Wellens syndrome comes in two electrocardiographic varieties – biphasic T waves (up then down, type A) or deeply inverted and symmetric T waves in the anterior precordial leads V1-V3 (type B). The syndrome requires these ECG findings in a patient that is chest pain free. If the patient develops chest pain and the T waves “pseudonormalize” (i.e., become upright), complete occlusion is suggested. Wellens syndrome represents a special category of high-risk acute coronary syndrome that should have an urgent catheterization planned with the cardiologist. Patients in whom Wellens syndrome is a consideration should not get a stress test given the risk of a large anterior myocardial infarction.
Wellens Syndrome
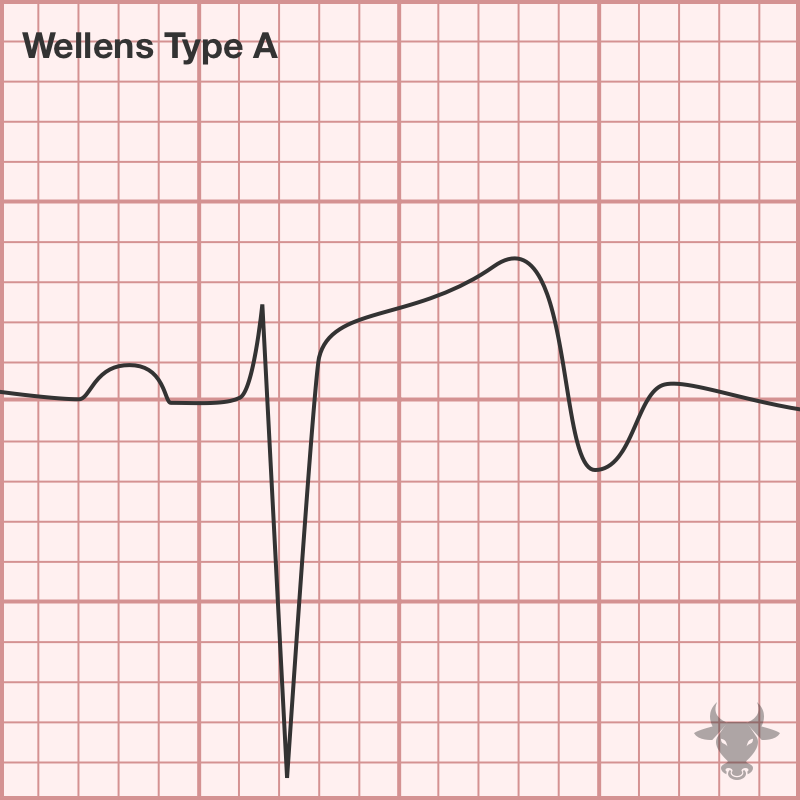
Examples
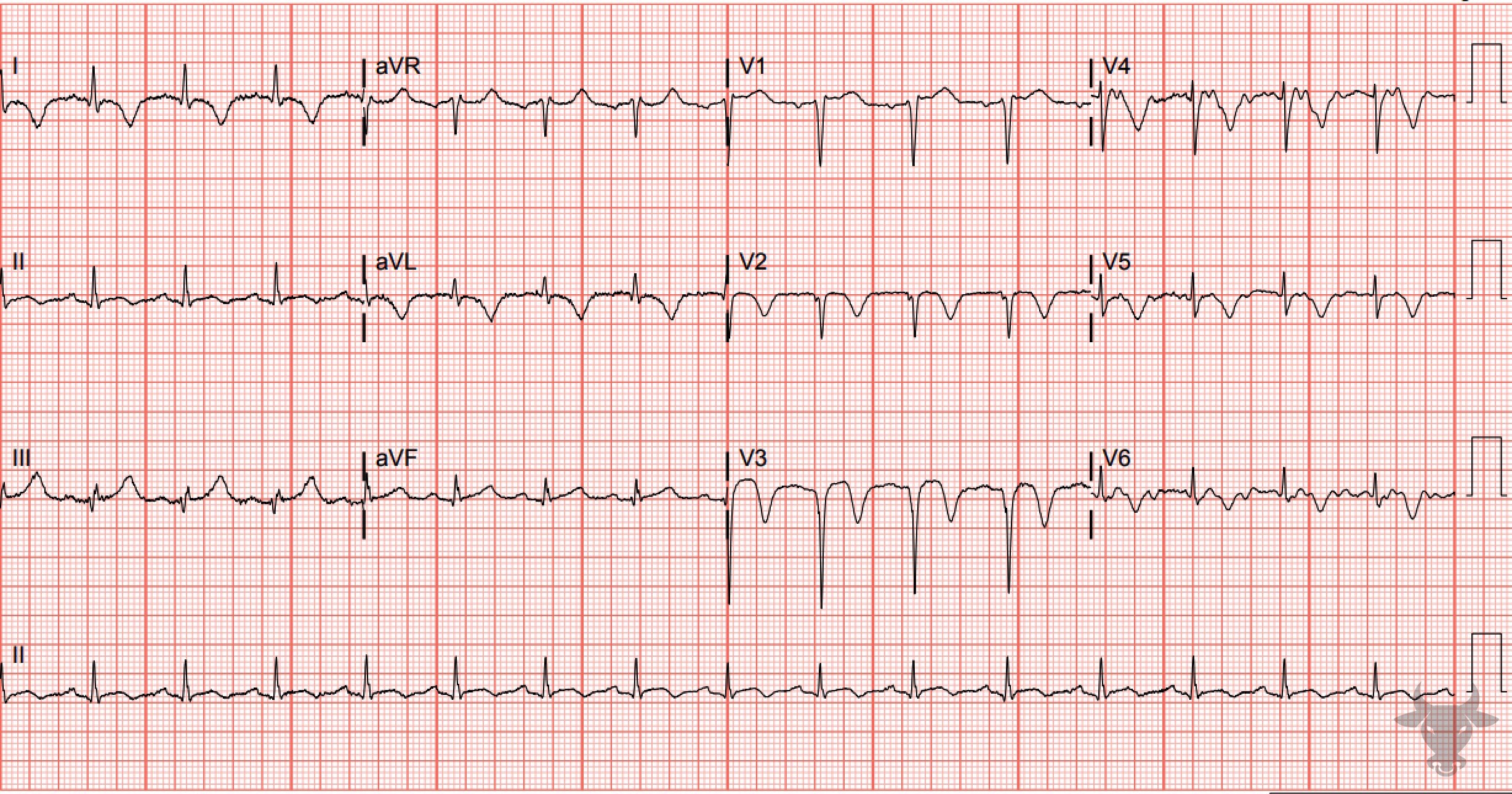
Wellens Syndrome
This is type B Wellens pattern with deeply inverted precordial T waves. This patient had a 95% proximal left anterior descending stenosis.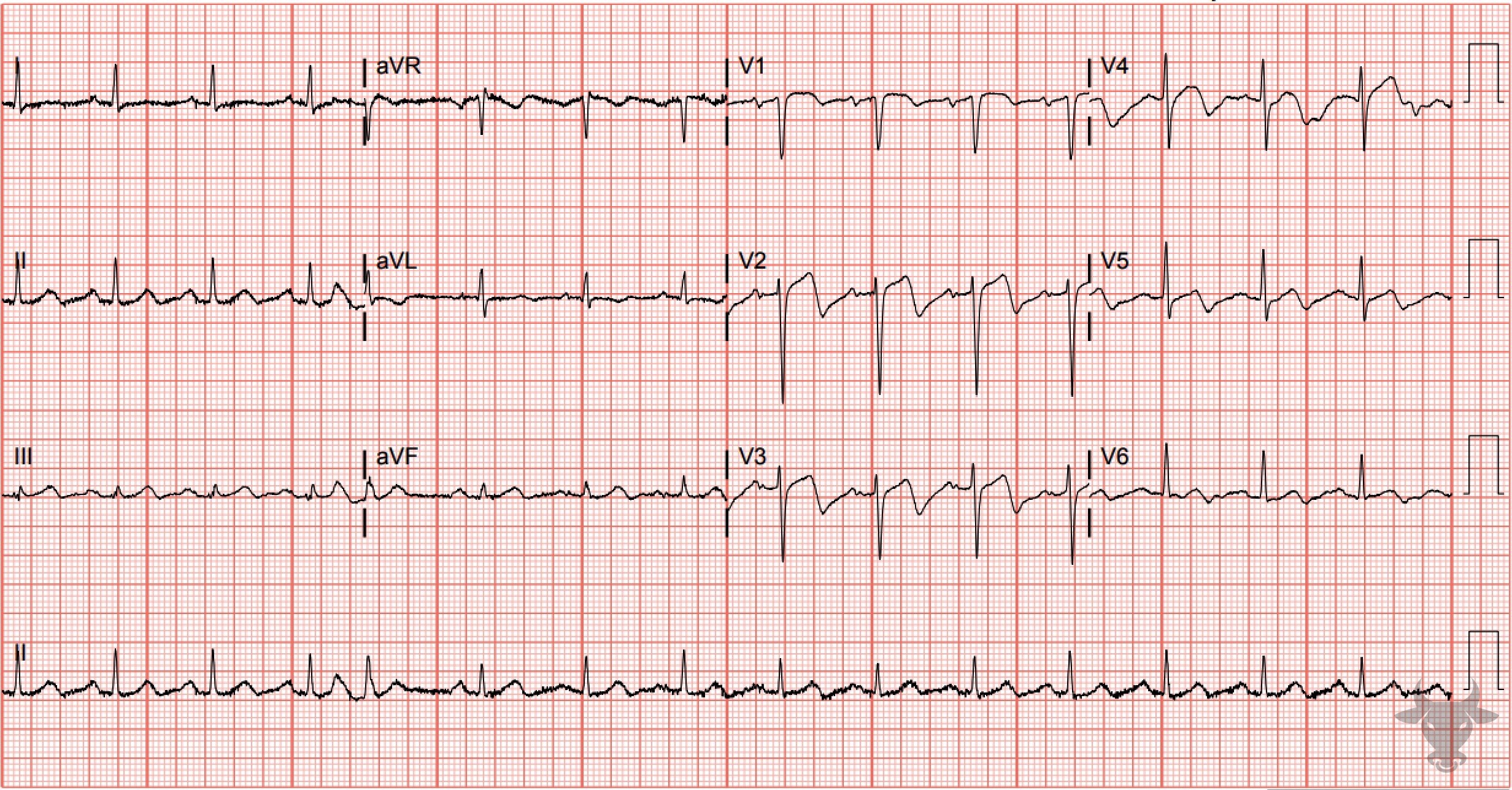
