ECG Stampede:
Glossary
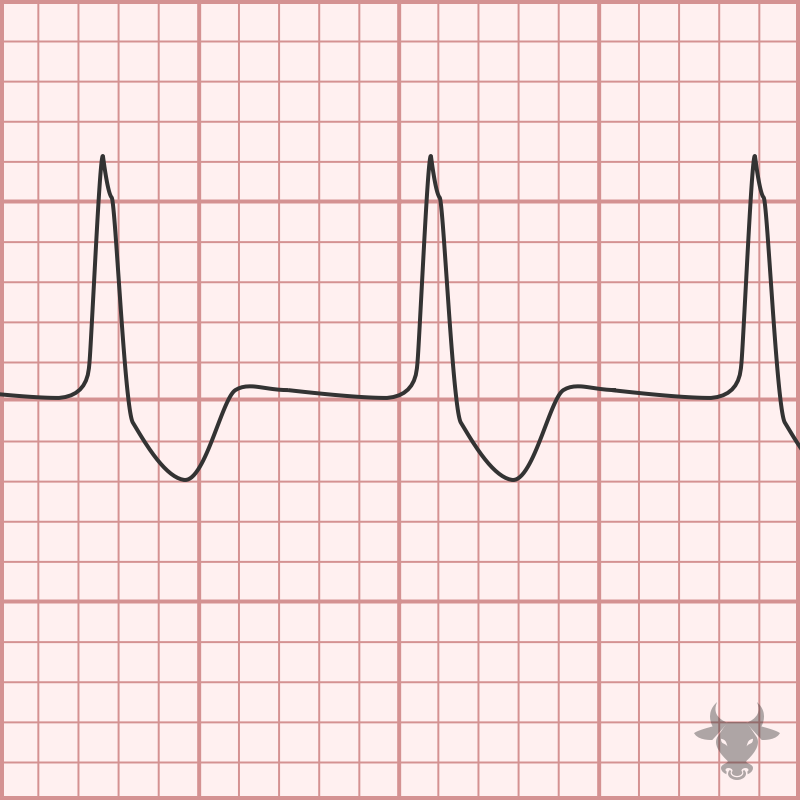
AIVR is a rhythm that occurs under conditions of enhanced automaticity. An enhanced ectopic ventricular pacemaker outpaces more superior pacemakers (e.g. sinus node) and, thus, becomes the dominant pacemaker by...
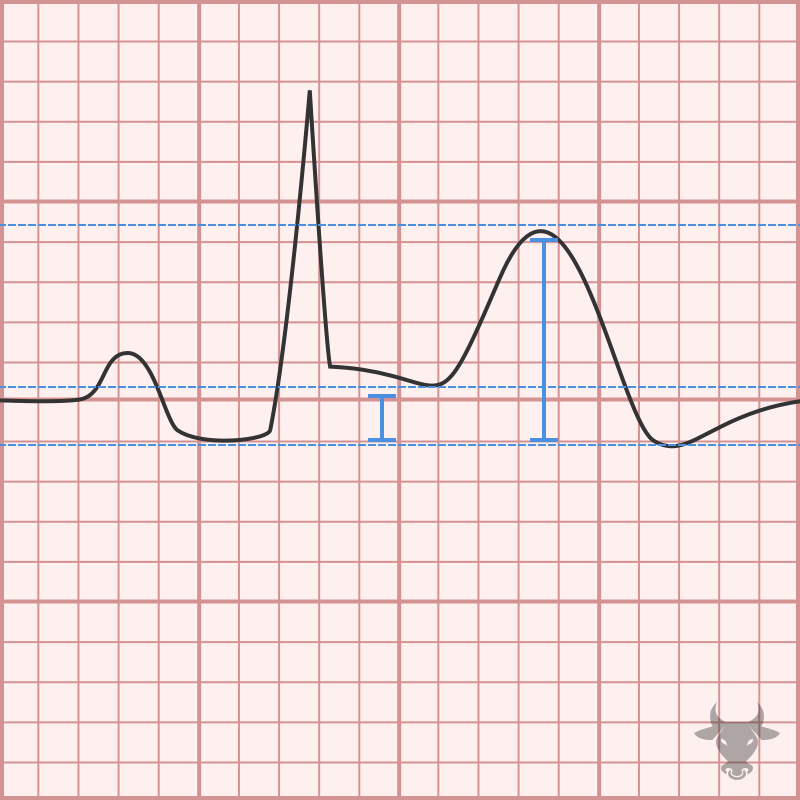
The diagnosis is made by meeting 2 of 4 criteria: Typical symptoms (pleuritic, sharp chest pain relieved when leaning forward) New pericardial effusion Presence of friction rub Typical ECG findings...
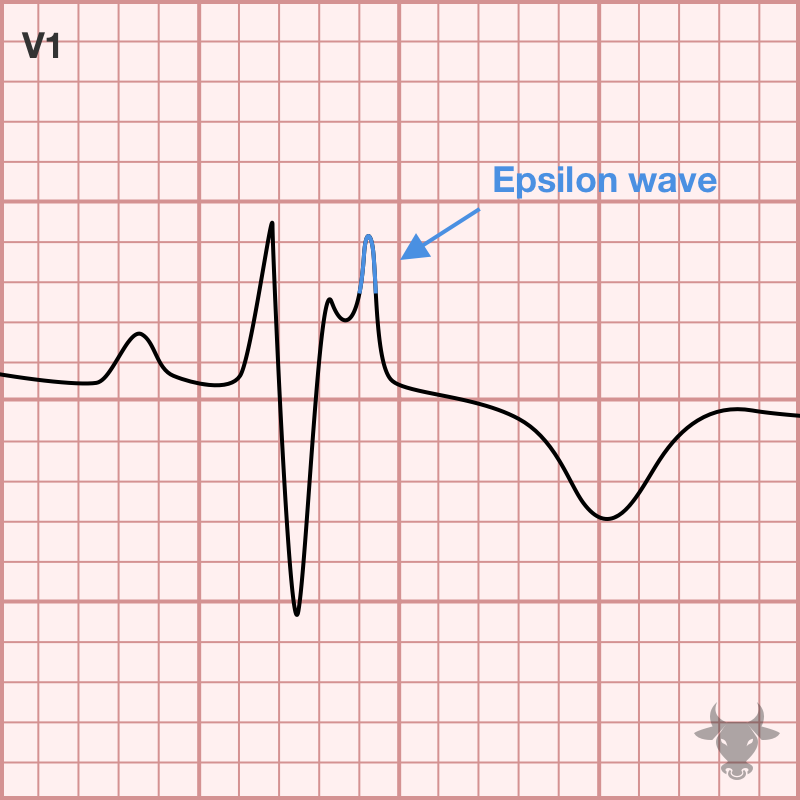
ARVC is an inherited and progressive condition characterized by structural abnormalities in the right ventricle that predispose to ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. The condition is more common in...
