Cerebral T waves are large T wave inversions and are likely the result of a sympathetic surge causing repolarization abnormalities. Cerebral T waves are rare and generally resolve over time.
Cerebral T waves
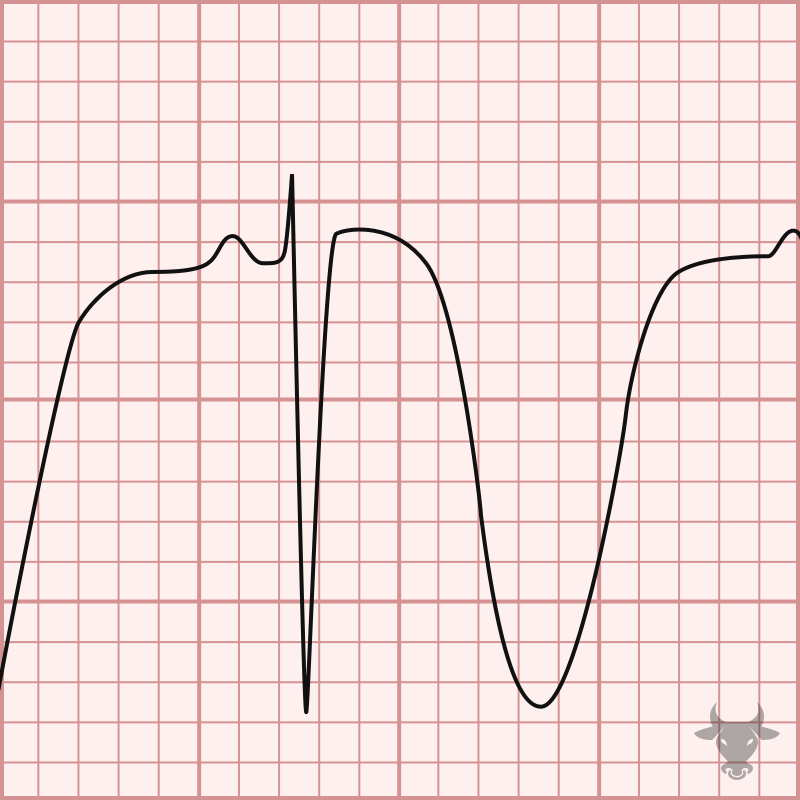
Examples
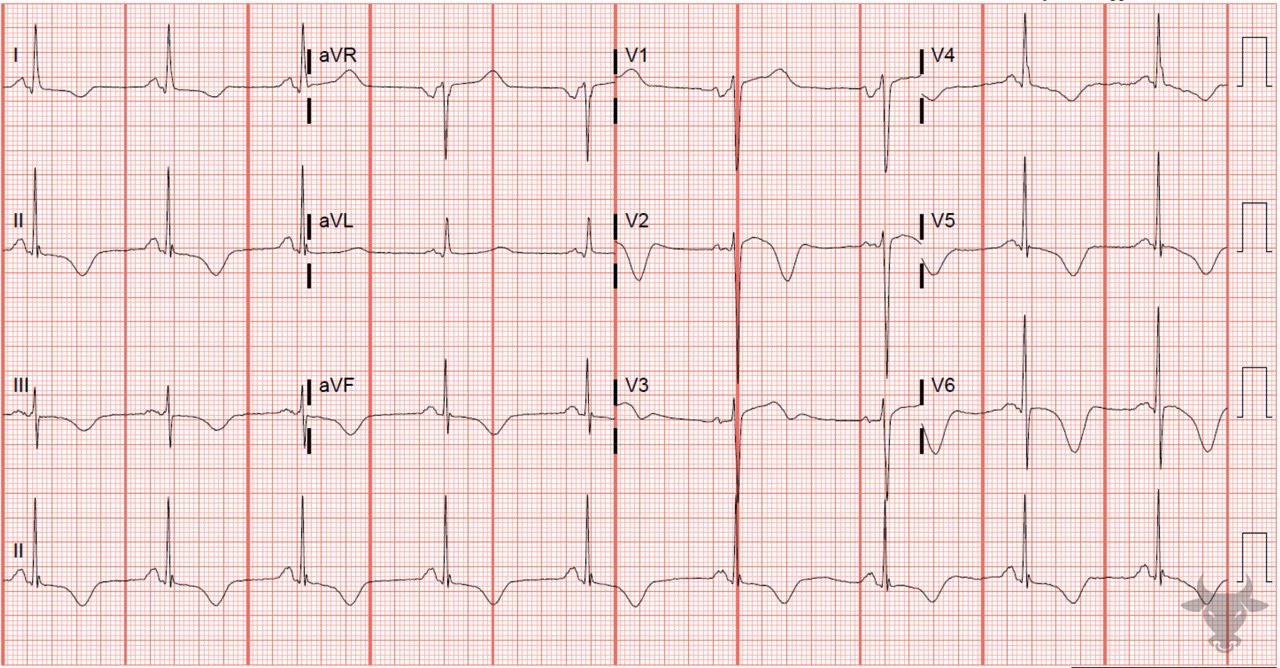
Cerebral T waves
The diffuse "roller coaster" T wave inversions and prolonged QT inteveral were due to a pontine hemorrhage.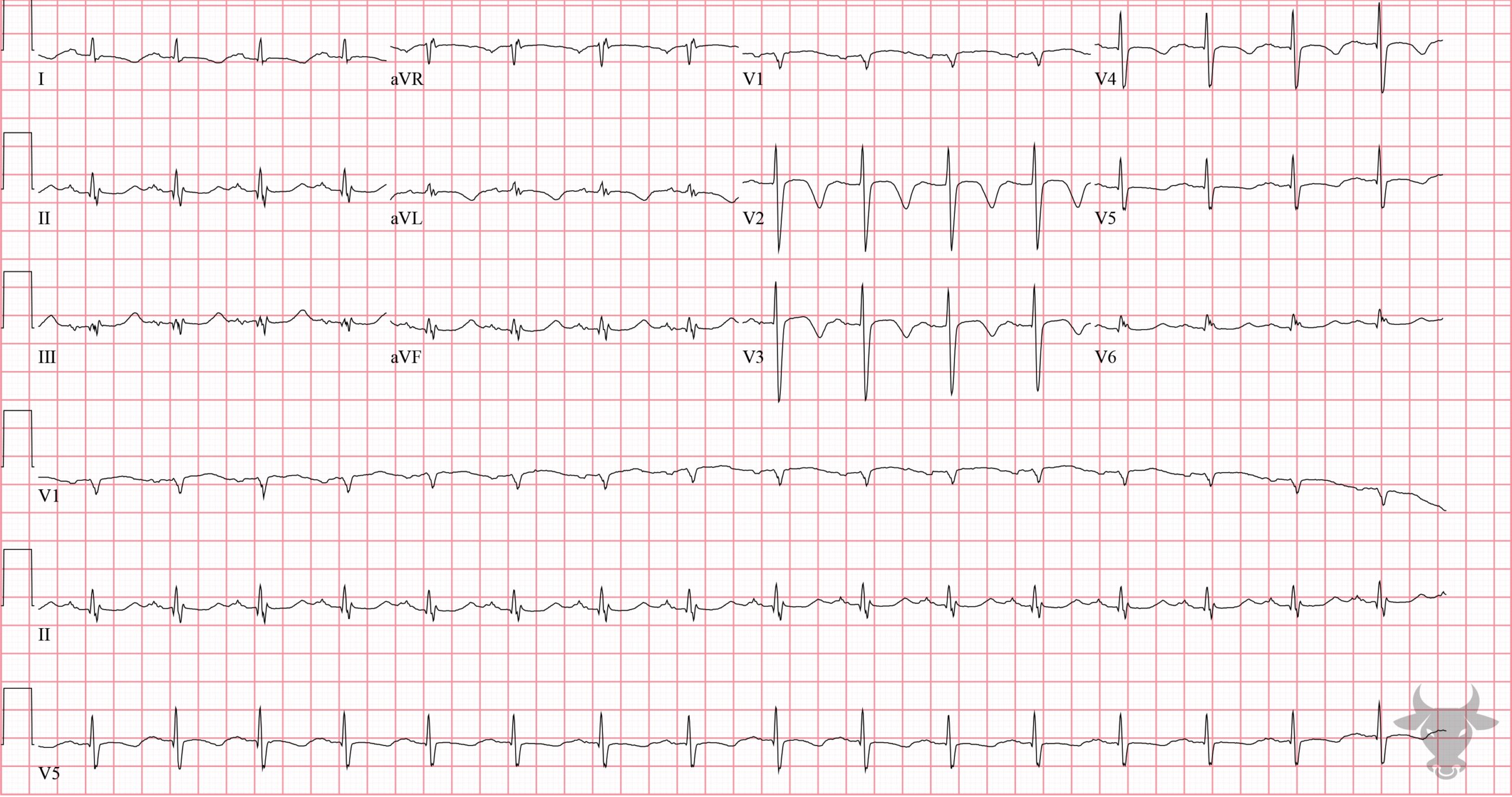
Cerebral T waves
The anterior precordial T wave inversions were due to a devastating subarachnoid hemorrhage.References
- Burch GE, Meyes R, Abildskov JA. A new electrocardiographic pattern observed in cerebrovascular accidents. Circulation. 1954;9(5):719-723.
- Stone J, Mor-Avi V, Ardelt A, Lang RM. Frequency of Inverted Electrocardiographic T Waves (Cerebral T Waves) in Patients With Acute Strokes and Their Relation to Left Ventricular Wall Motion Abnormalities. American Journal of Cardiology. 2018;121(1):120-124.
