Tachycardia, S1Q3T3, tall P wave in II, ST elevation in right-sided leads (aVR, V1, III), right axis deviation, new right bundle branch block, new incomplete right bundle branch block, and T wave inversions especially in the inferior and right-sided precordial leads (II, III, aVF, V1, V2, and V3) have all been suggested as right heart strain patterns.
Pulmonary Embolism
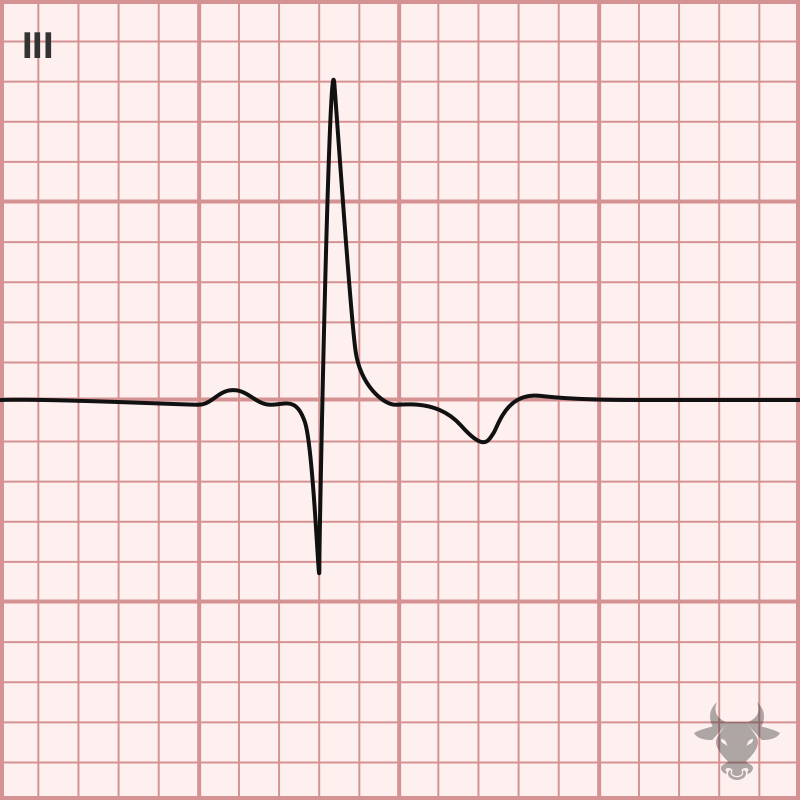
Examples
Pulmonary Embolism
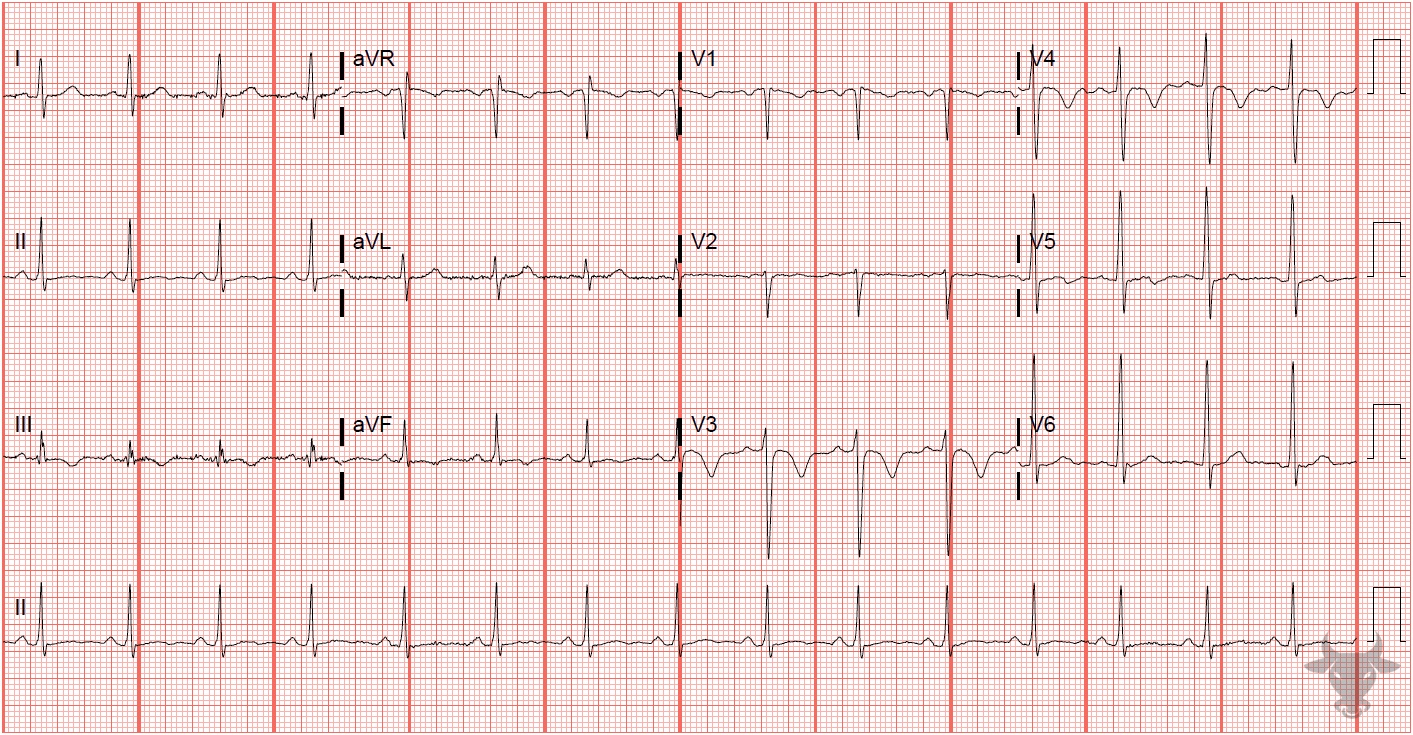