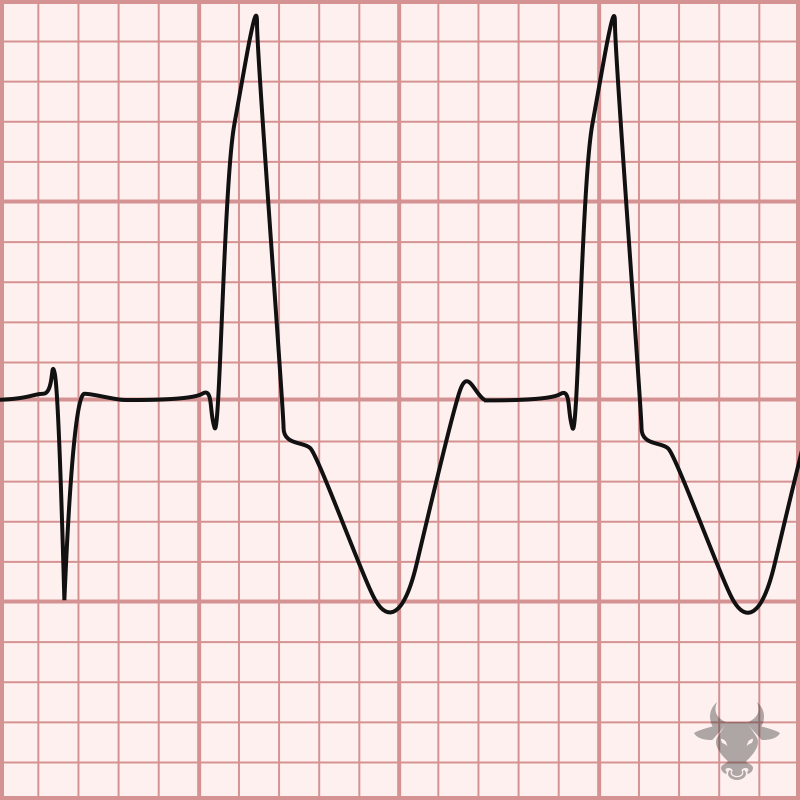
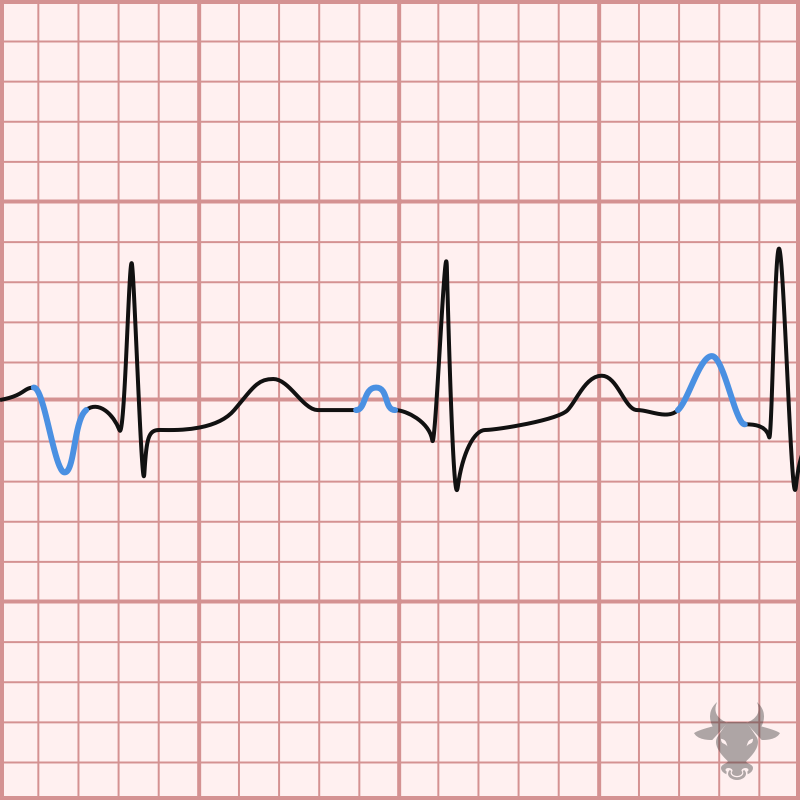
This is a phenomenon first described in 1947 in which the refractory period of the conduction system is proportional to the length of the preceding cycle, resulting in aberrant conduction...
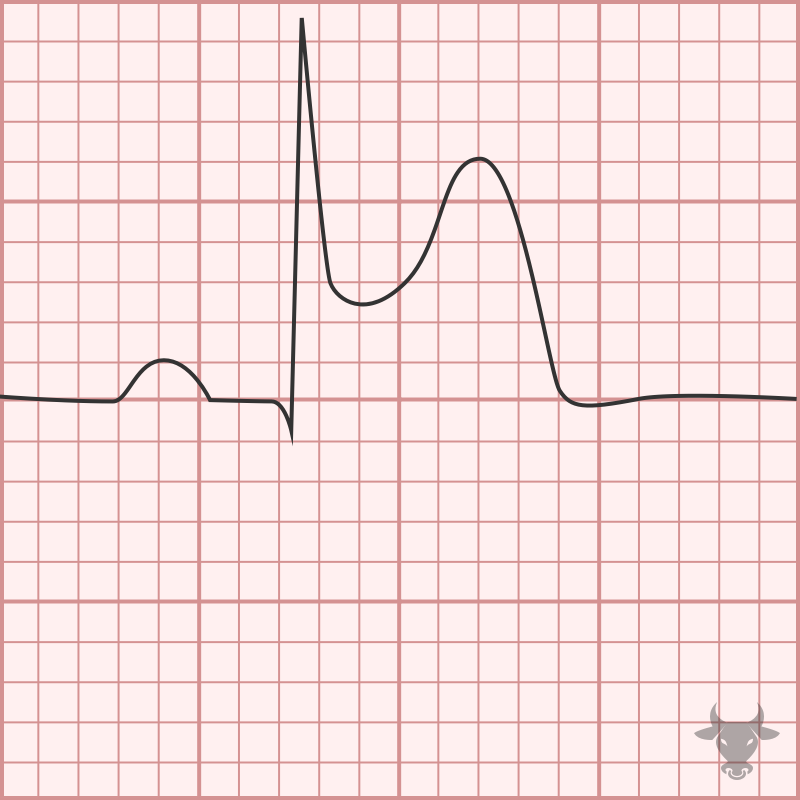
This pattern of isolated ST-segment elevation in lead III, ST-segment depression in V4 through V6, and ST-segment elevation in V1 greater than V2 was first introduced and published in 2020....
