Third degree, or complete, heart block is characterized by atrioventricular dissociation – atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles and, therefore, the atria and ventricles act independently of each other. Perfusion is maintained only by a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm from an ectopic focus. If the block is the result of a diseased atrioventricular node, a junctional focus escapes and produces a ventricular rate between 40 and 60 bpm. However, when infra-Hisian conduction disease exists (i.e. below the bundle of His), the escape focus is ventricular in origin, slower and less reliable. Complete heart block is life-threatening and it is typical for patients with this condition to experience severe bradycardia and hypotension. If no escape rhythm is present the patient will arrest due to cardiac standstill. An external pacemaker is the necessary treatment for complete heart block.
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
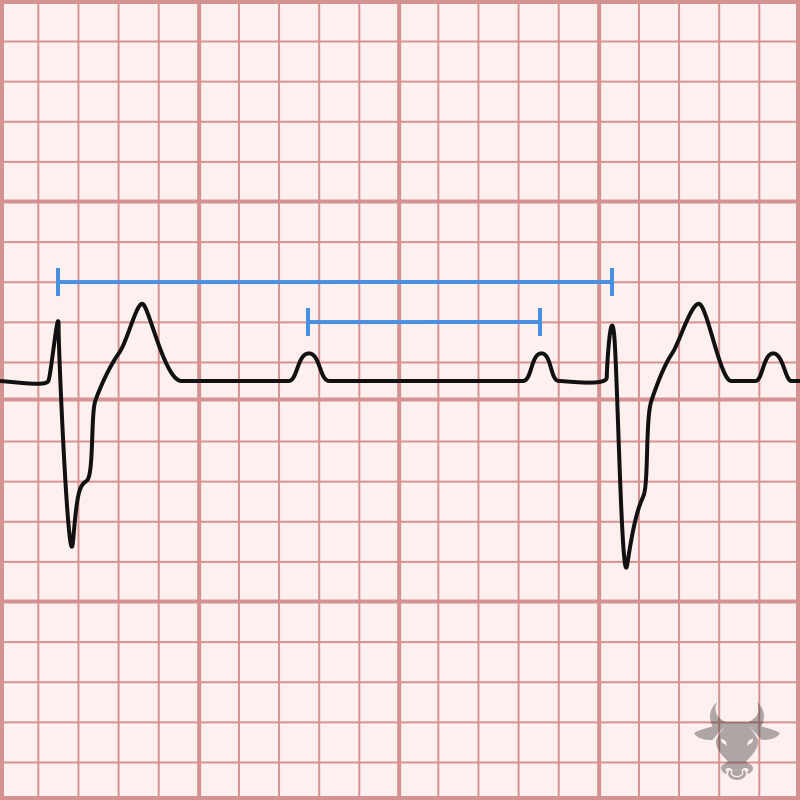
