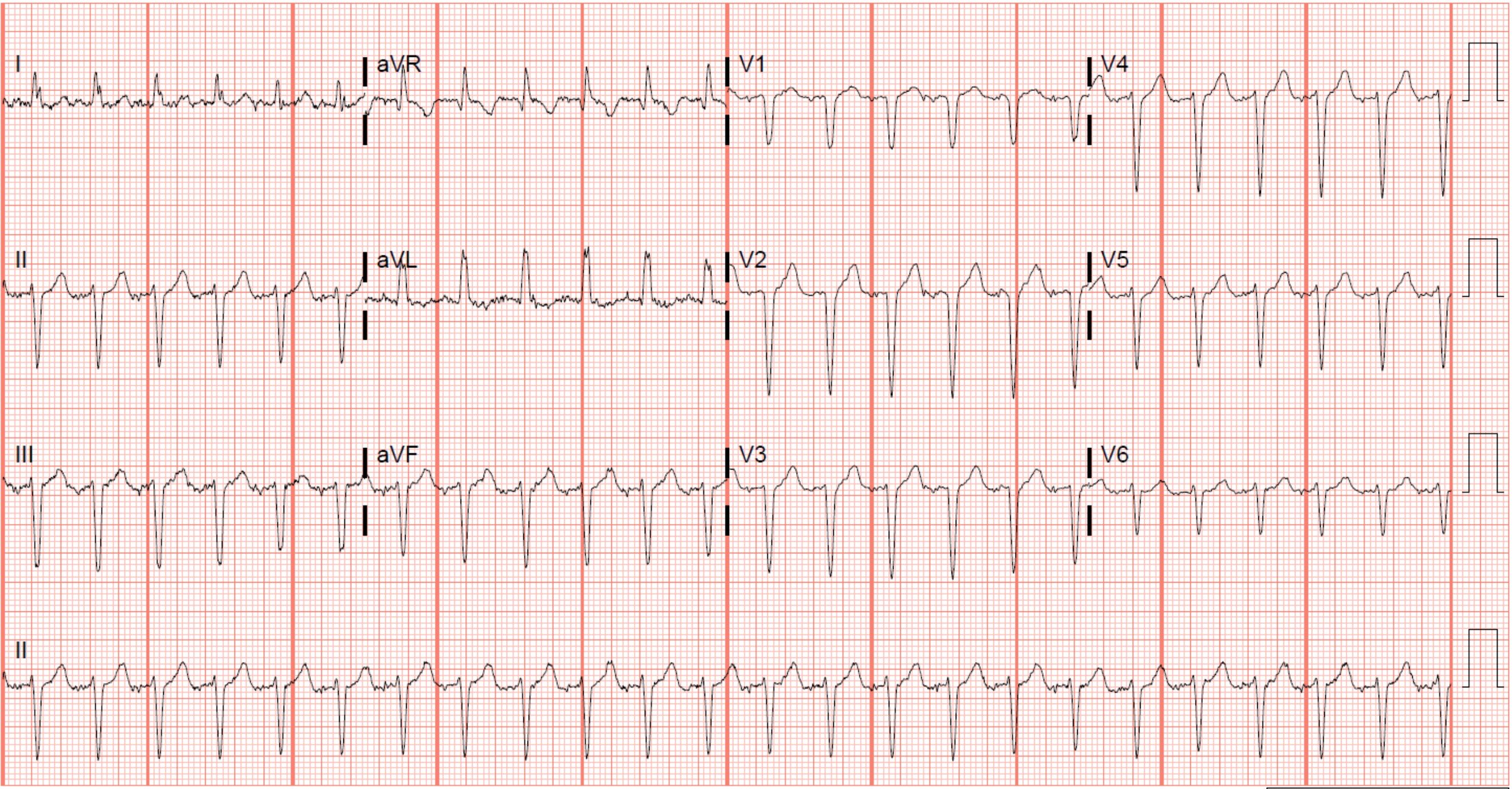
Which is the most likely rhythm shown on this elderly patient’s ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 83 of 99
83. Question
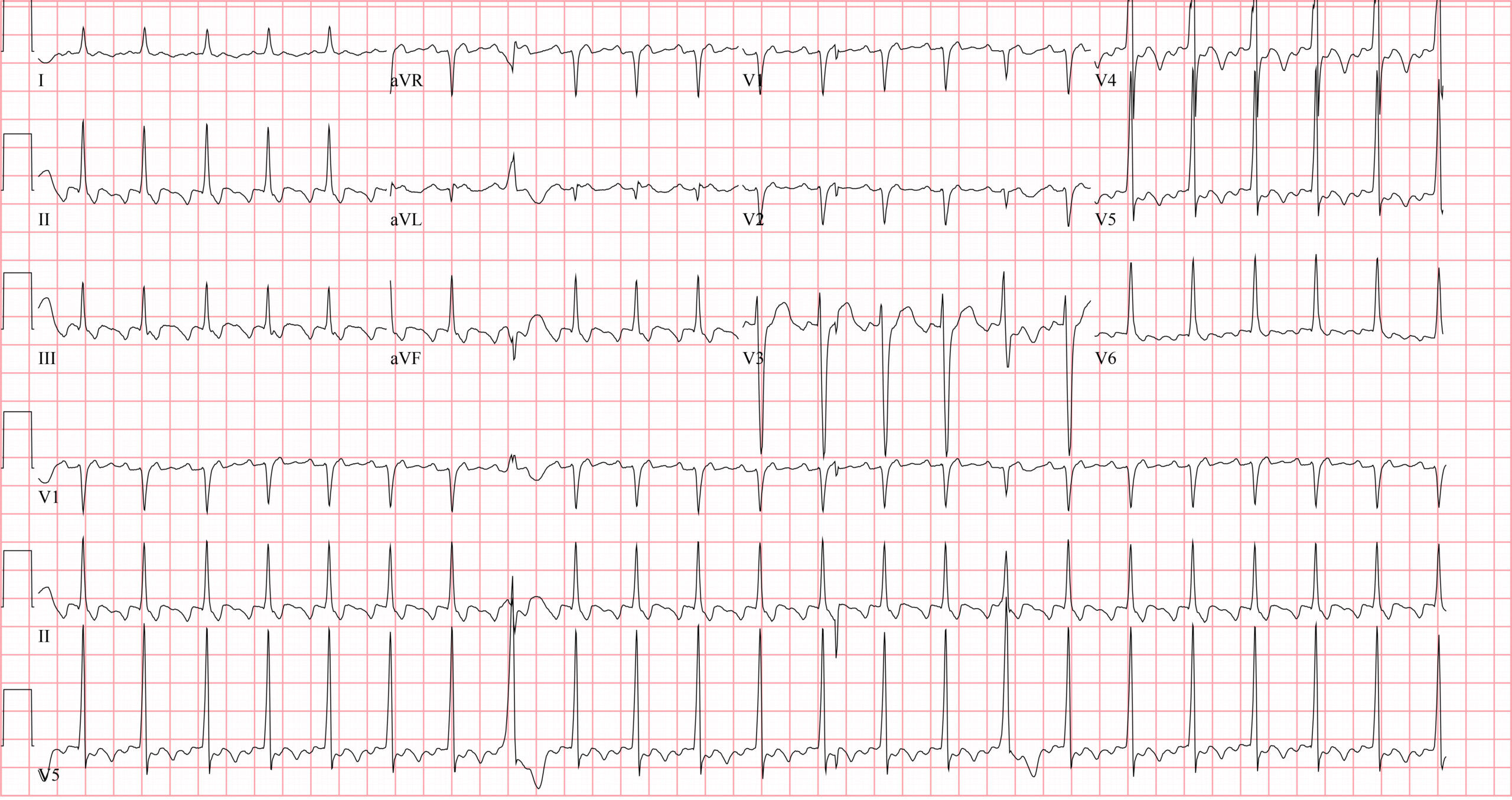
Which is the most likely rhythm shown on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 84 of 99
84. Question
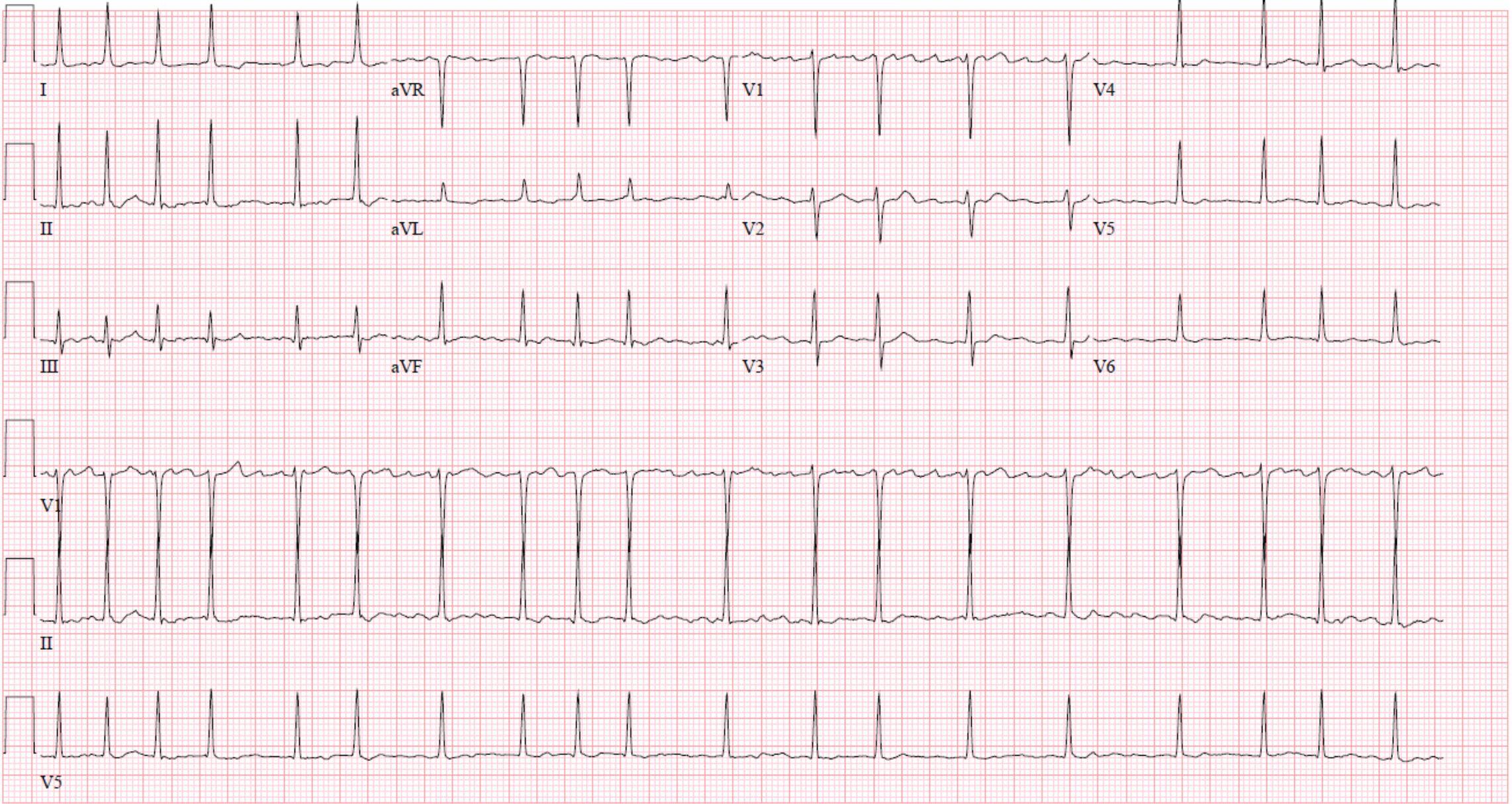