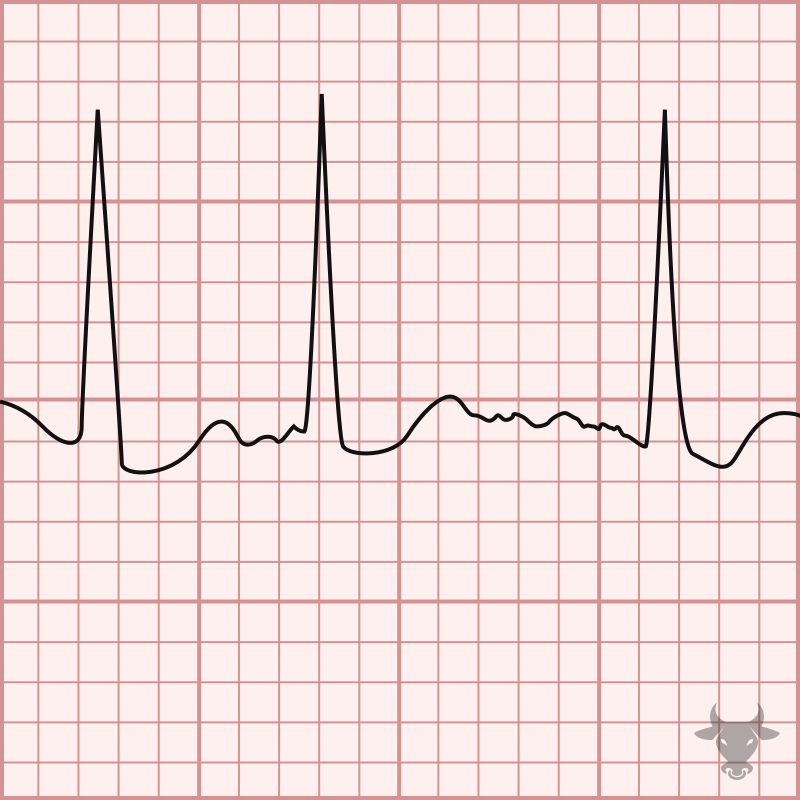
Atrial fibrillation occurs when the atria fibrillate and send rapid impulses to the atrioventricular node. The atrioventricular node serves as the "gatekeeper," deciding which signals get through to the infranodal...
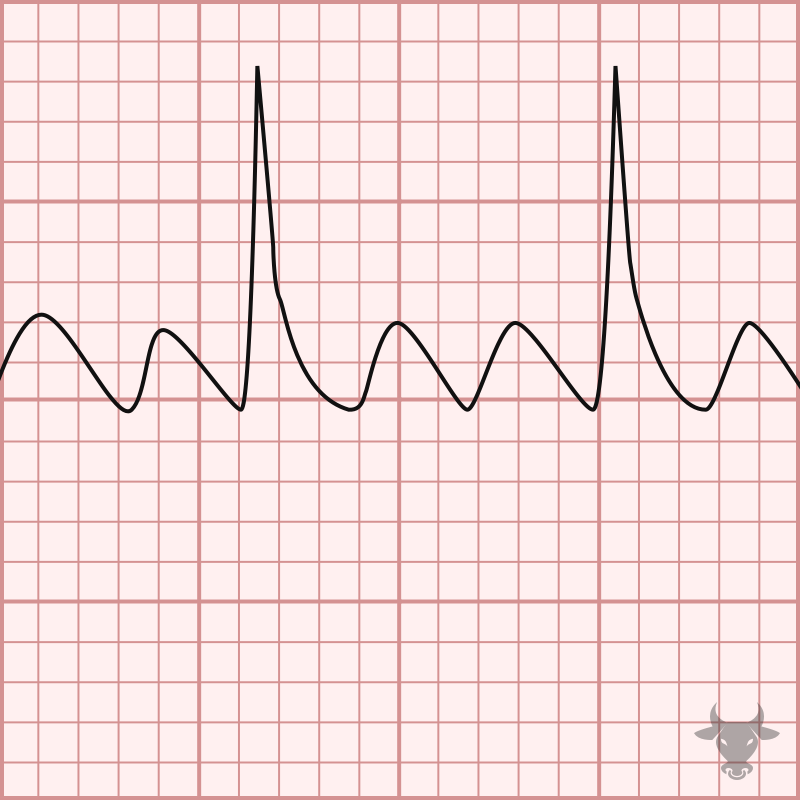
Normally, the atrioventricular node serves as the “gatekeeper” for signals arising from the atria – it has a refractory period that does not allow ventricular rates much faster than about...