Wellens Syndrome
This is a type A Wellens pattern with biphasic T waves that have negative terminal deflections. This patient had a 90% proximal left anterior descending artery stenosis.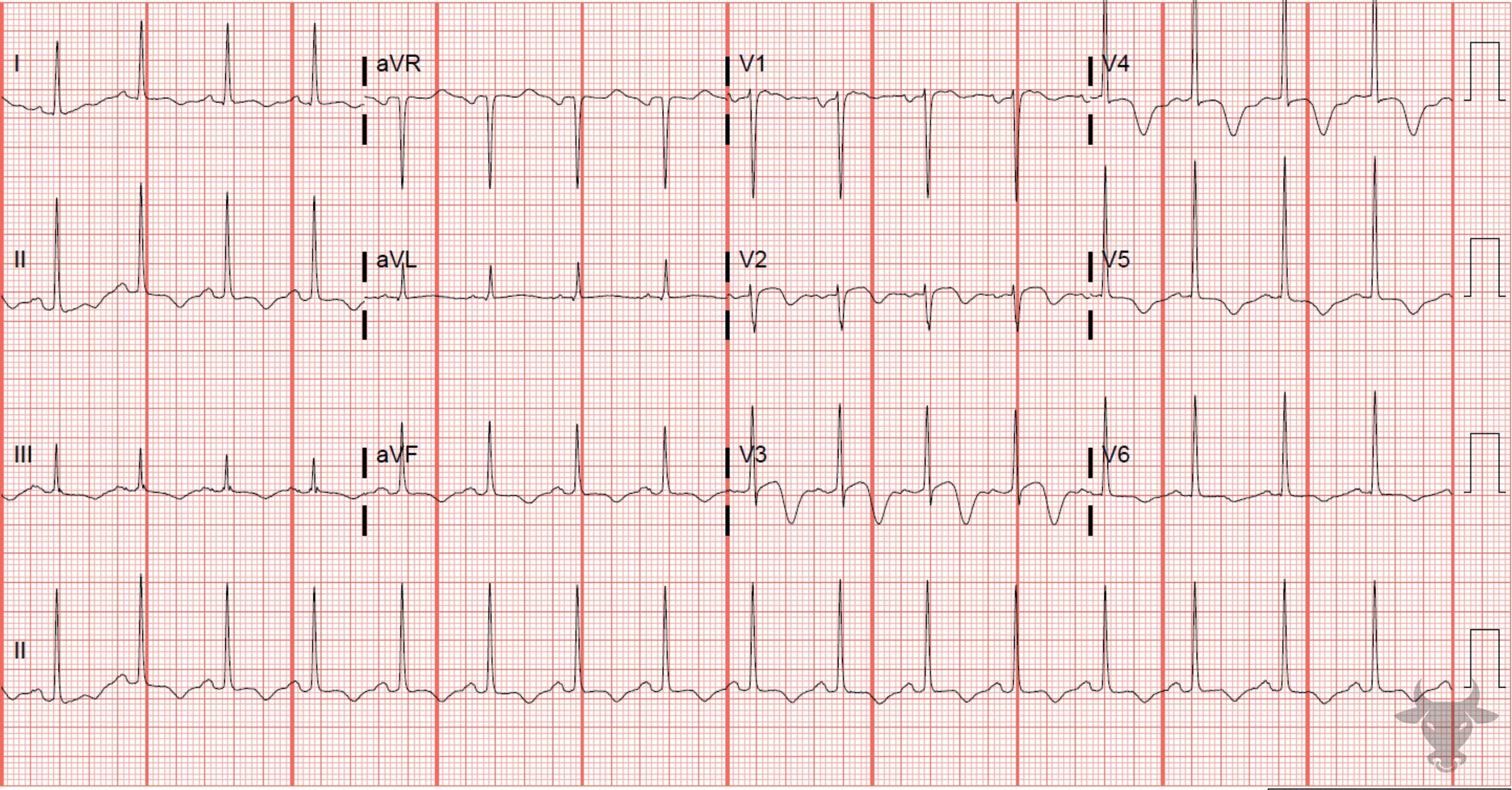
Wellens Syndrome
Type B Wellens pattern. Left heart catheterization revealed a 95% proximal left anterior descending artery stenosis.