Which is the most likely rhythm shown on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 85 of 99
85. Question
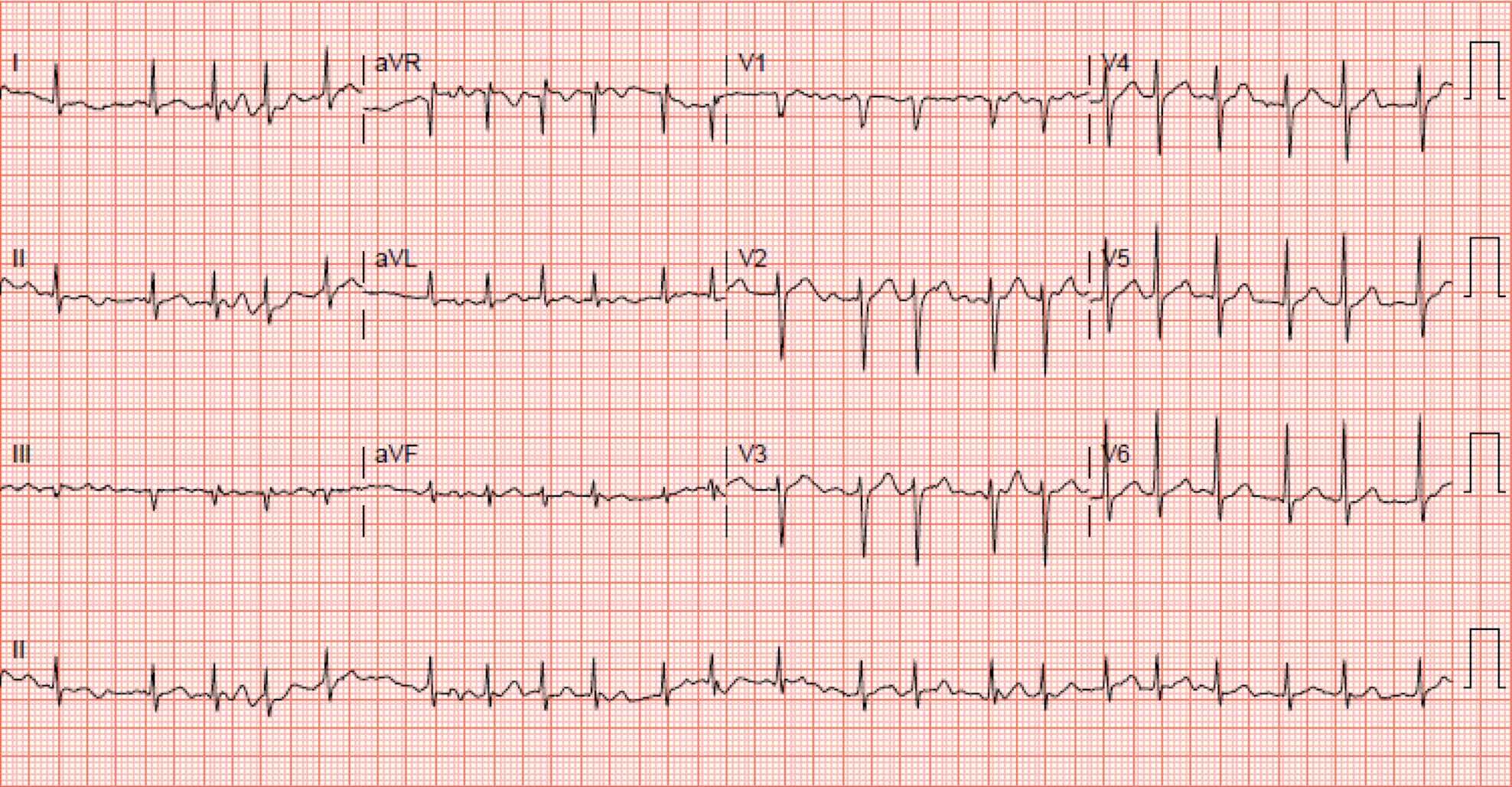
Which of the following is not expected to cause the rhythm seen in this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 86 of 99
86. Question
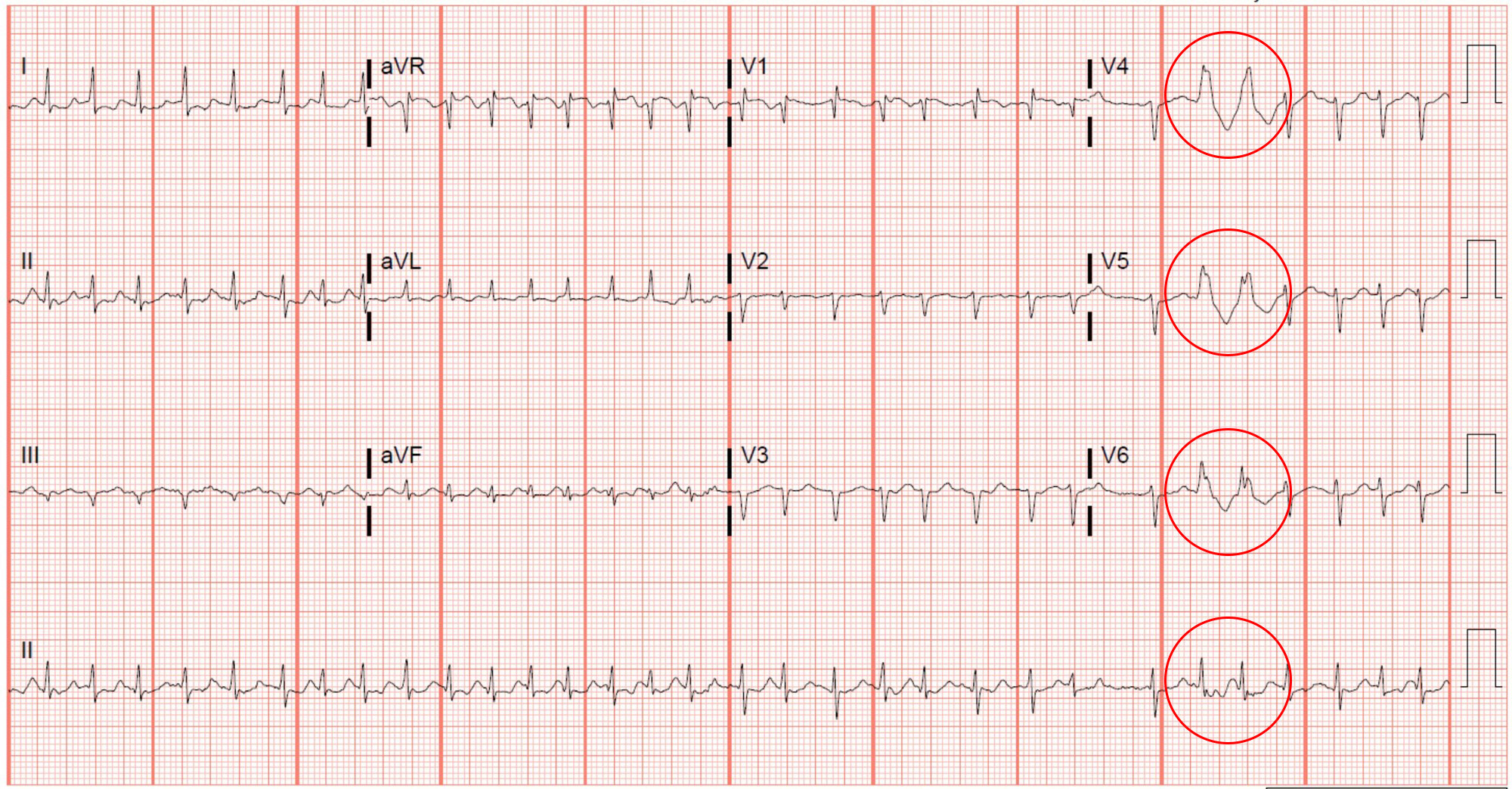