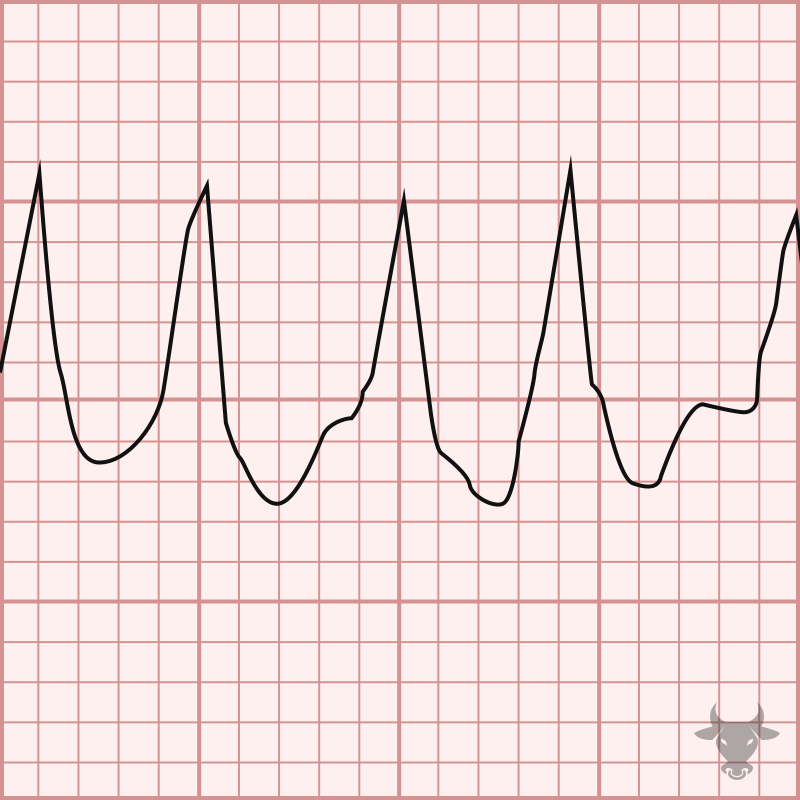
Atrial flutter occurs from a reentrant circuit around the tripcuspid valve in the right atrium. It is an organized rhythm that is generally characterized by an atrial rate around 300...
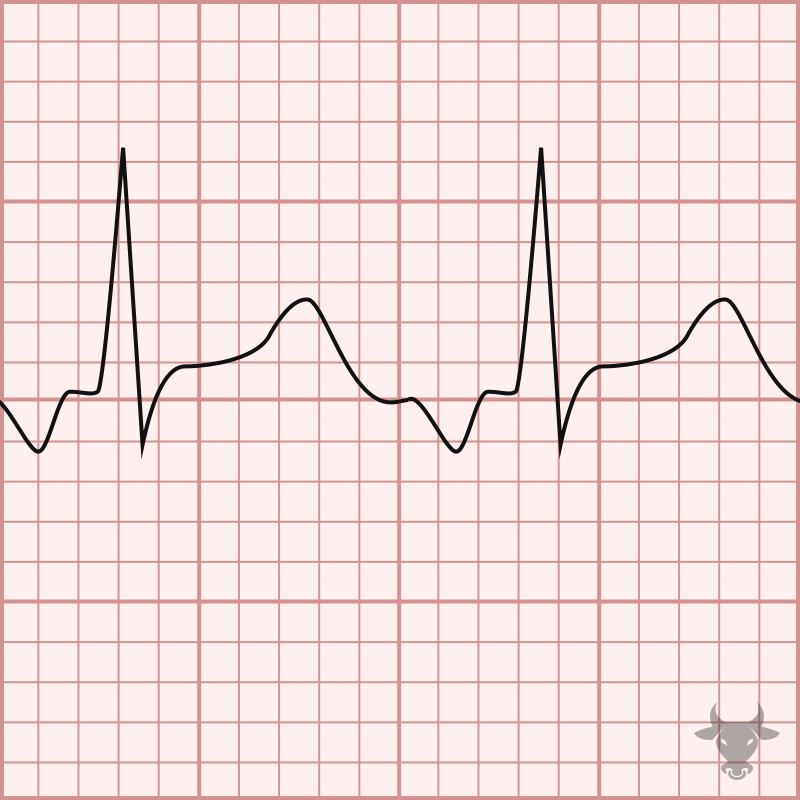
Atrial tachycardia, or focal atrial tachycardia, is result of a micro-reentrant circuit or an automatic focus. The atrial rate is greater than 100 bpm and less that 250 bpm. Atrial...
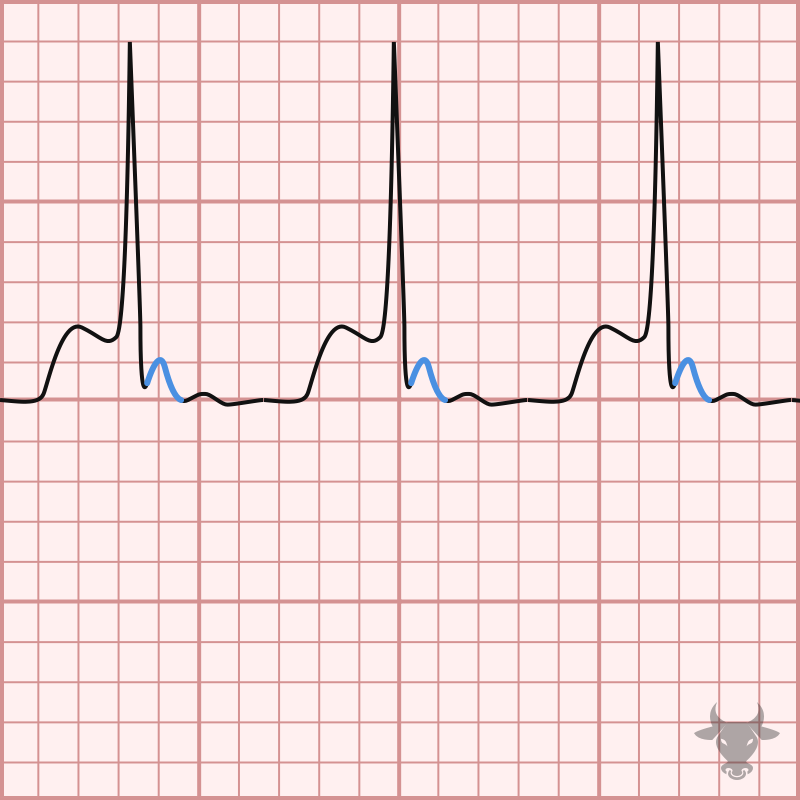
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is caused by a reentrant loop within the atrioventricular node. With AVNRT, the atrioventricular node has two pathways, fast and slow, which allows for a...