Examples
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete atrioventricular block with atrioventricular dissociation.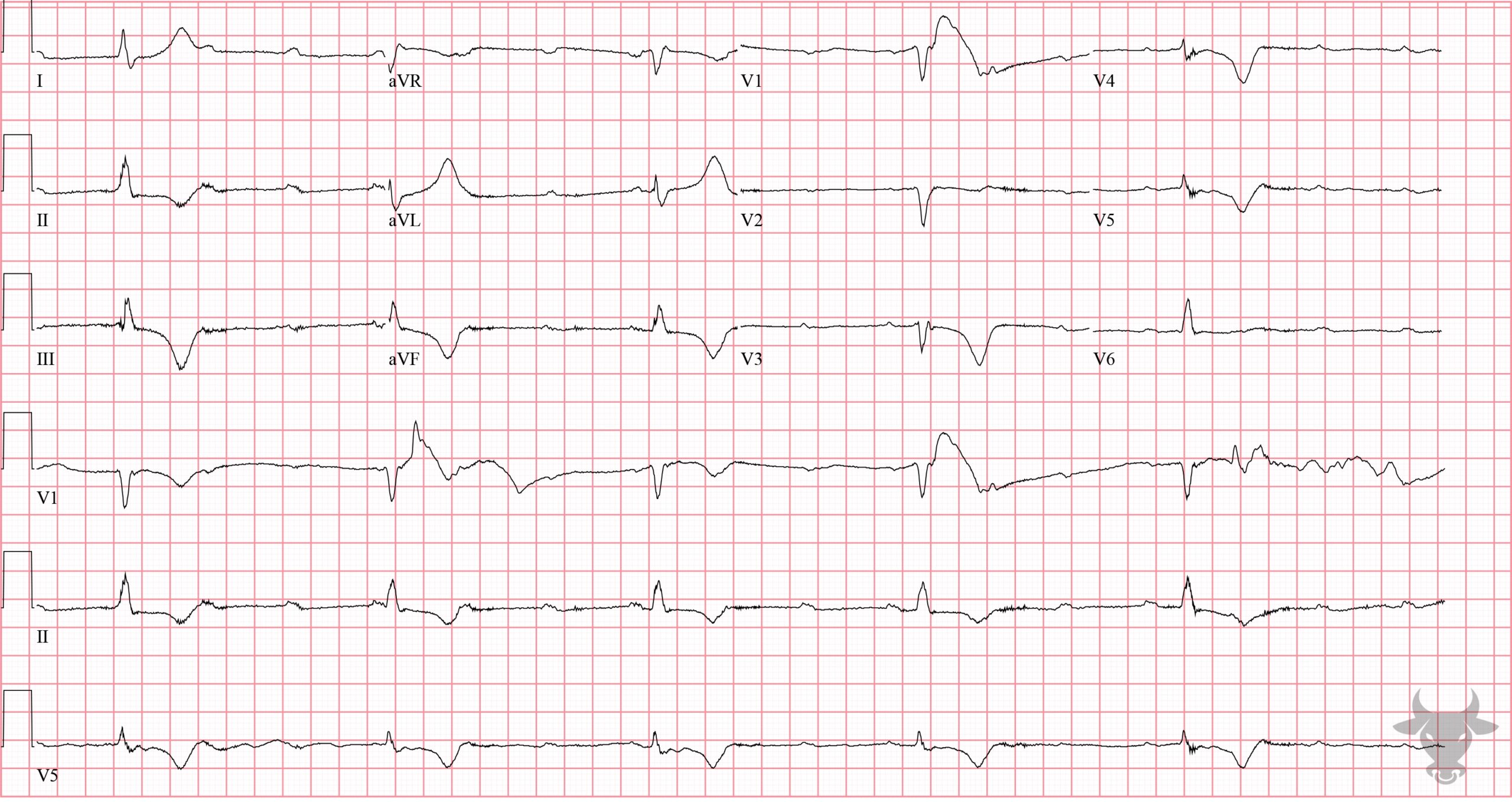
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete atrioventricular block with atrioventricular dissociation.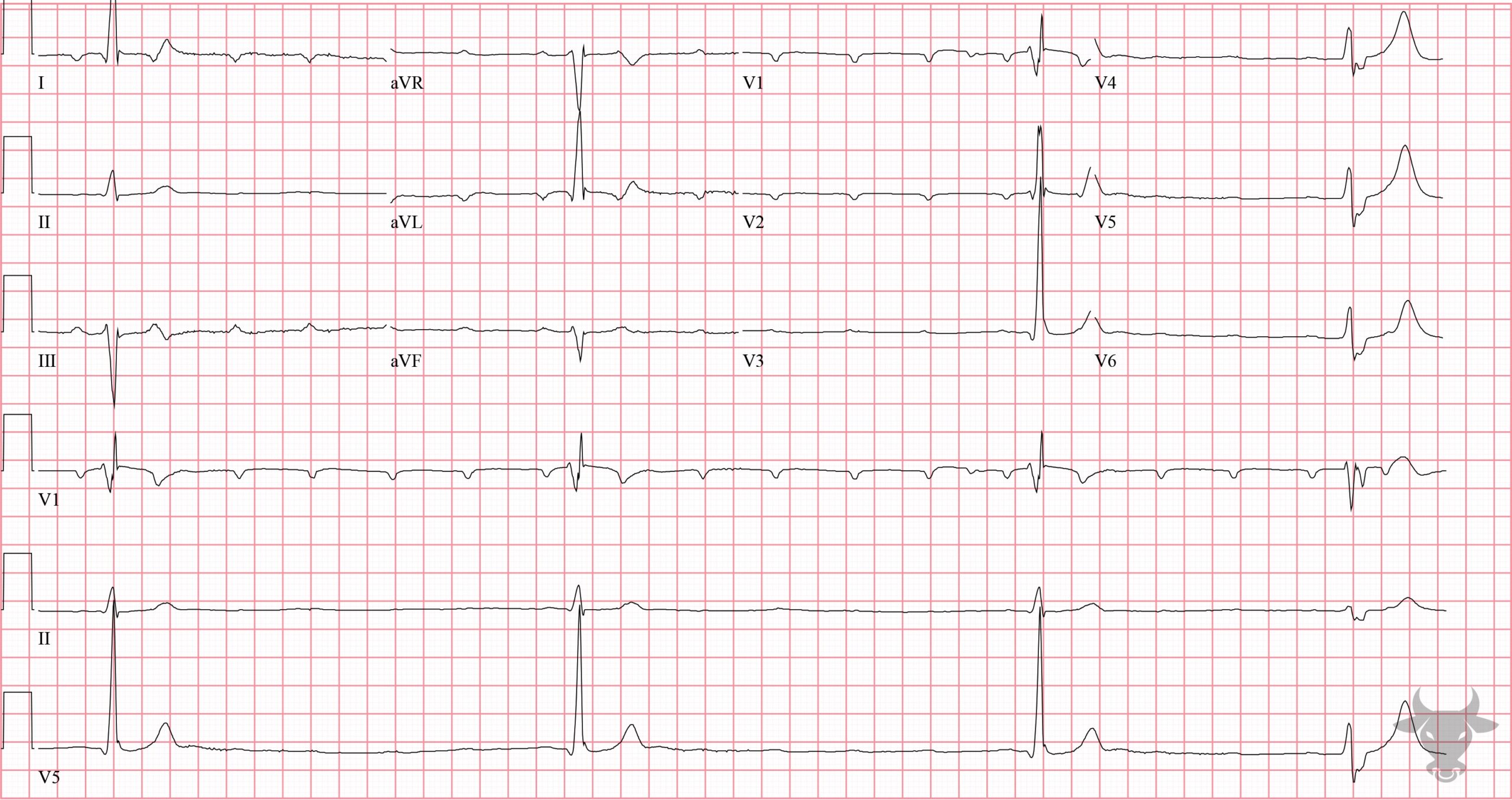
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete heart block with ventricular escape.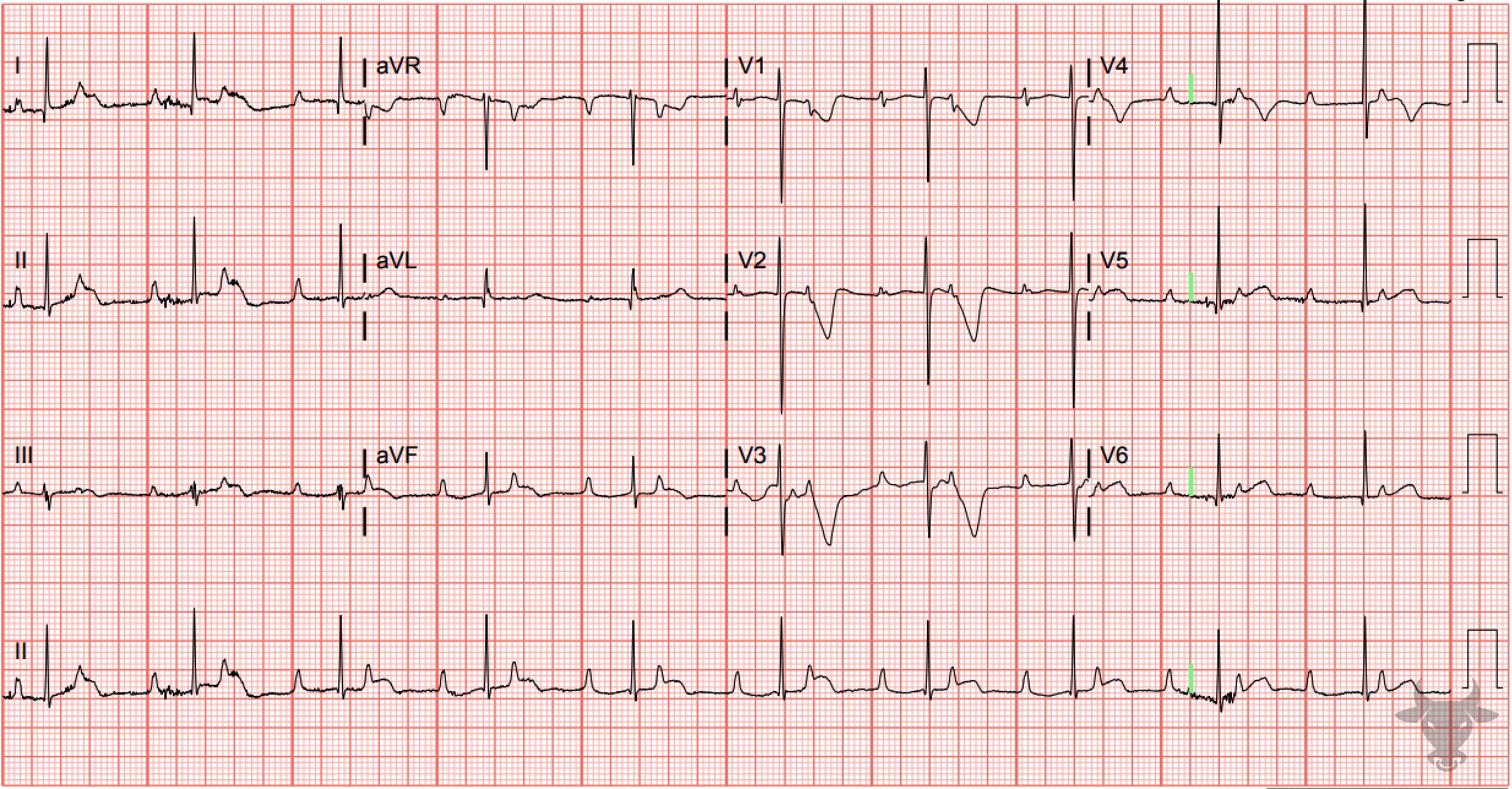