Which answer best explains the presence of the complexes shown in the red circles?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 87 of 99
87. Question
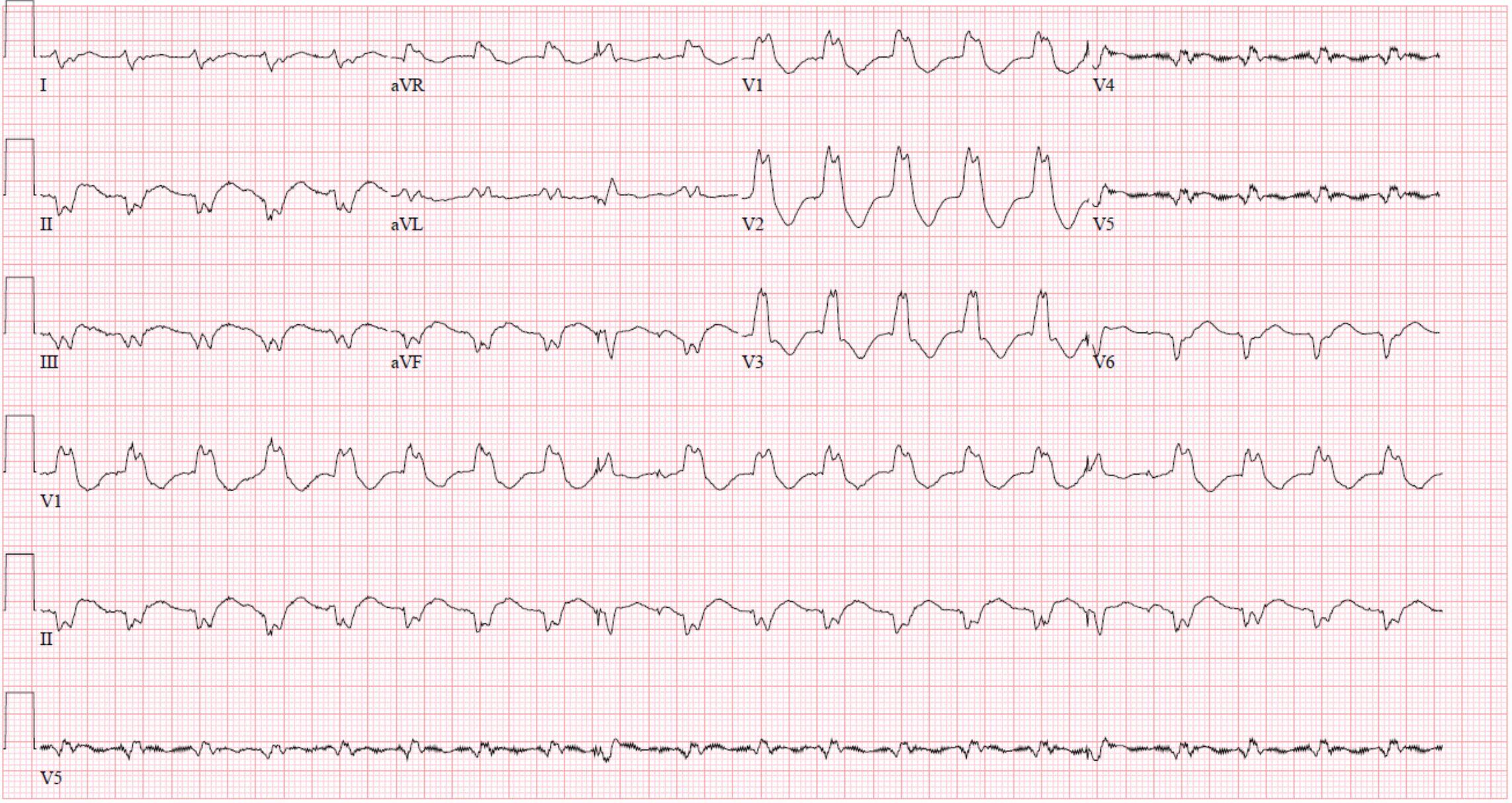
In this stable patient, which of the following are acceptable next steps in management? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 88 of 99
88. Question