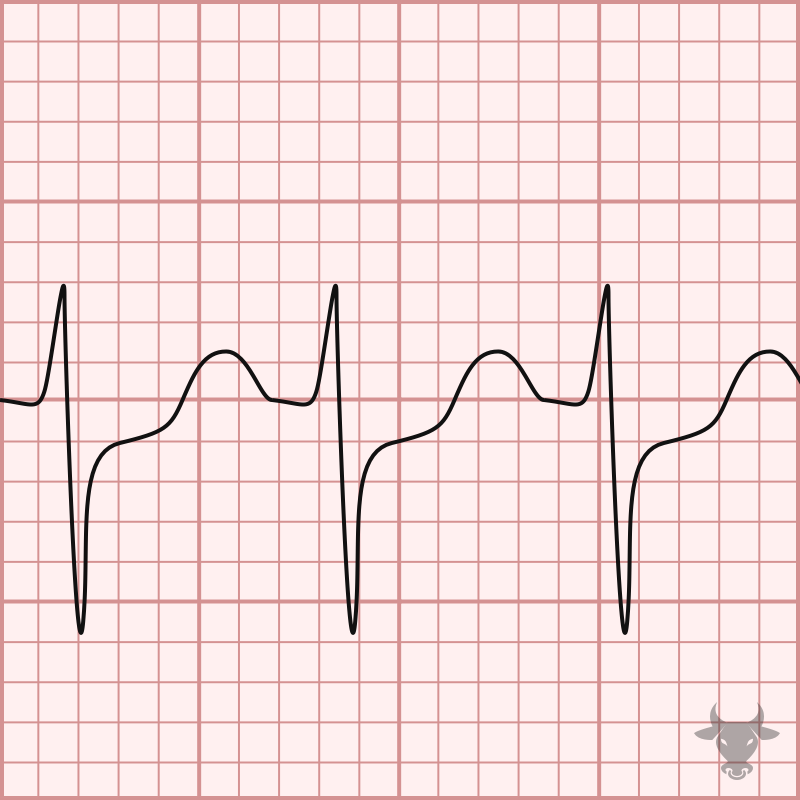
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia, or atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia, is a type of supraventricular tachycardia in which an accessory pathway provides an abnormal connection between the atria and ventricles. Patients with an...
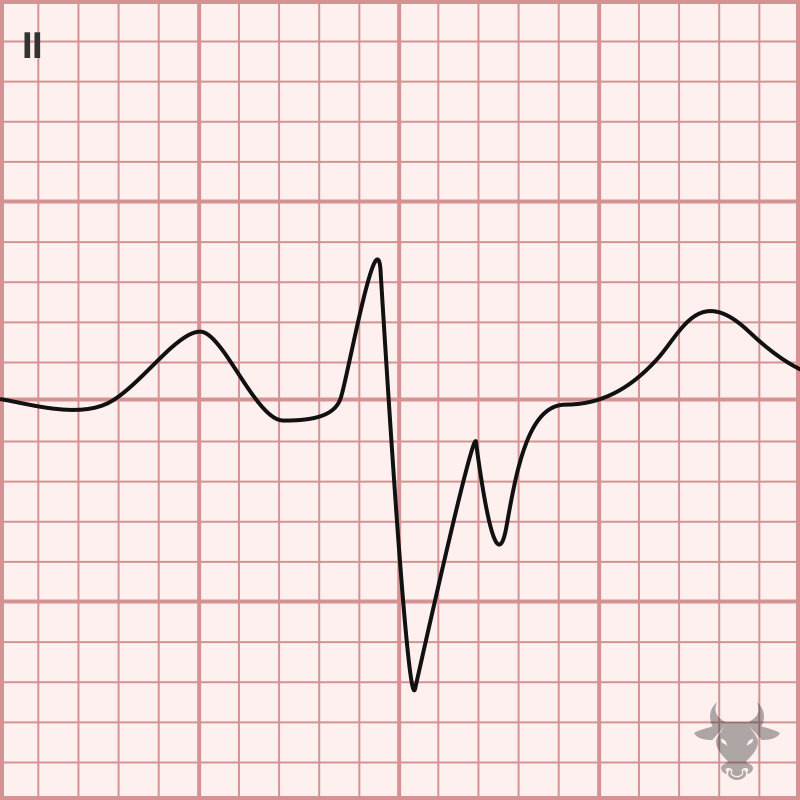
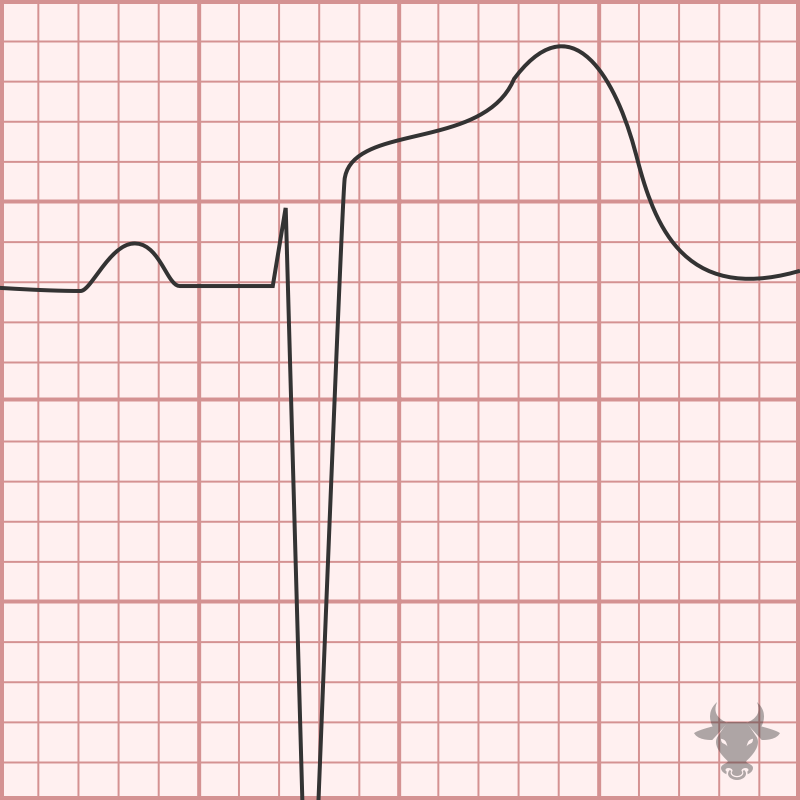
When two of three fascicles are blocked, it is termed bifascicular block. While a left bundle branch block (LBBB) technically involves disruption of two fascicles, this term is typically reserved...