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete heart block with junctional escape in an infant. Infants tend to tolerate junctional escape rhythms quite well.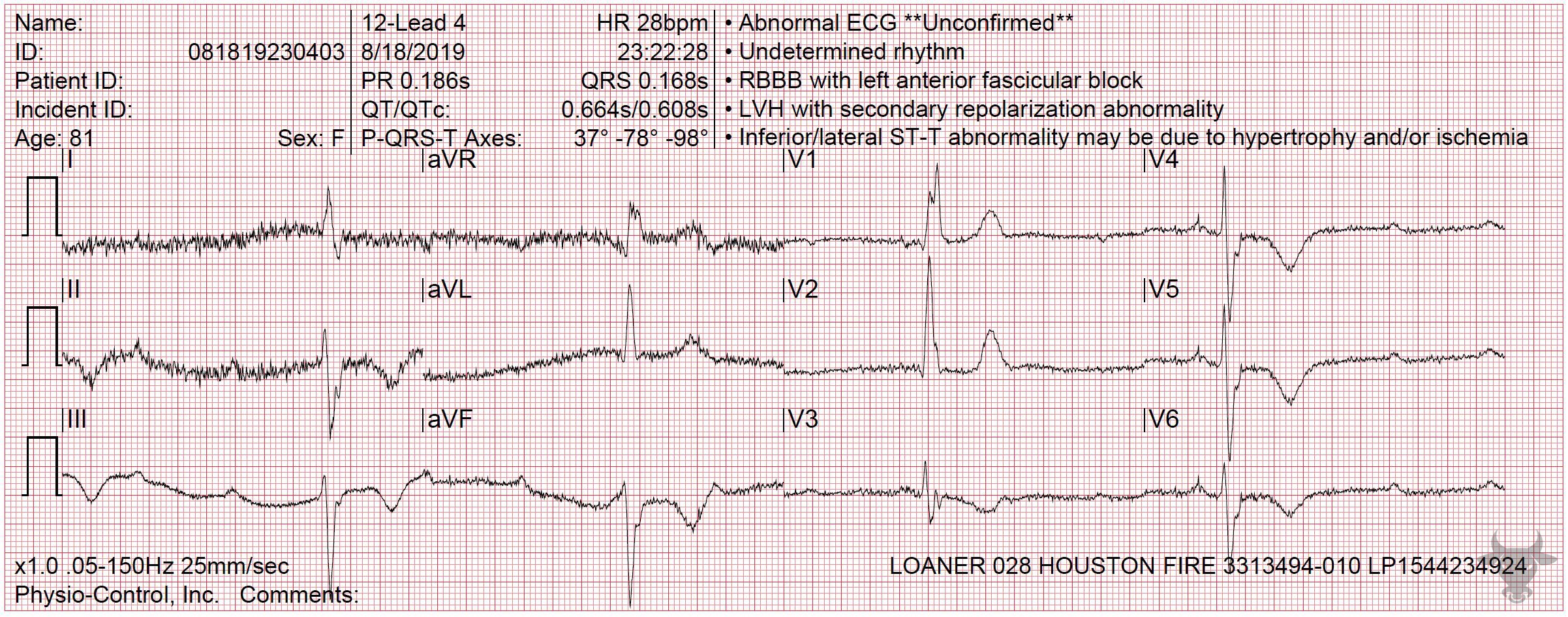
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete heart block with ventricular escape.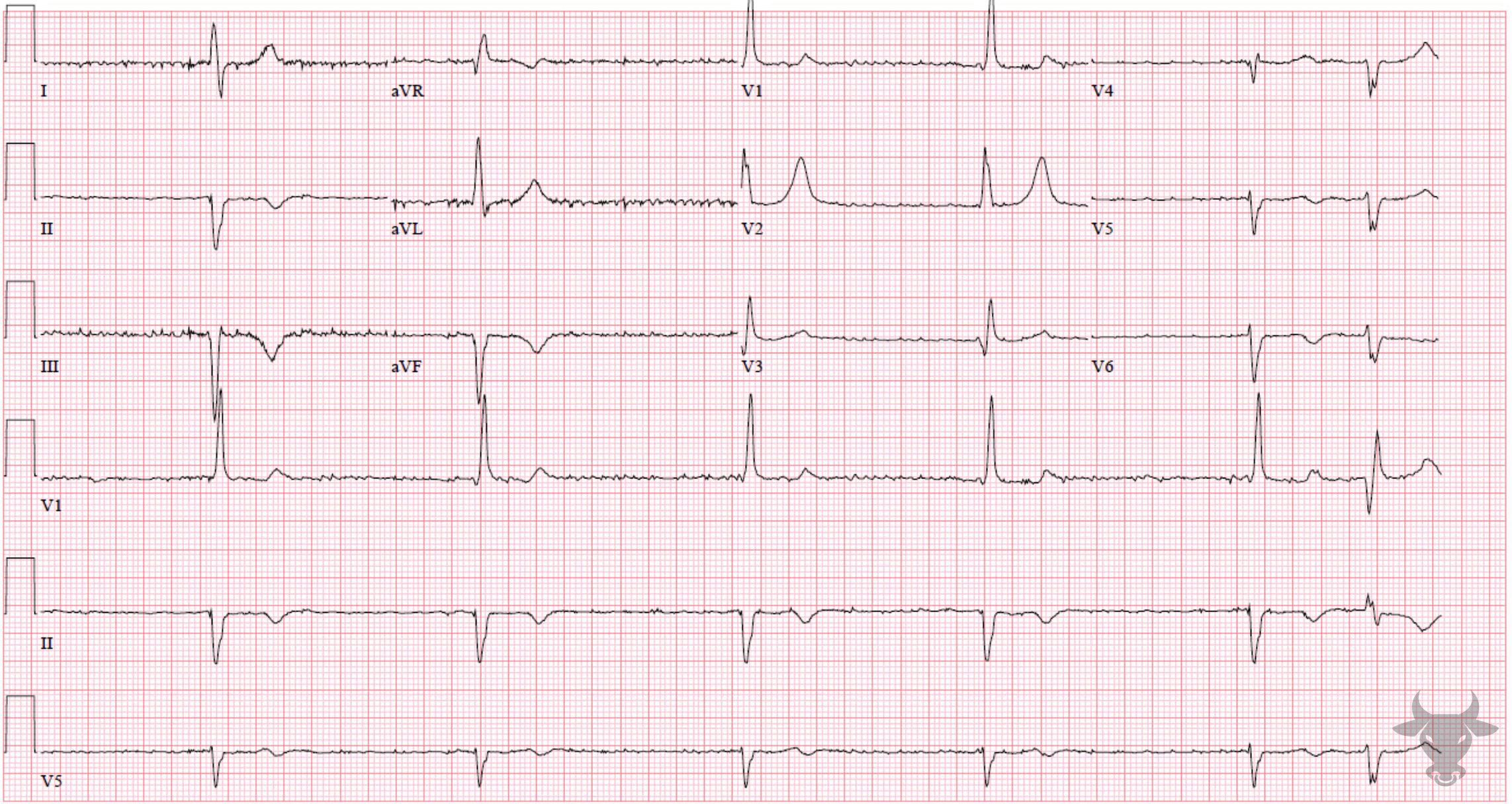
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
This patient had known atrial fibrillation yet has a regular rhythm (aside from the final premature complex). Atrial fibrillation with complete