What ST/T changes are most consistent with supraventricular tachycardia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 89 of 99
89. Question
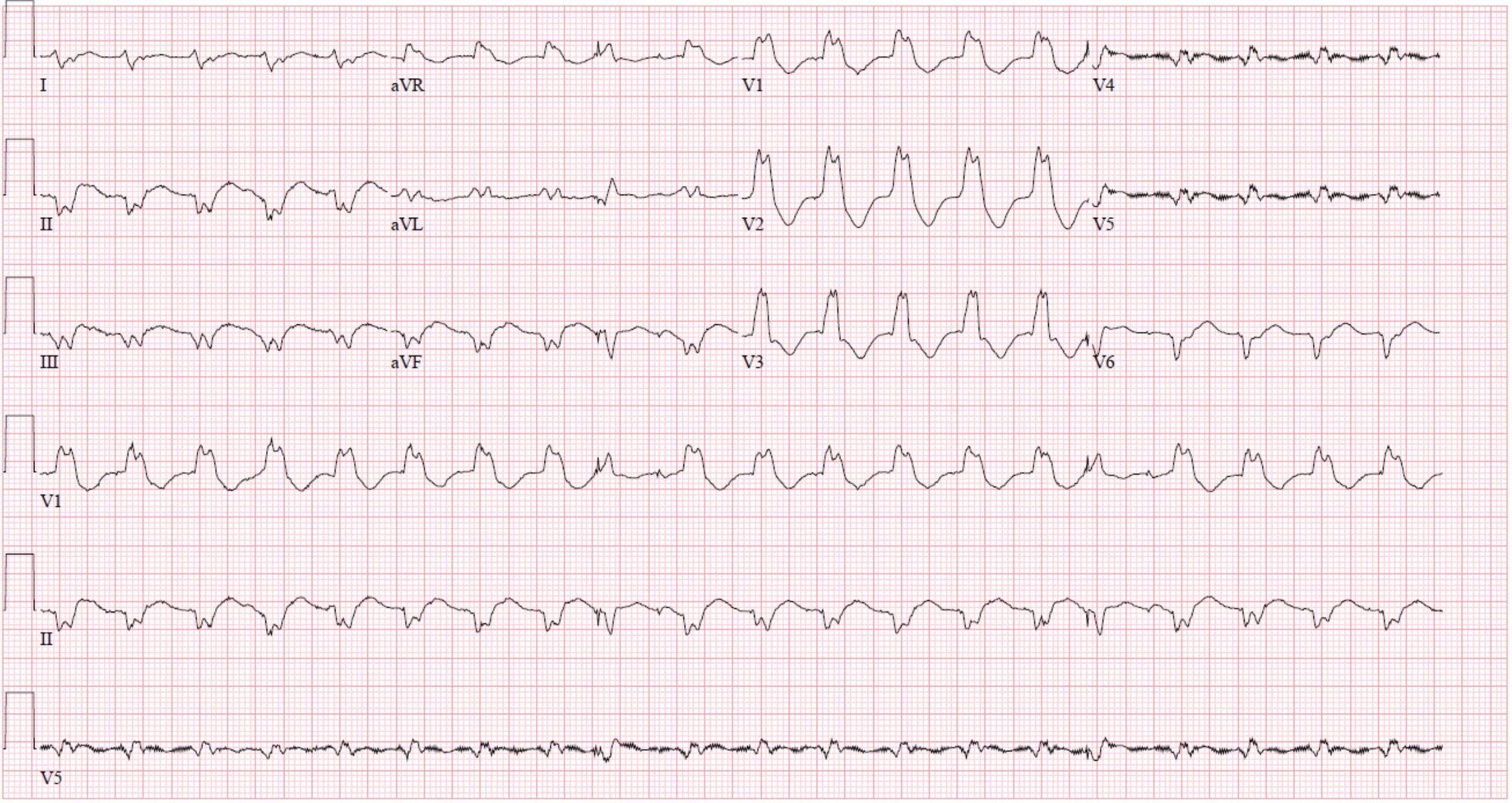
What features suggest ventricular tachycardia in this ECG? (Select all that apply)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 90 of 99
90. Question
Which of the following statements is true regarding wide complex