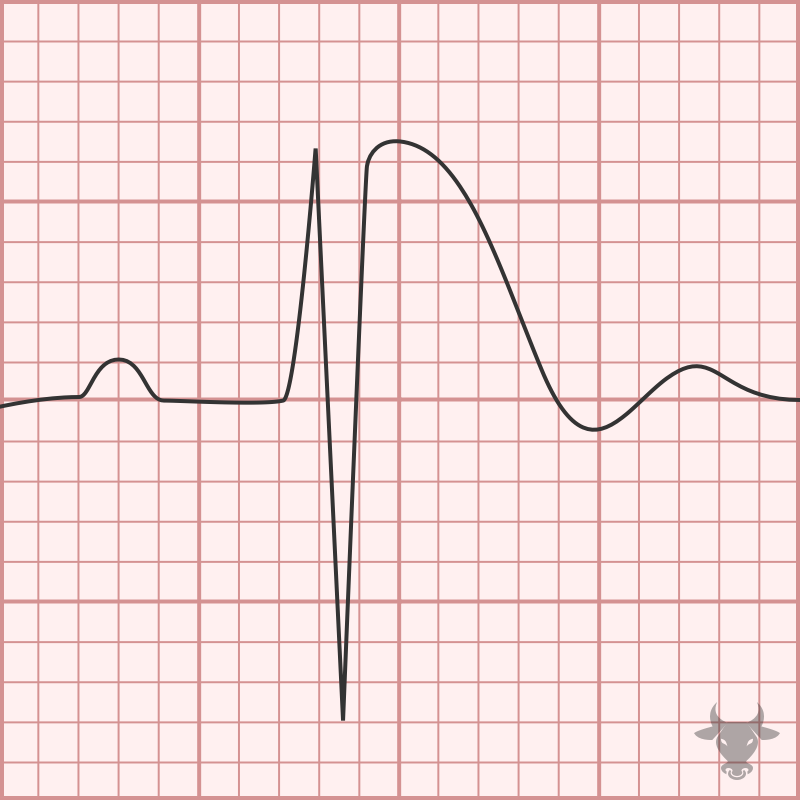
Brugada syndrome is a sodium channelopathy with a characteristic ECG pattern (pseudo-right bundle branch block pattern with down sloping ST segment elevation in V1 and/or V2) and an increased risk...
Cerebral T waves are large T wave inversions and are likely the result of a sympathetic surge causing repolarization abnormalities. Cerebral T waves are rare and generally resolve over time.
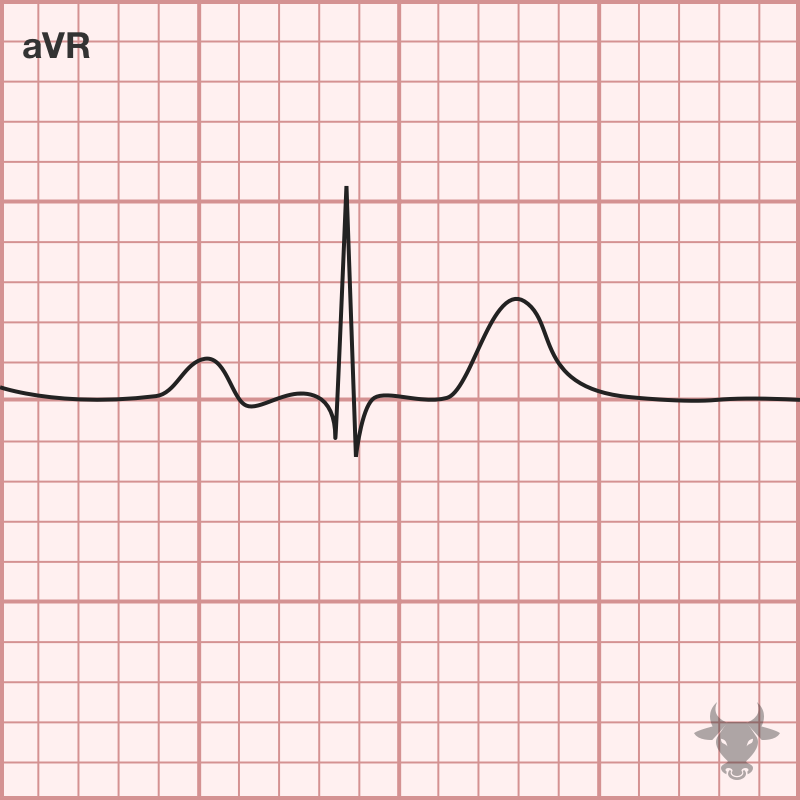
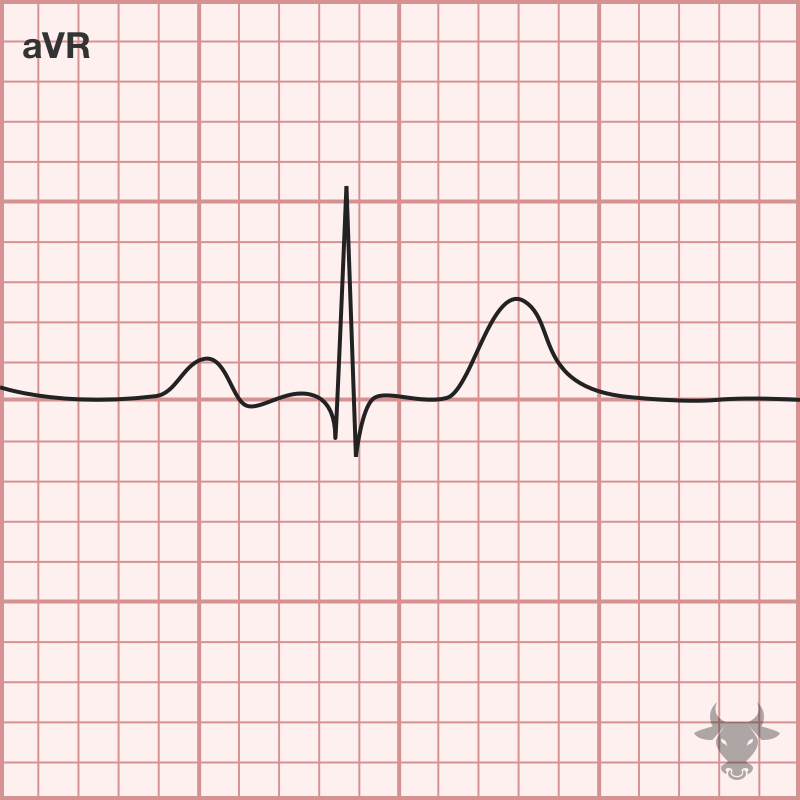
A rare congenital condition where the heart is on the right side of the thorax. Electrocardiographically, this results in right axis deviation and positive QRS complex in aVR with upright...