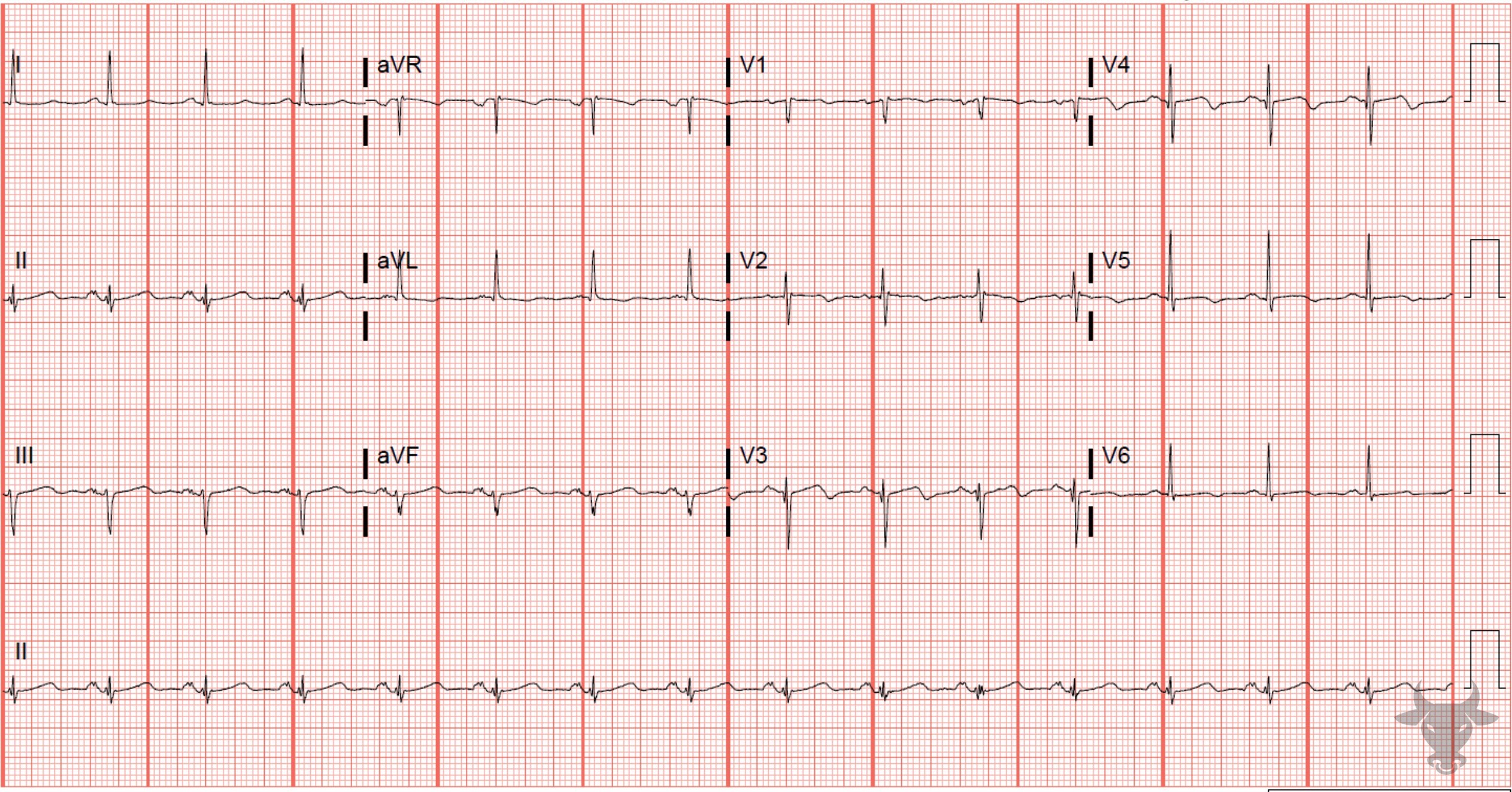
Wellens Syndrome
This is a more subtle type A Wellens pattern in leads V2 through V5. Left heart catheterization revealed 99% proximal left anterior descending artery stenosis.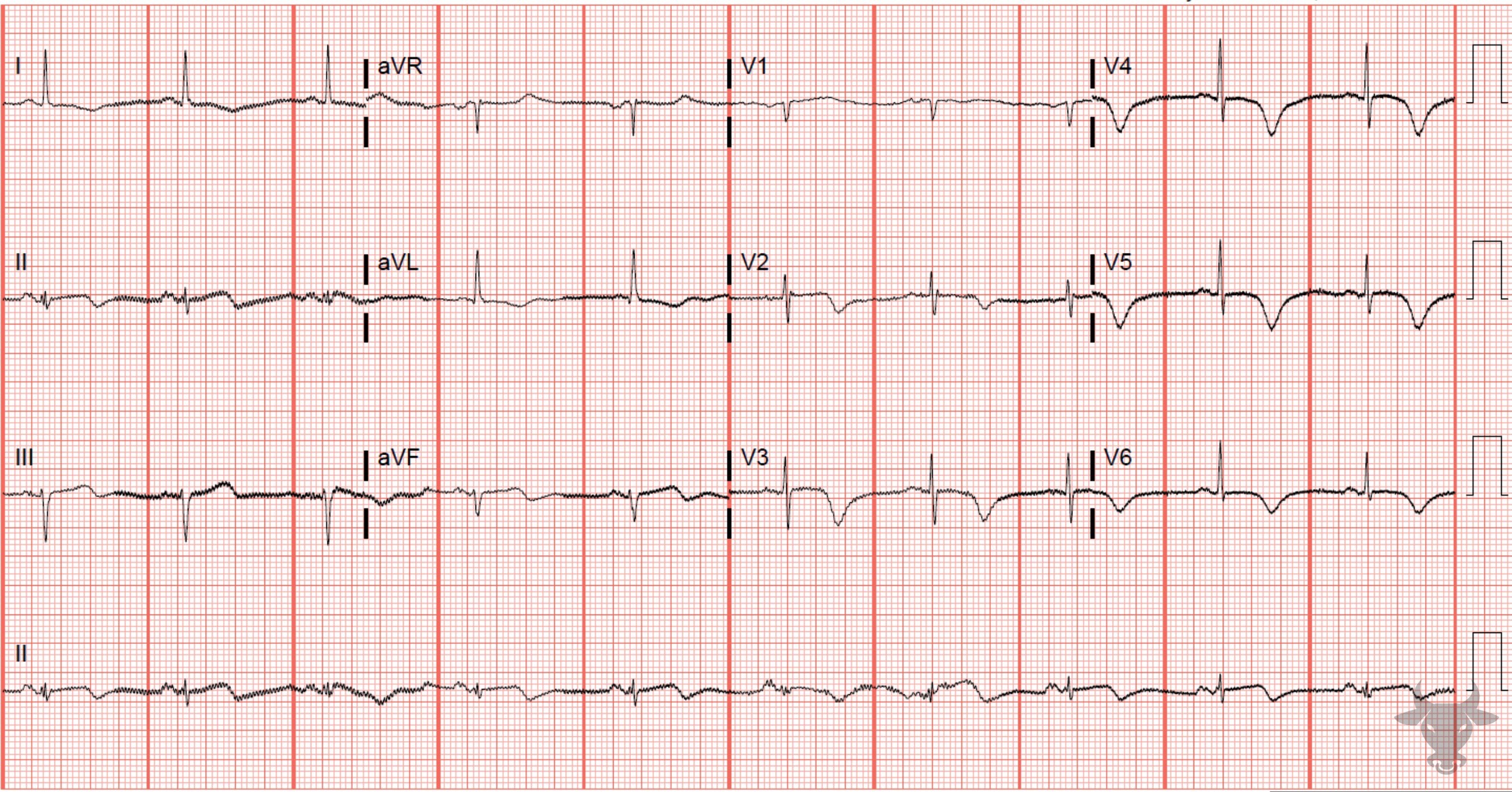
Wellens Syndrome