tachycardia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 91 of 99
91. Question
What do the first three letters of pacemakers modes represent?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 92 of 99
92. Question
What happens if you put a magnet on a pacemaker?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 93 of 99
93. Question
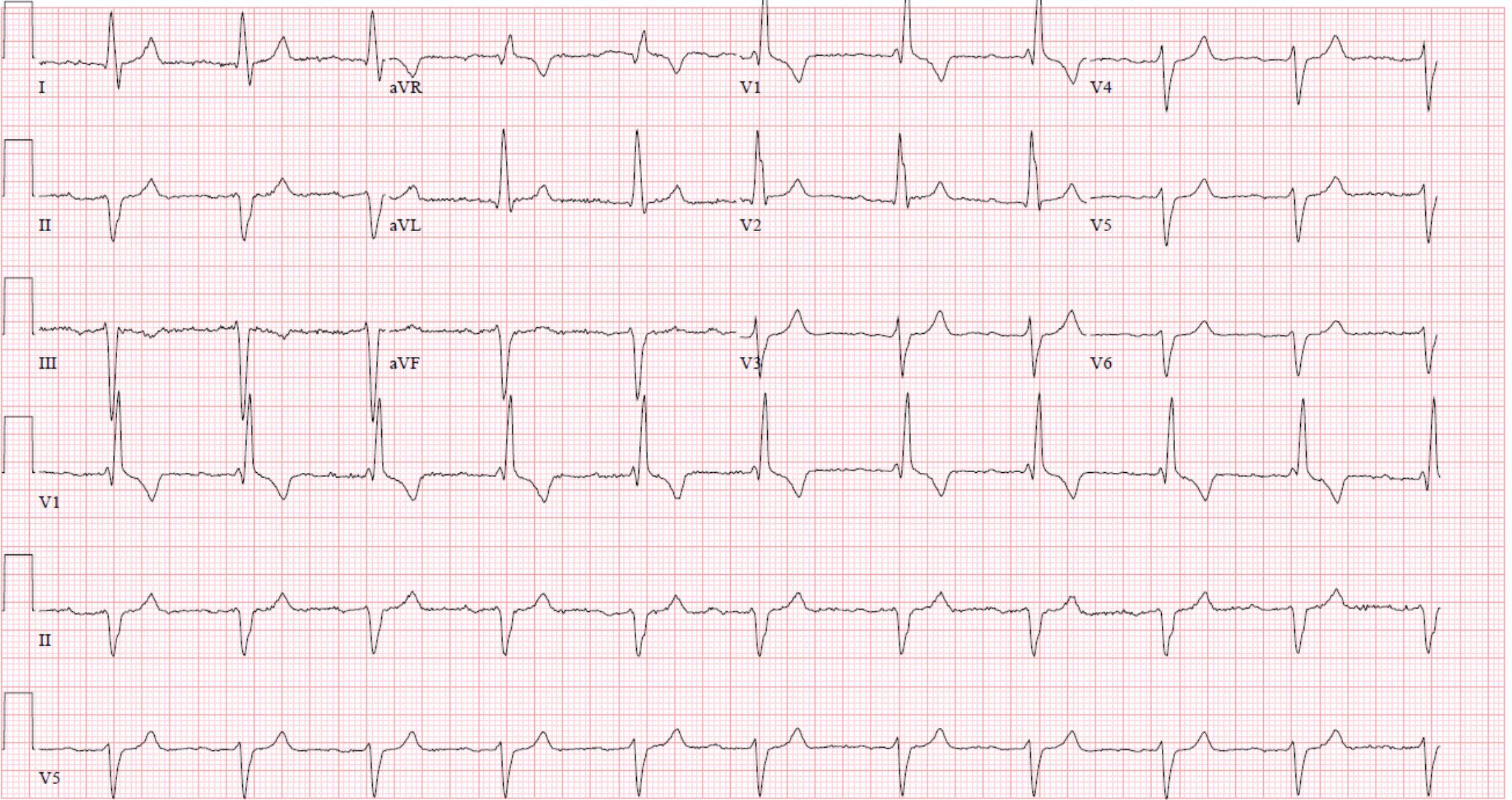