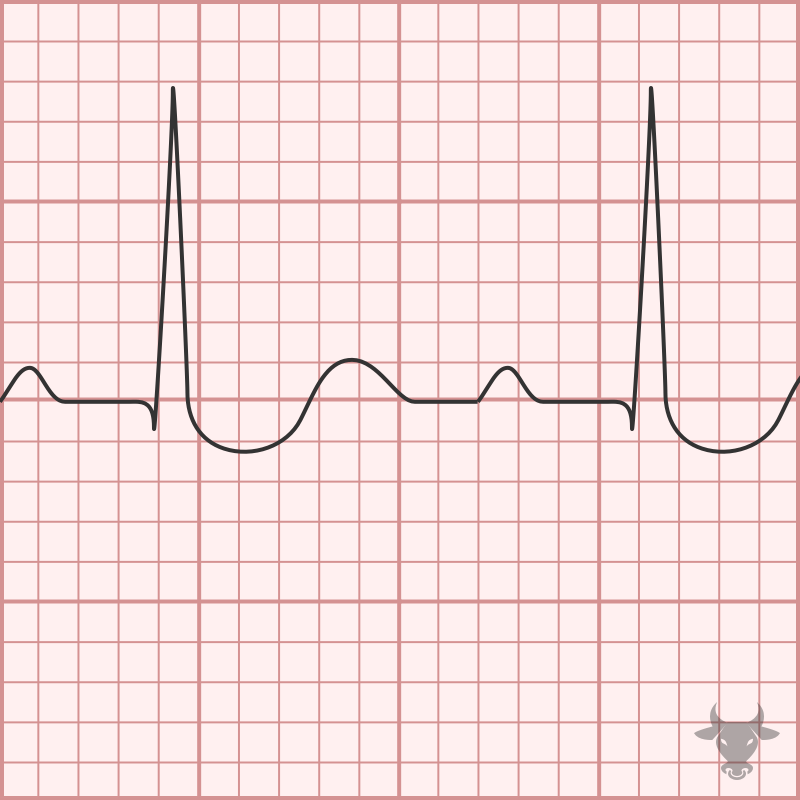
Digoxin, or digitalis, is associated with several electrocardiographic changes and, in toxicity, can precipitate a myriad of tachydysrhythmias and bradydysrhythmias. Increased intracellular calcium increases automaticity, and atrioventricular blockade increase vagal...
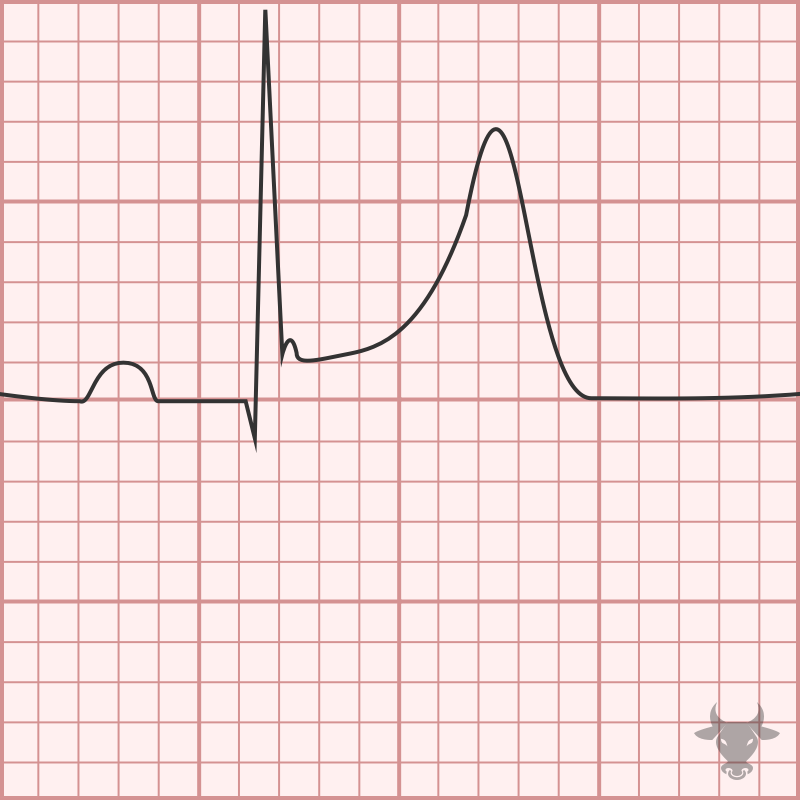
Electrocardiographic features of early repolarization include diffuse ST elevations that are most pronounced in the precordial leads (typically V2-5) and in proportion to the amplitude of the QRS complex. The...