Type B Wellens pattern. Left heart catheterization revealed 99% proximal left anterior descending artery stenosis.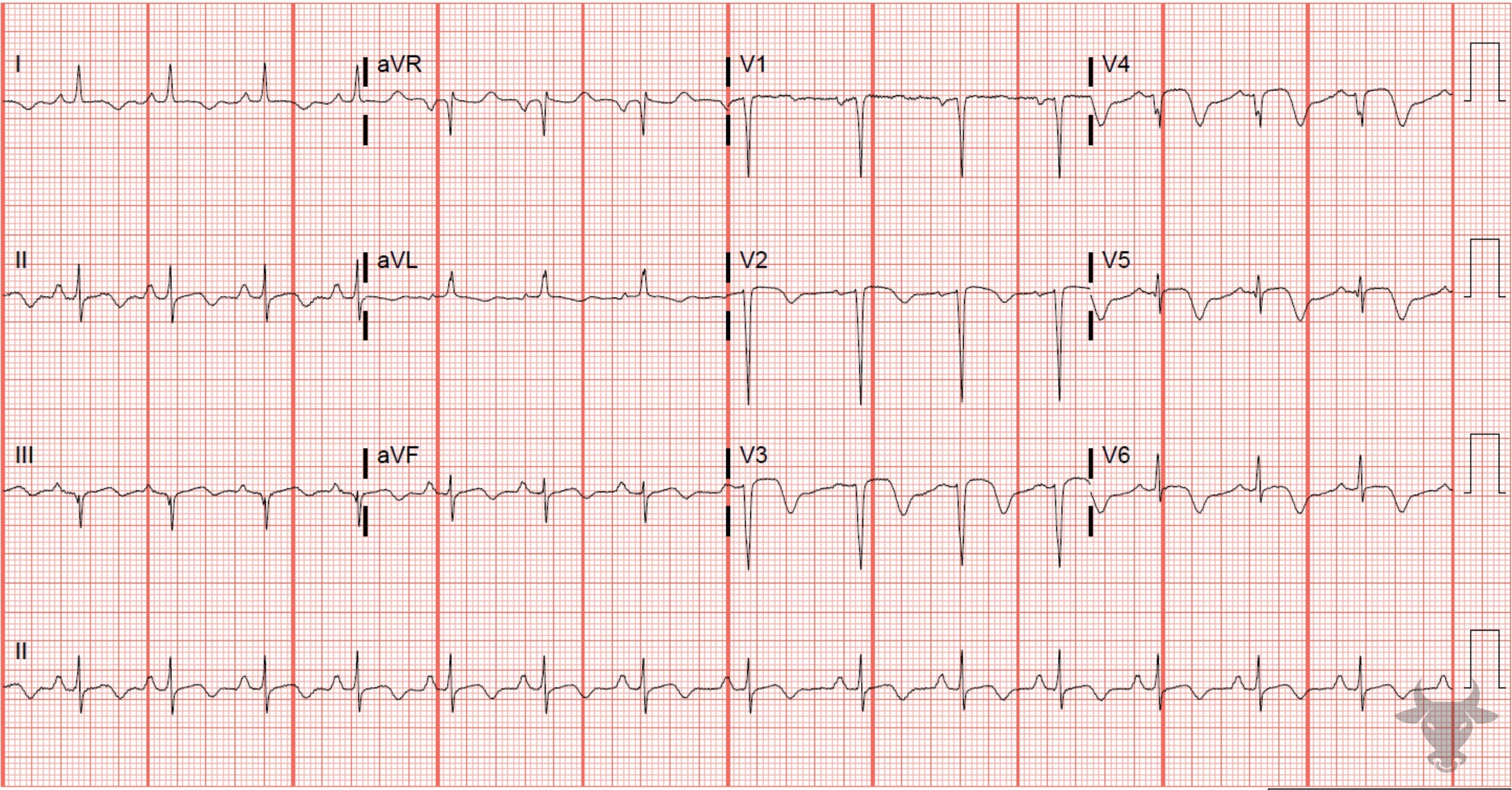
Wellens Syndrome
The repolarization abnormalities seen here represent "reperfusion T waves." This ECG was performed immediately after percutaneous coronary intervention of the left anterior descending