heart block will characteristically have a fibrillatory baseline but with a regular escape rhythm.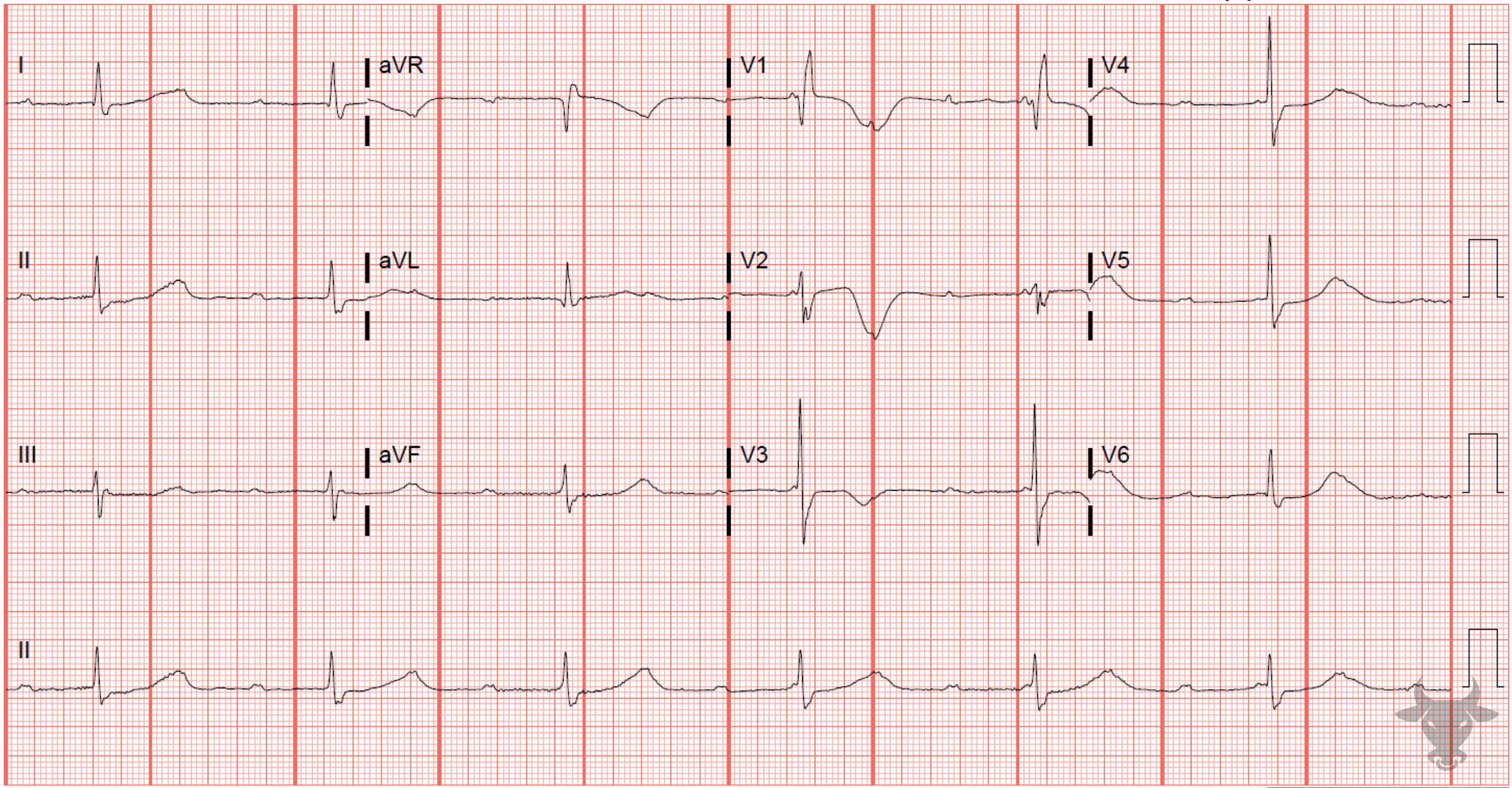
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete heart block with junctional escape.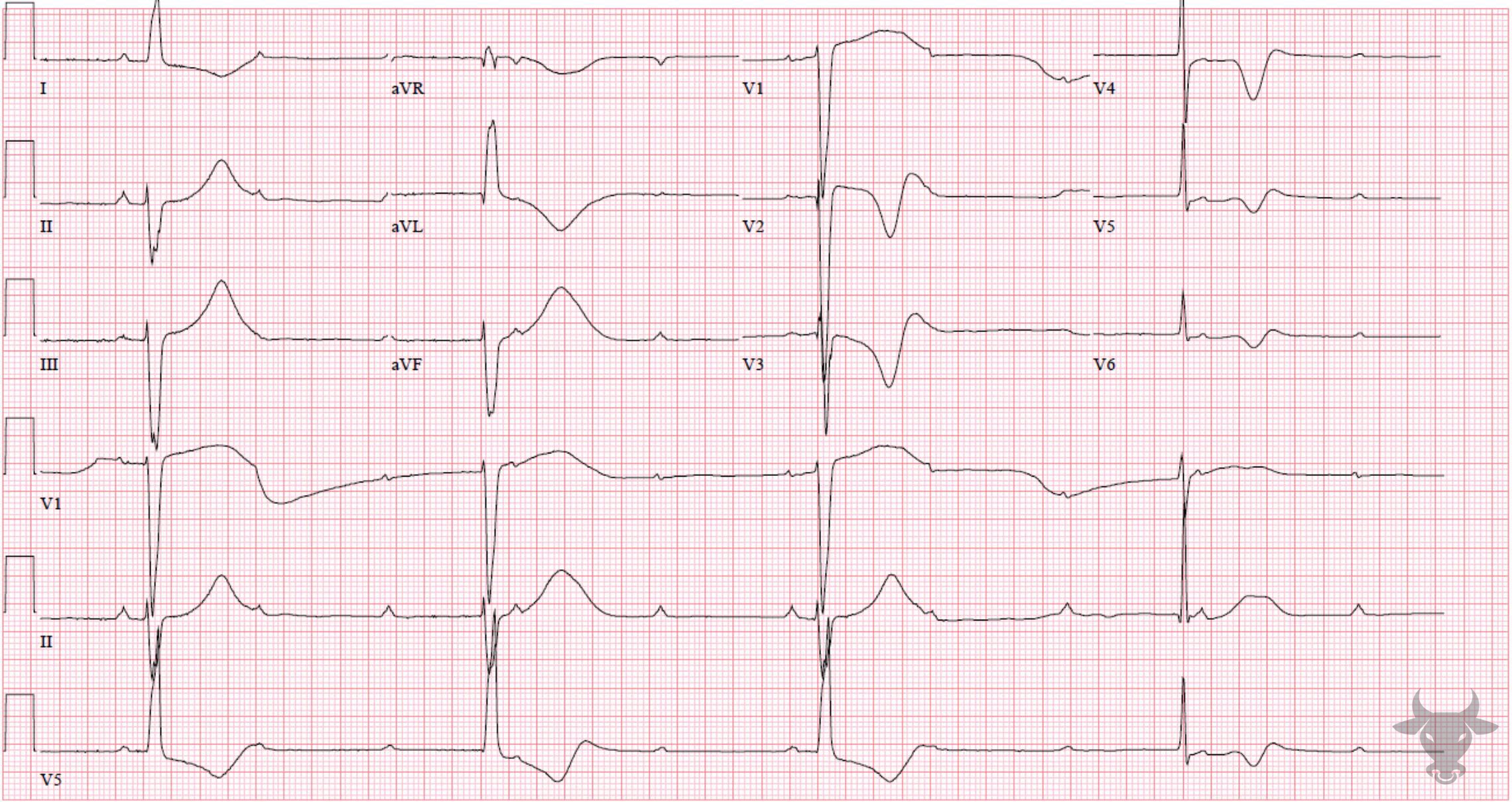
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete heart block with ventricular escape.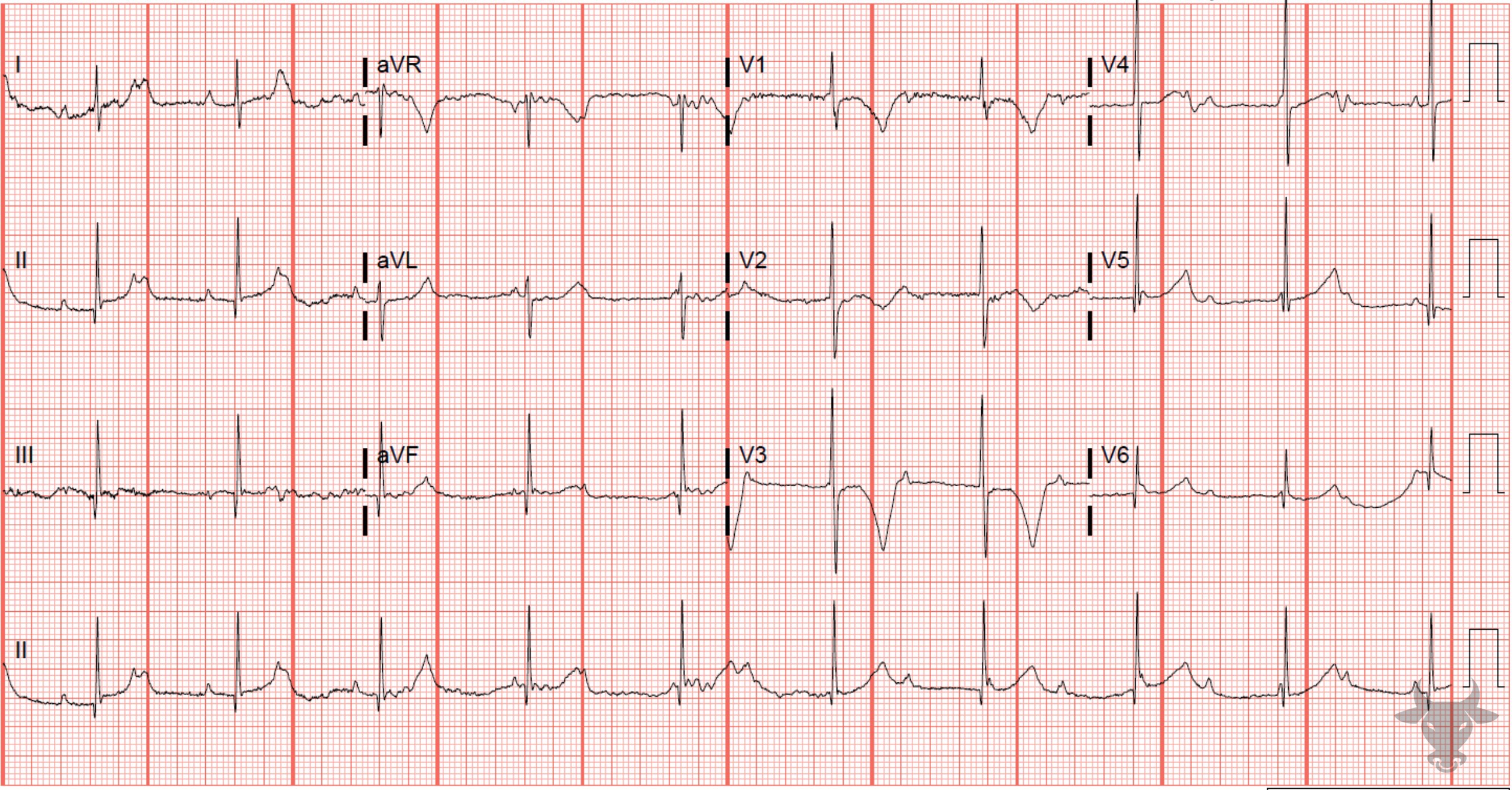
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Complete heart block with junctional escape in an infant. Infants with junctional escape tend to tolerate heart block well.