What conduction disturbance is illustrated on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 94 of 99
94. Question
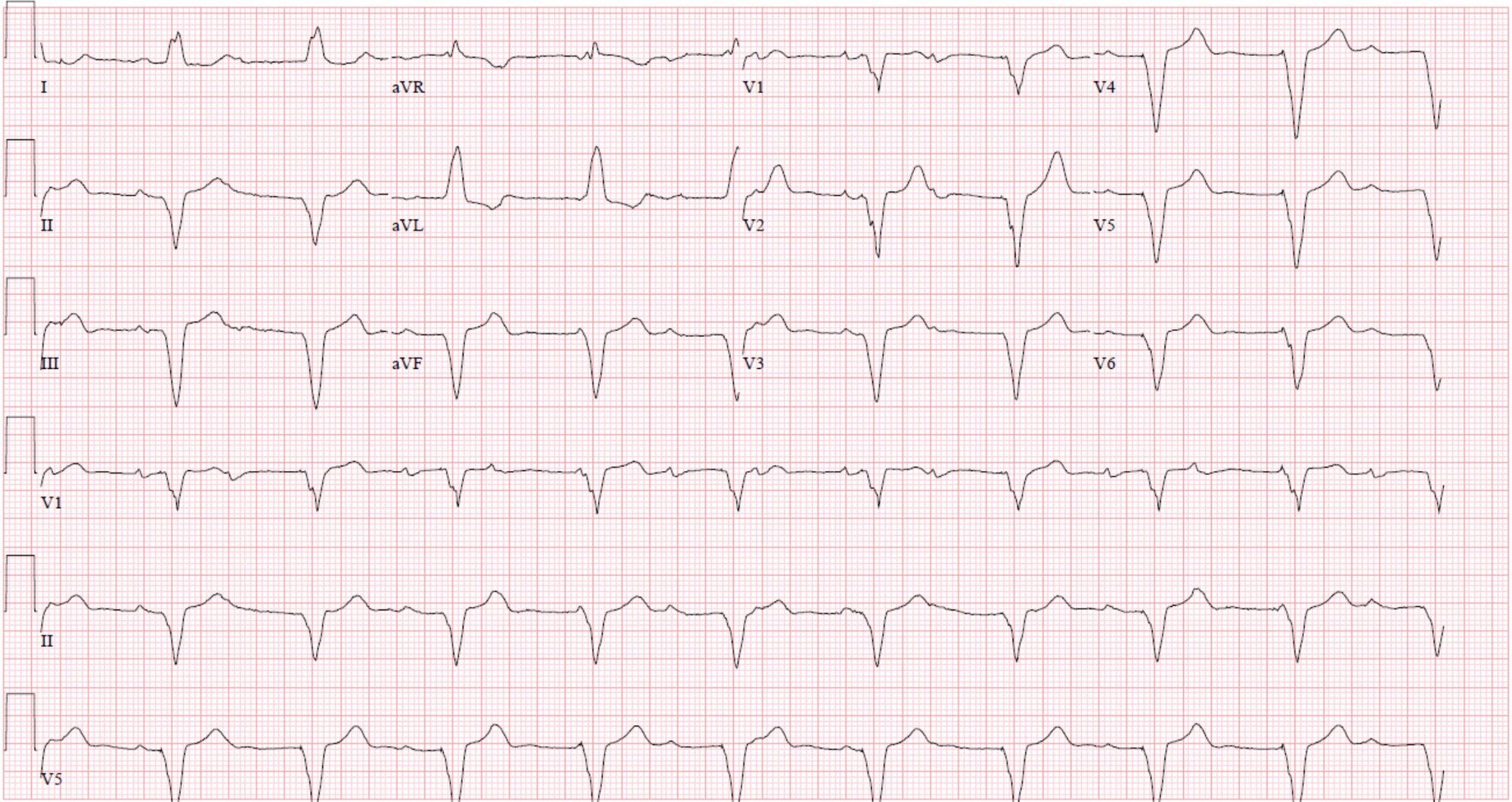
What is the most likely pacemaker mode demonstrated on this ECG?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 95 of 99
95. Question
What is it called when a pacemaker does not detect native cardiac activity, resulting in asynchronous pacing?