artery. Reperfusion T waves are expected repolarization changes associated with reperfusion. They can be seen, also, with unstable lesions representing ischemia (i.e., Wellens syndrome).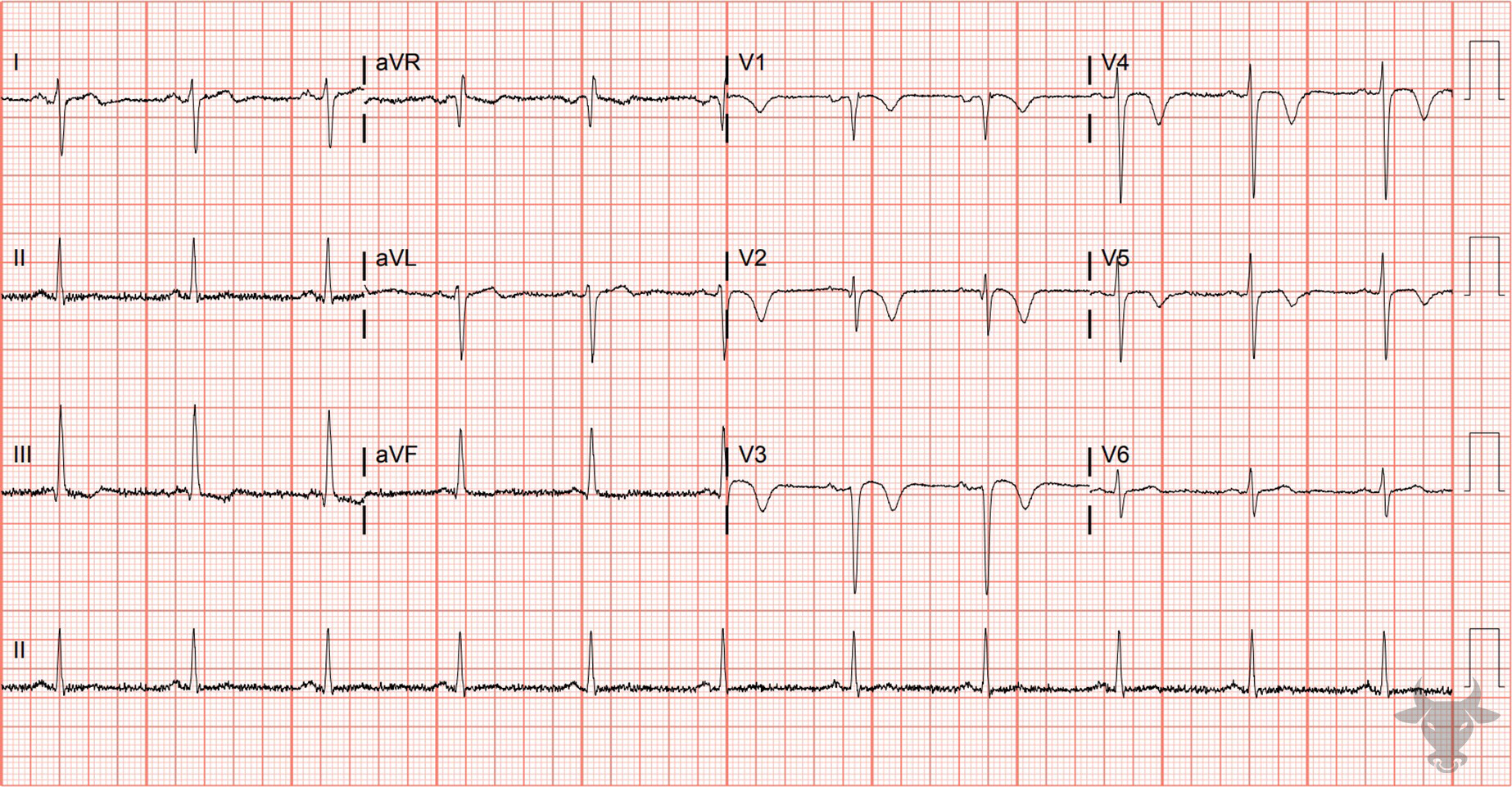
Wellens Syndrome
This is type B Wellens pattern with deeply inverted precordial T waves. This patient had a 90% proximal left anterior descending stenosis.References
- Zwaan D, Biir FWHM, Wellens HJJ. Characteristic electrocardiogric pattern indicating a critical stenosis high in left anteior descending coronary artery in patients admitted because of impending myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1982;103(4):730-736.