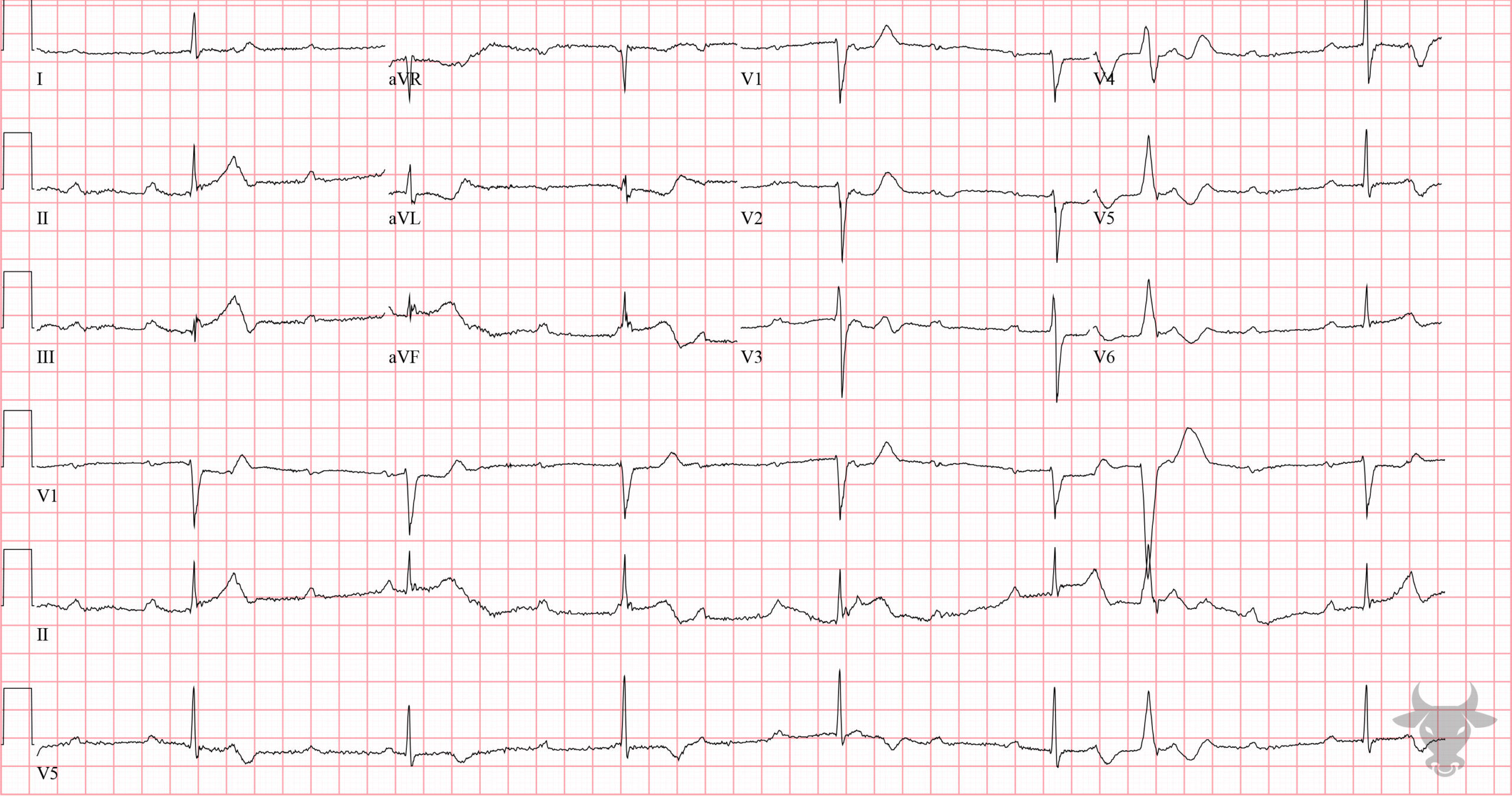
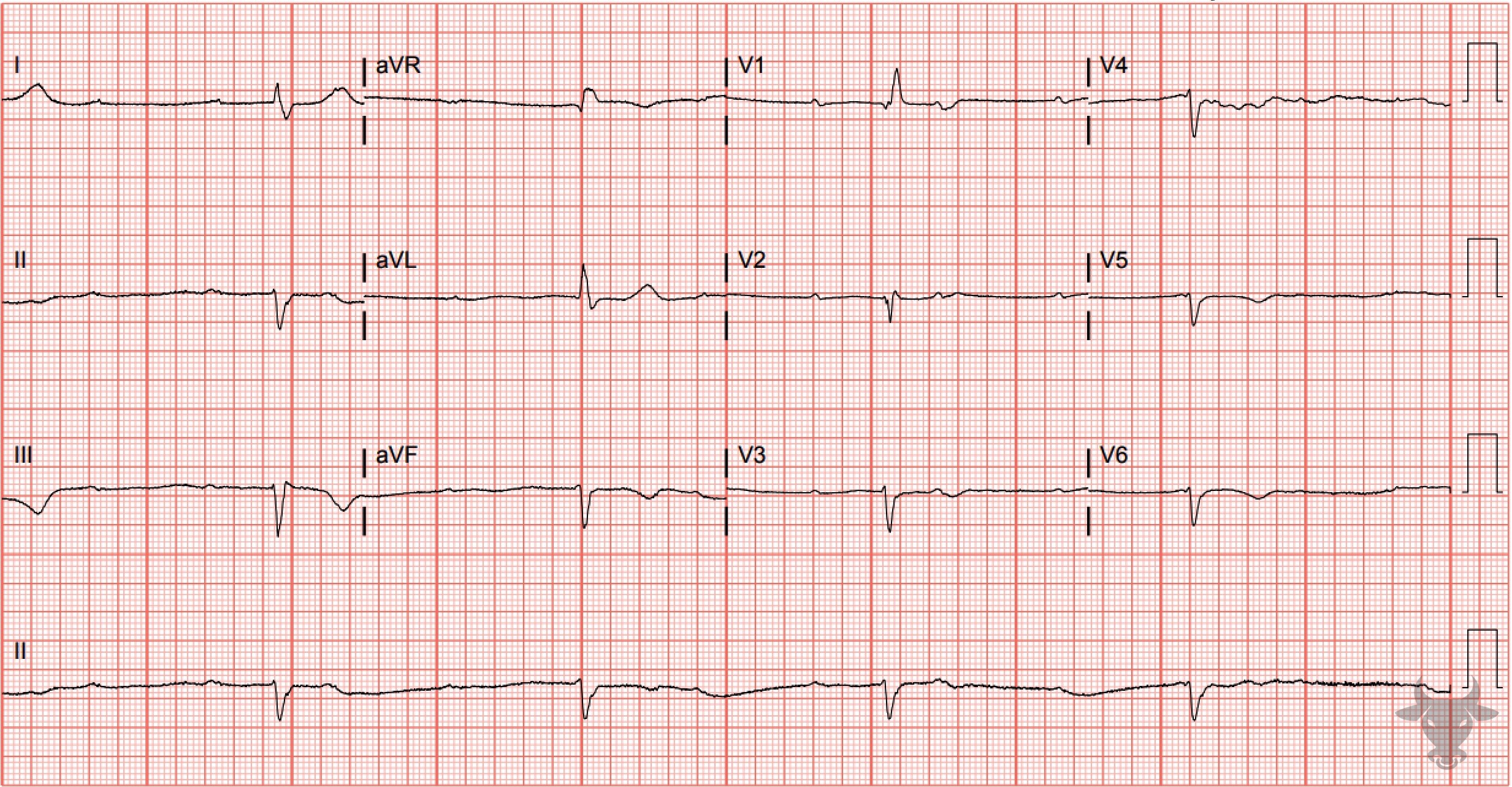
Inferior ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction, Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
Inferior STEMI with associated complete heart block. The inferior ST segments are “straightened,” and take-off directly from the R wave - an early finding of evolving ST-segment elevation. There are reciprocal ST-segment depressions