Anterior precordial and inferior T-wave inversions are common findings of acute right heart strain. This patient had a submassive pulmonary embolism.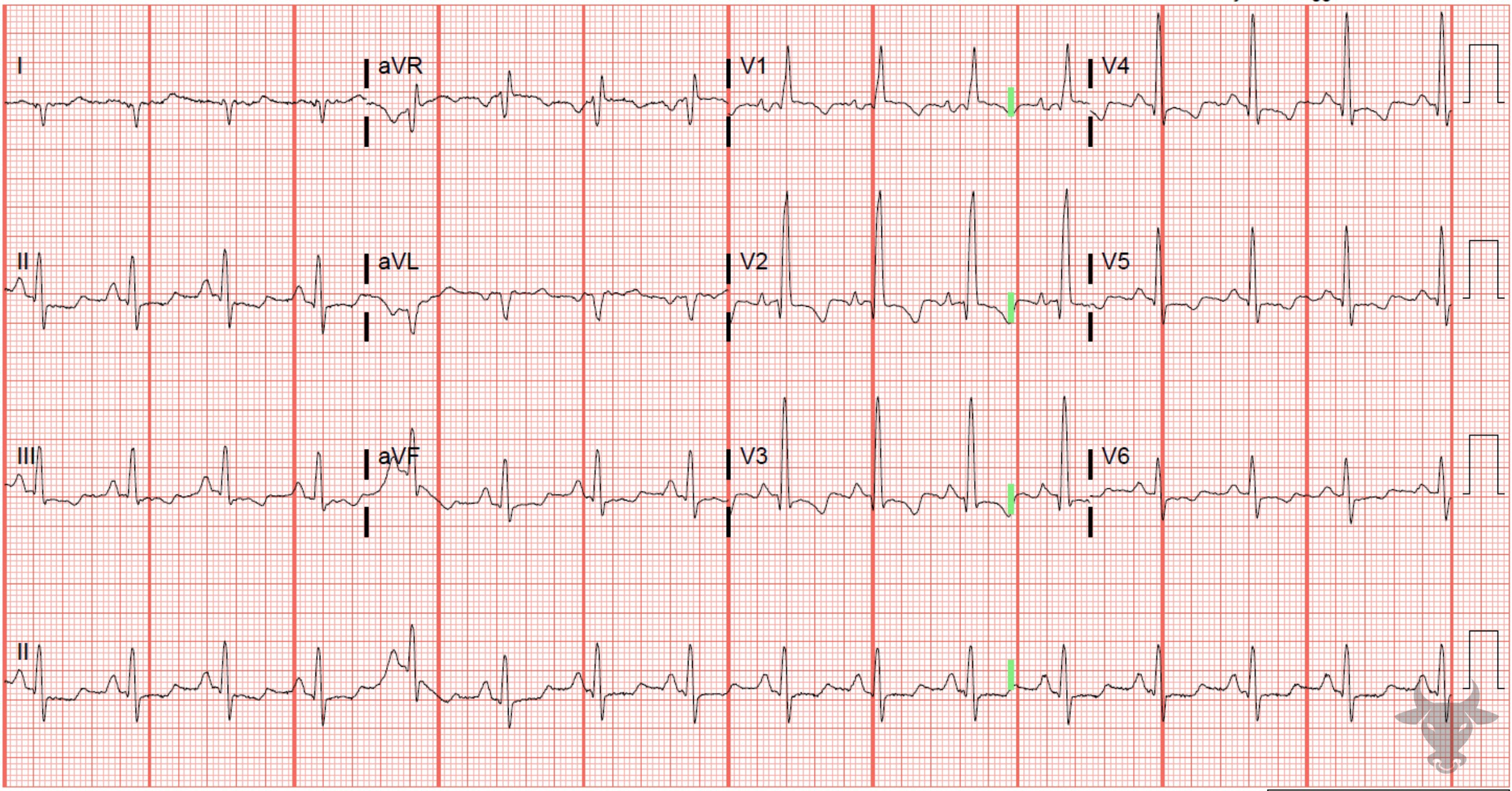
Pulmonary Embolism
This patient was discovered to have a pulmonary embolism with right heart strain. The ECG demonstrates early R wave progression, right axis deviation, right atrial enlargement, ST-segment depressions and T-wave inversions in inferolateral leads – all consistent with right heart strain.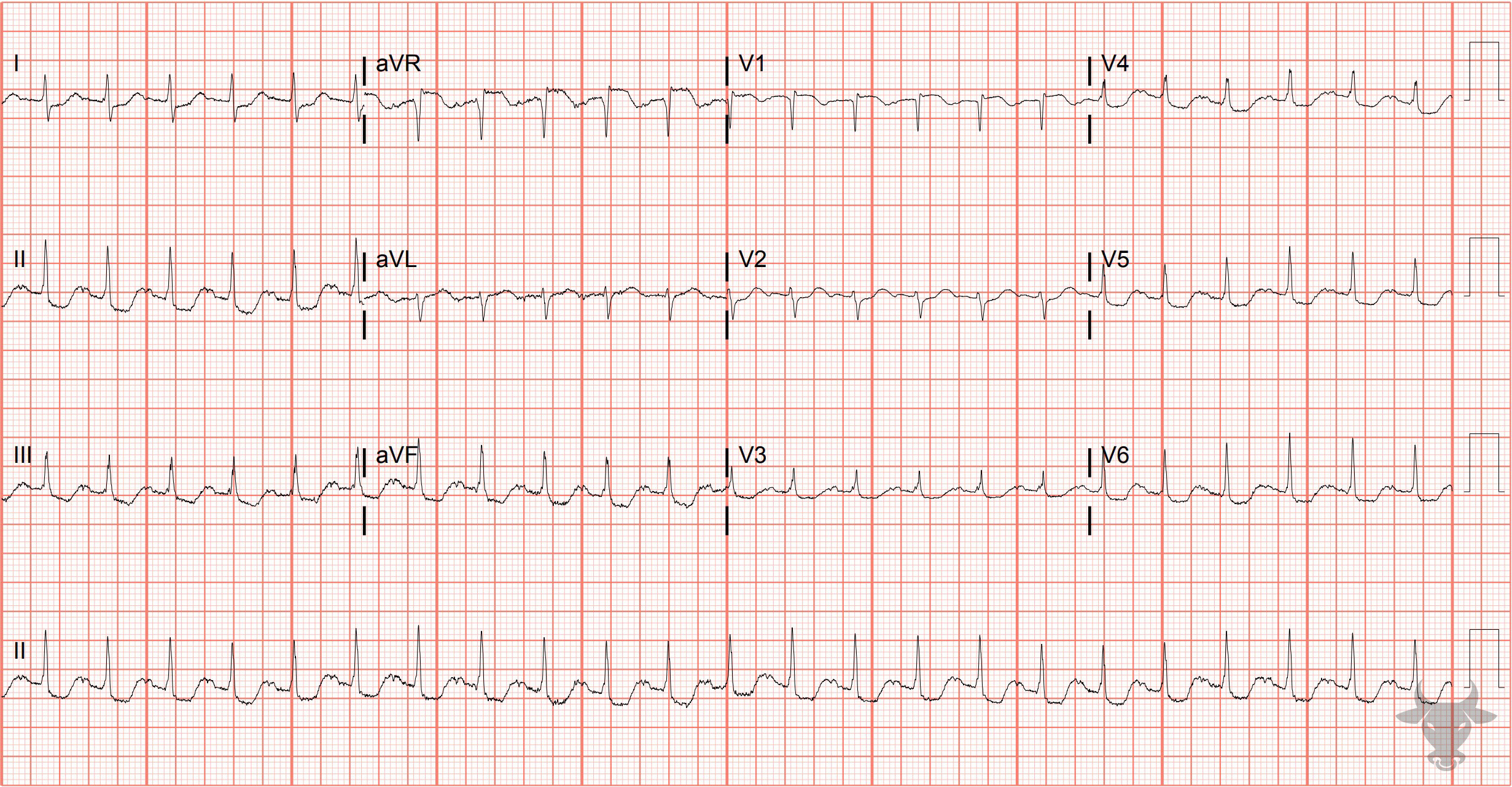
