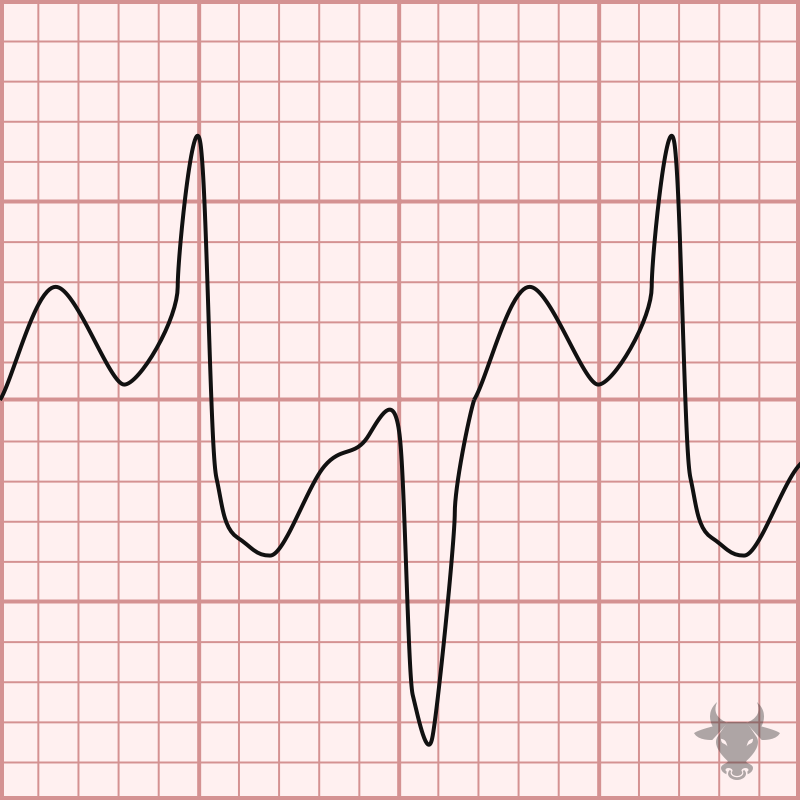
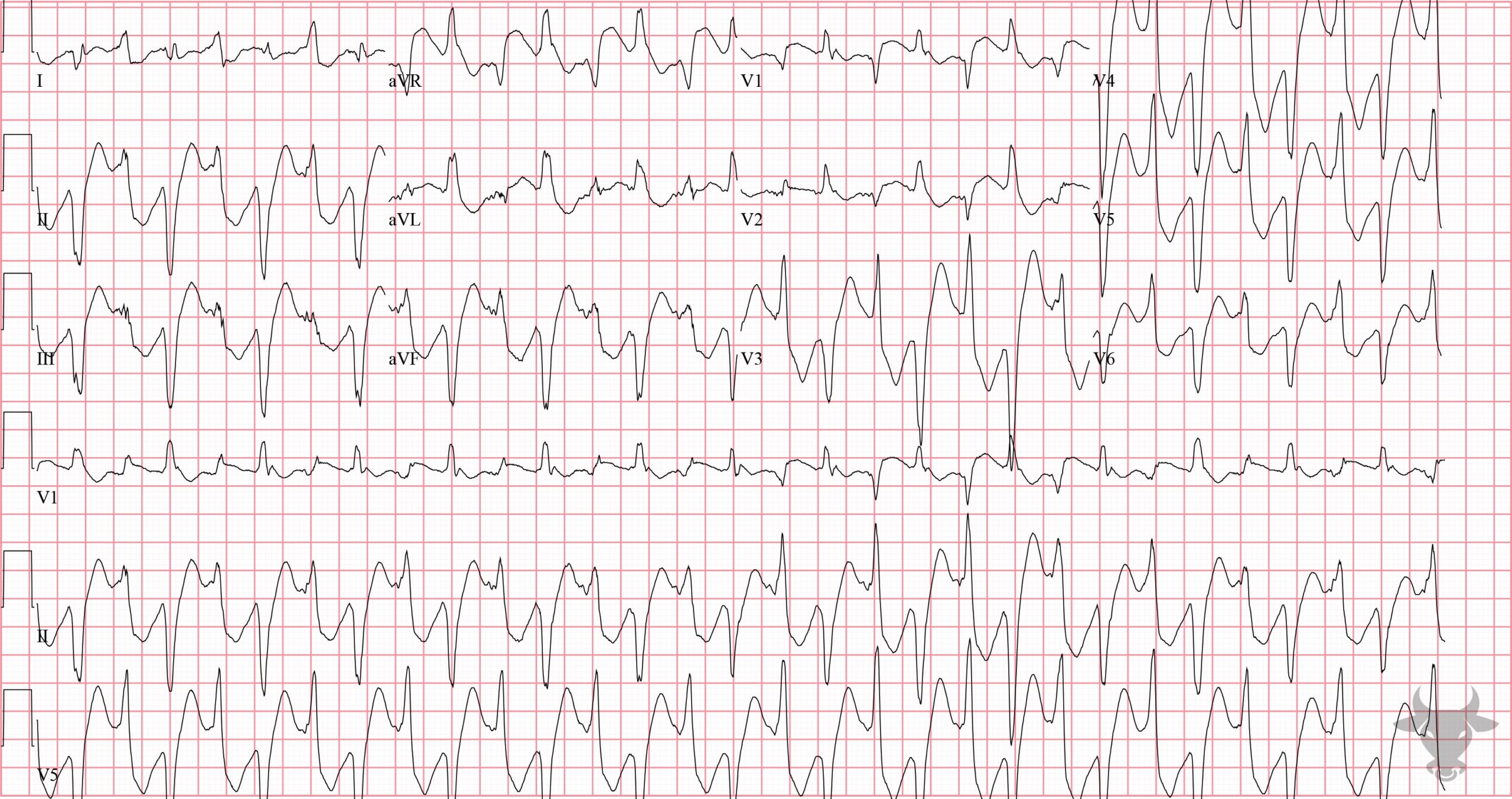
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (PVT) is a form of ventricular tachycardia in which there are multiple ventricular foci with the resultant QRS complex varying in amplitude, axis, and duration. The most common cause of PVT is myocardial ischaemia/infarction. Torsades de pointes (TdP) is a specific form of PVT occurring in the context of QT prolongation — it has a characteristic morphology in which the QRS complexes “twist” around the isoelectric line.

Torsades de Pointes.