in aVL and V2. In the setting of inferior STEMI, heart block is usually transient and due to either ischemia or edema of the atrioventricular node, resulting in a junctional escape rhythm. This patient received percutaneous coronary intervention to the right coronary artery after an occlusion was discovered on catheterization.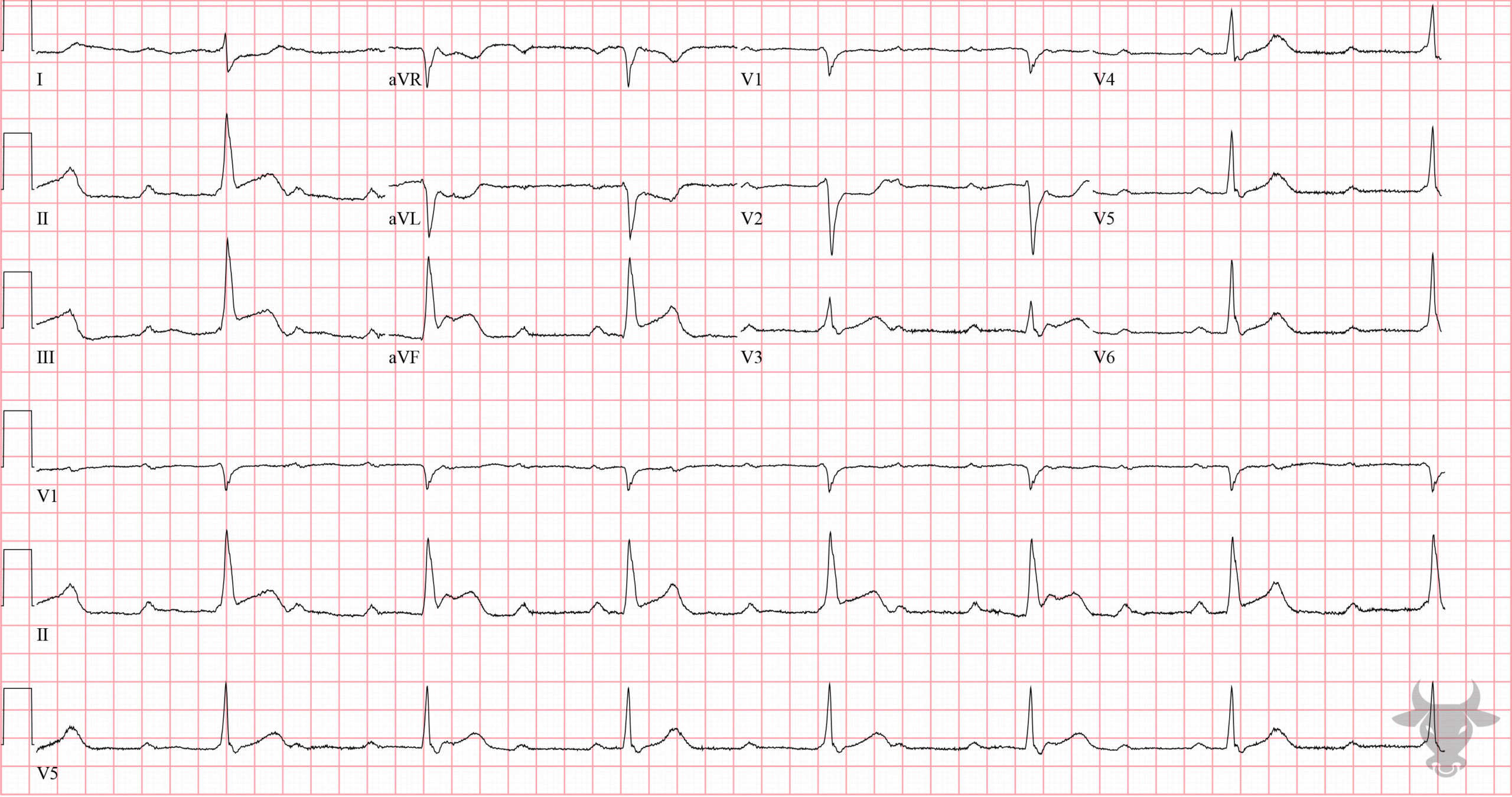
Inferior ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction, Third Degree Atrioventricular Block
There are inferior ST-segment elevations with reciprocal changes in I, aVL, and V2. Additionally, there is atrioventricular dissociation with consistent P-P intervals and R-R intervals, but the atria and ventricles are acting independently. The narrow QRS (<120 msec) indicates the escape rhythm is junctional. Left heart catheterization revealed an occluded right coronary artery.References
- Kusumoto FM, Schoenfeld MH, Barrett C, et al. 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhyth. Circulation. 2019;140(8):e382-e482.