Global Subendocardial Ischemia Due to Pulmonary Embolism
There are diffuse ST-segment depressions along with ST-segment elevation in aVR. This patient was discovered to have a saddle pulmonary embolism for which thrombectomy was performed. The ST changes and tachycardia resolved after mechanical retrieval of the embolus.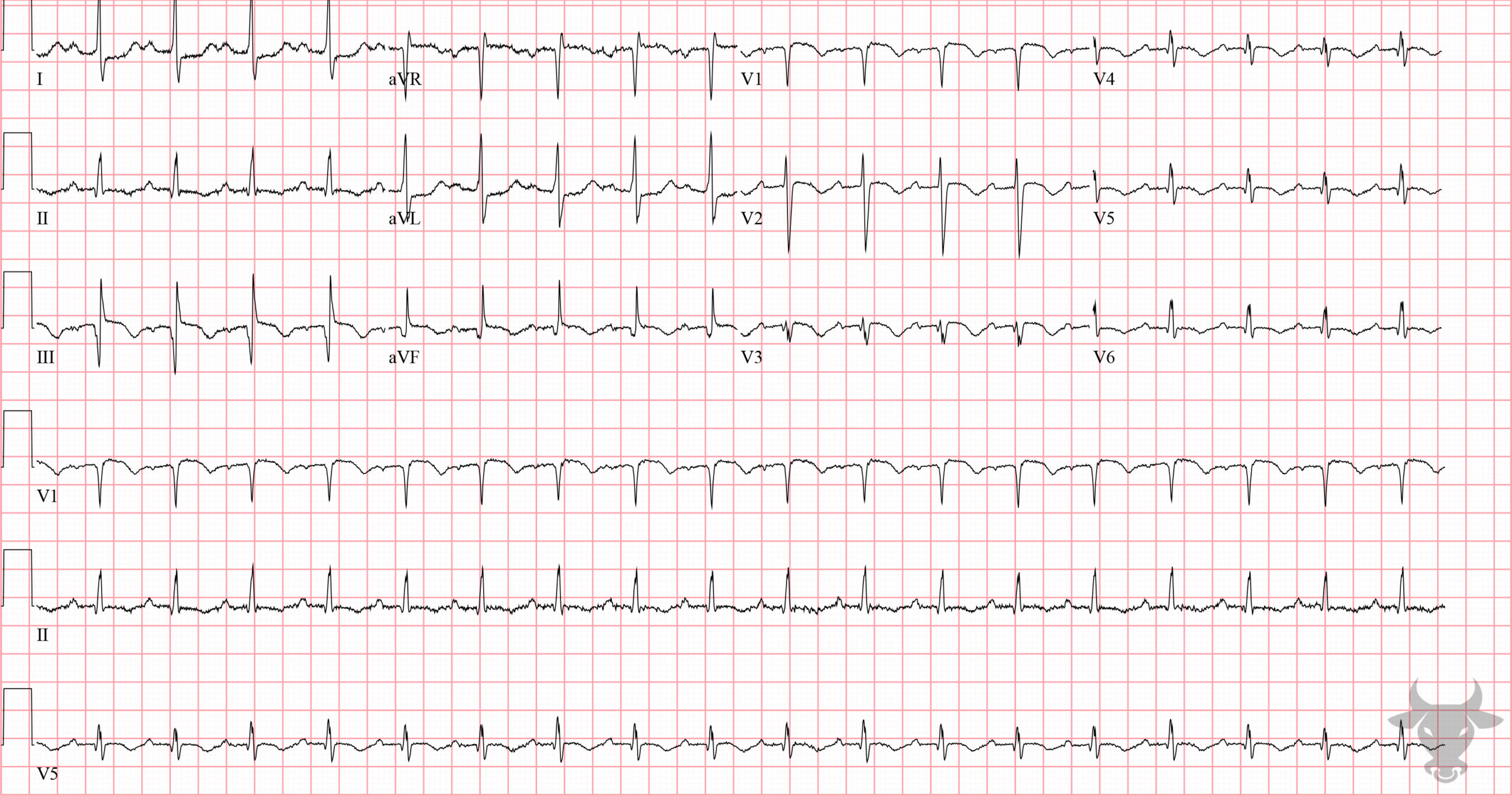
Pulmonary Embolism Masquerading as Inferior Myocardial Infarction
Massive pulmonary embolism can masquerade as right ventricular infarct, as with this case. There is subtle inferior ST-segment elevation with reciprocal ST-segment depression in I and aVL, S1Q3T3, and T-wave inversions across the precordium. Saddle and lobar pulmonary emboli were diagnosed on CT angiography.References
- Kukla P, Macintyre W, Fijorek K. Electrocardiographic abnonmralities in patients with acute pulmonary emoblism complicated by cardiogenic shock. American Journal of Emergency Medicine2. 2014;32:507-510.
- Surawicz B, Knilans TK. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice. 6th ed. Elsevier; 2008.
