Atrial tachycardia, or focal atrial tachycardia, is result of a micro-reentrant circuit or an automatic focus. The atrial rate is greater than 100 bpm and less that 250 bpm. Atrial tachycardia can be differentiated from atrial flutter by the rate (flutter waves are usually greater than 250 bpm) and the presence of an isoelectric baseline. The P wave axis and morphology is usually abnormal.
Atrial Tachycardia
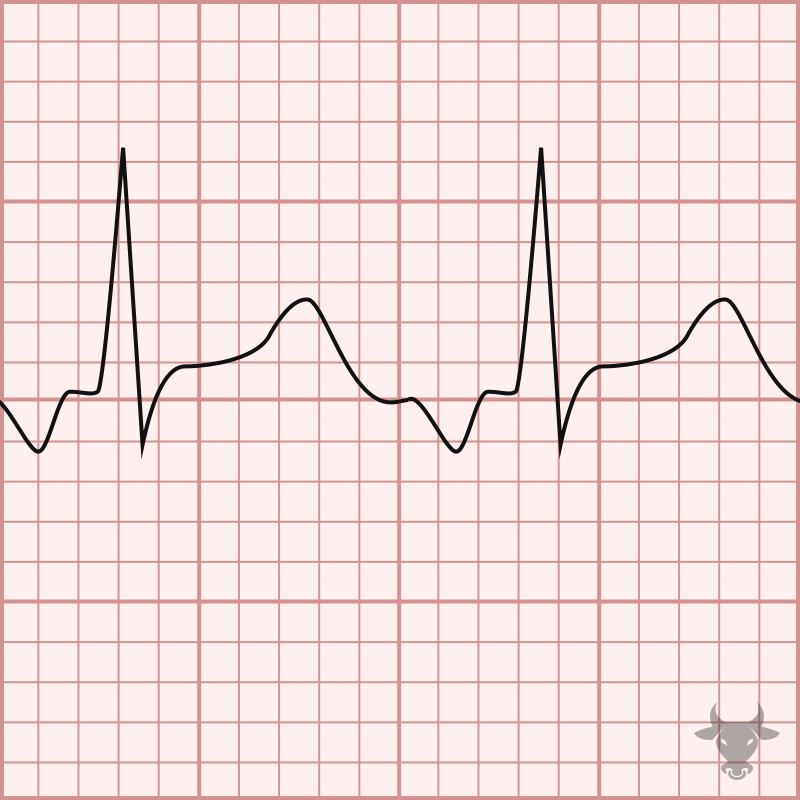
Examples
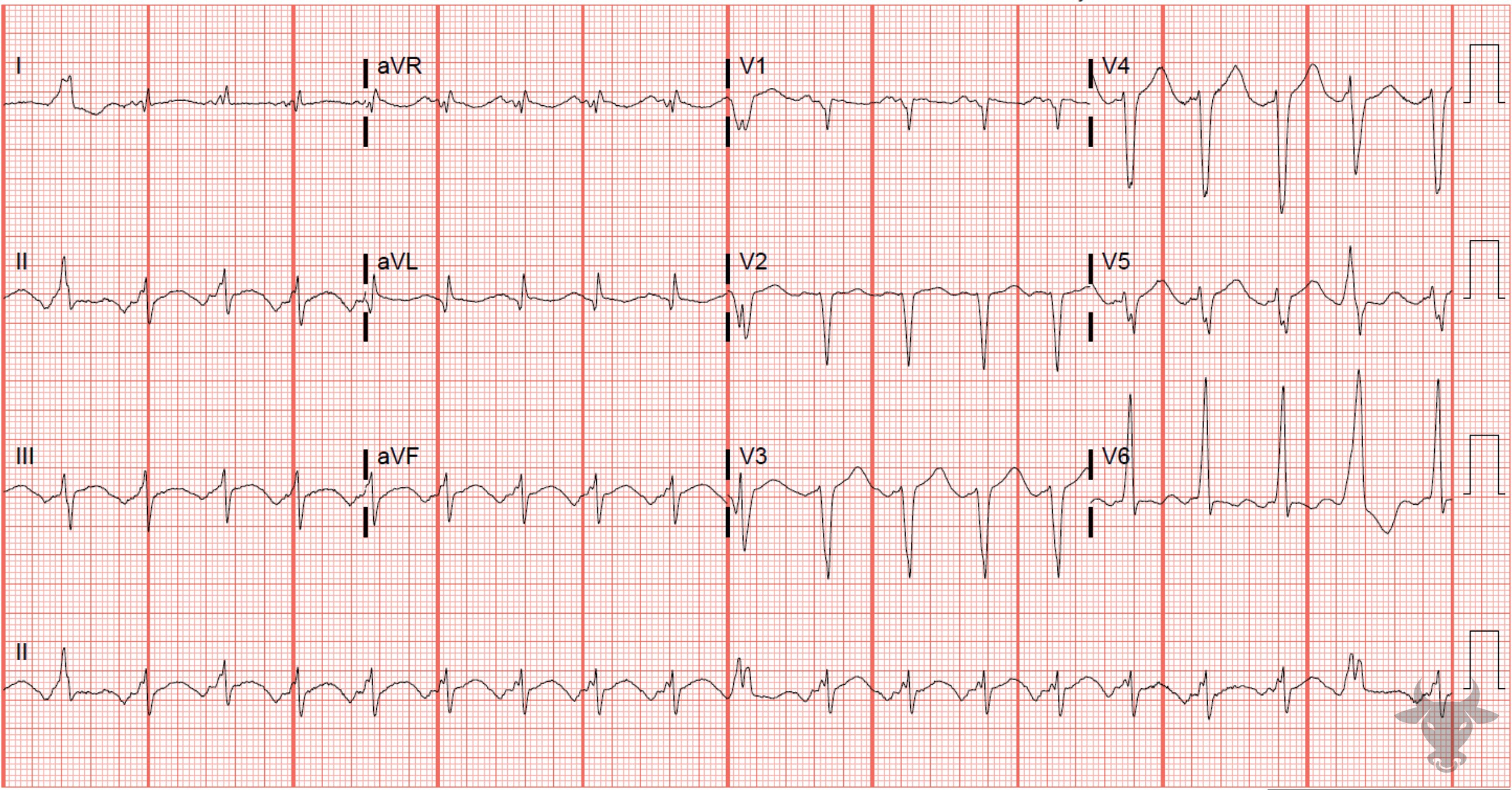
Atrial Tachycardia
The normal P wave axis is down in lead V1 and up in lead II. The abnormal P wave axis in this ECG reveals an ectopic atrial source.References
- Link MS. Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia. New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367(15):1438-1448.