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 96 of 99
96. Question
What is it called when pacemaker activity is inappropriately inhibited by non-cardiac activity (such as movement of skeletal muscle)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 97 of 99
97. Question
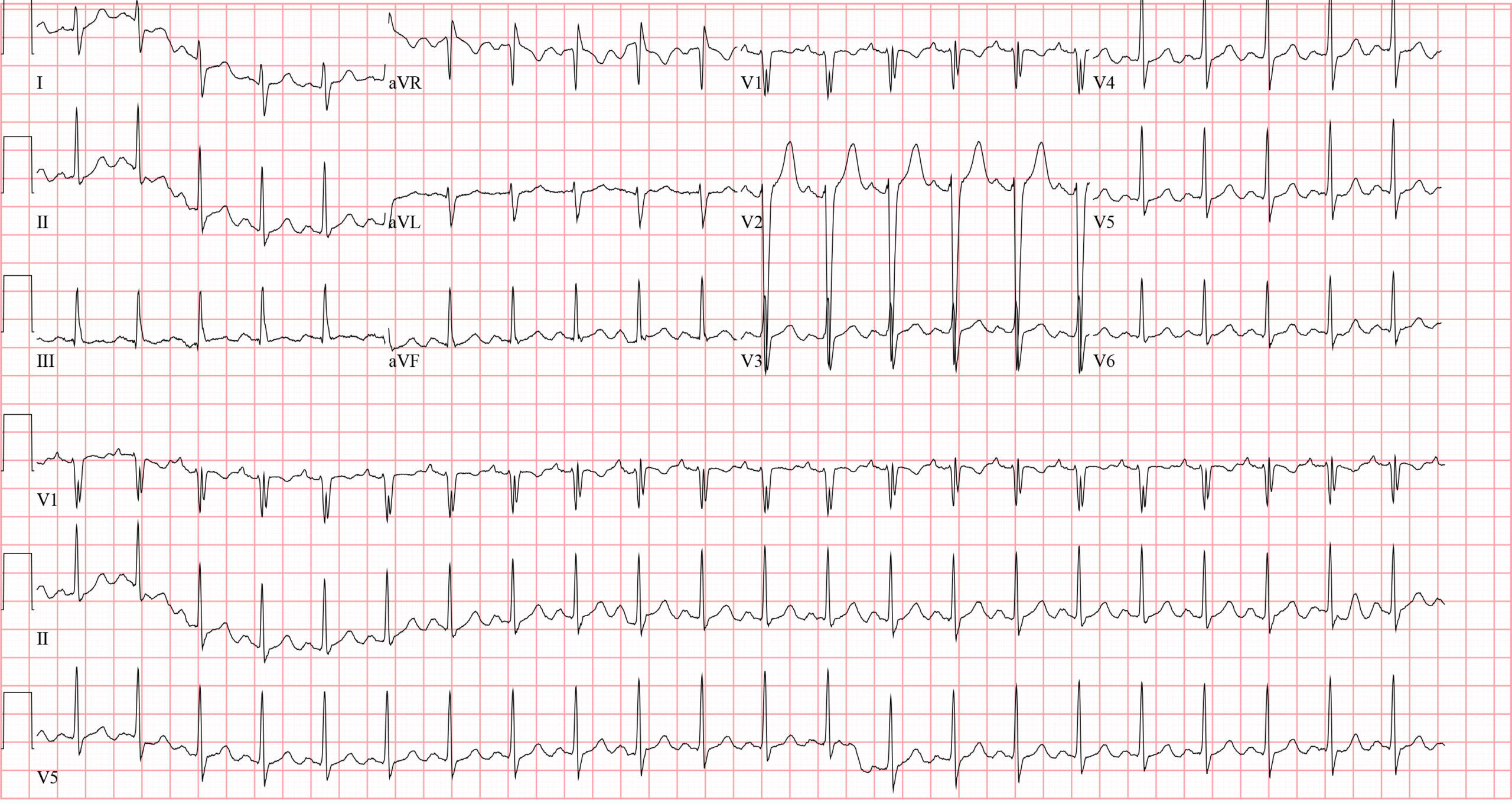
The following ECG may be caused by what kind of overdose?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 98 of 99
98. Question
With sodium channel blocker overdose, what is the goal of treatment with sodium bicarbonate to avoid seizures or arrythmias?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 99 of 99
99. Question
What is your level of training?
CorrectIncorrect