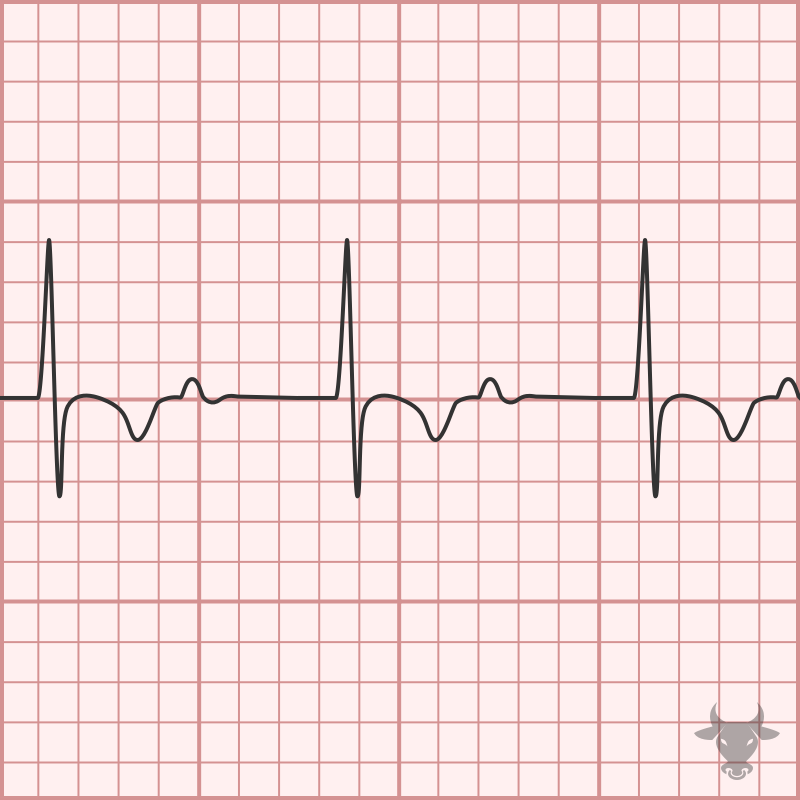
First degree blocks are characterized by a prolonged PR interval (greater than 200 ms) and are usually seen it active, healthy patients without heart disease. It usually represents high vagal...

Multilead ST-segment depression with ST-segment elevation in aVR is a pattern that has been recognized as a strong predictor of left main coronary artery or 3-vessel disease; however, occlusive coronary...
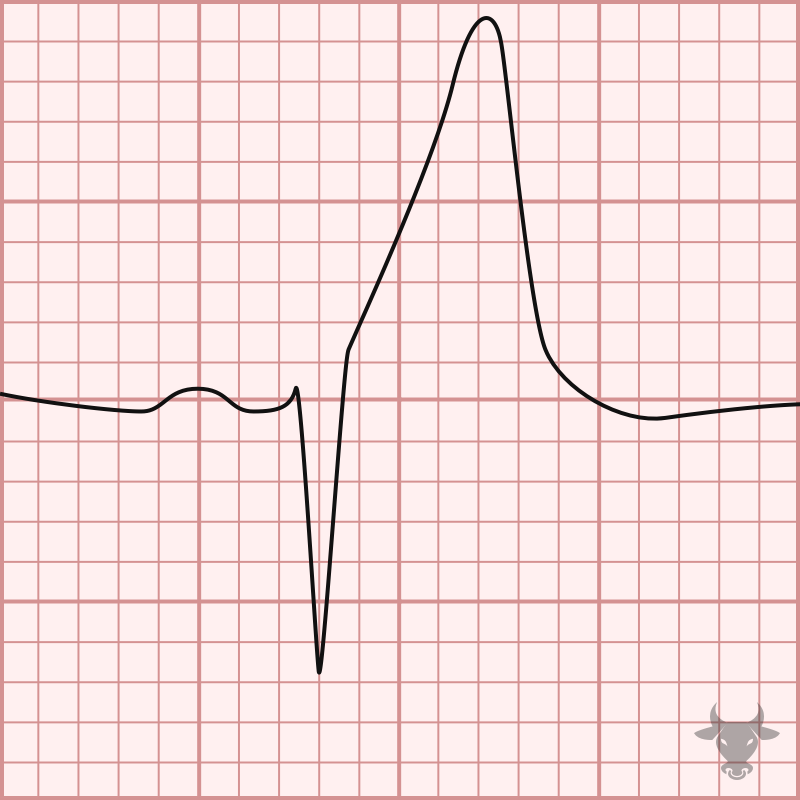
Hyperacute T waves are seen early in occlusive myocardial infarction and are characterized by a broad base and rounded top; they are large in amplitude when compared to the QRS...
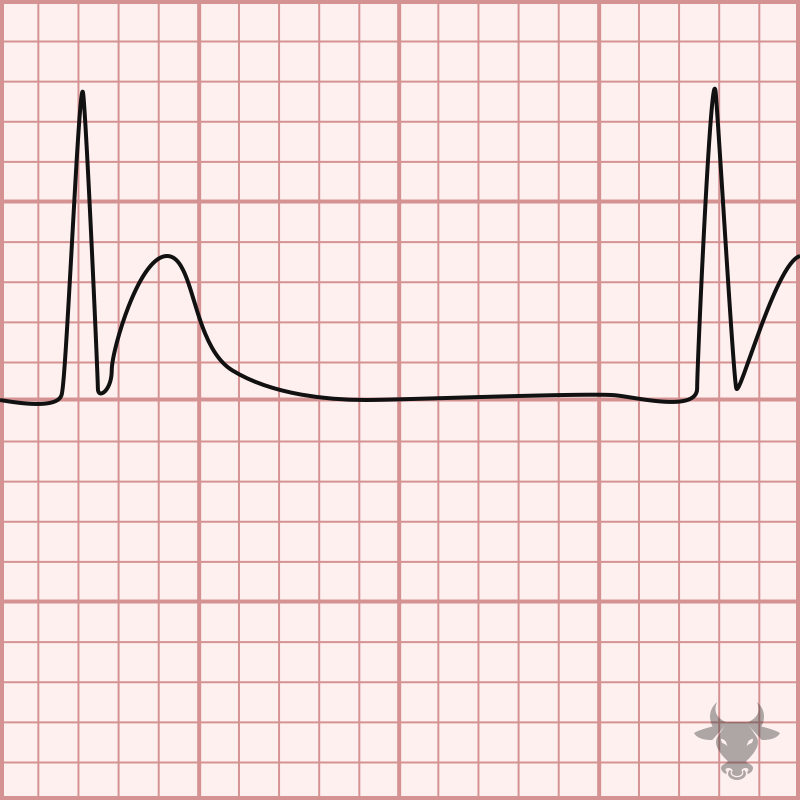
The identification of ECG changes associated with electrolyte derangements including hypercalcemia is critical as the associated conduction abnormalities carry the risk of progression to fatal ventricular dysrhythmias (such as ventricular...
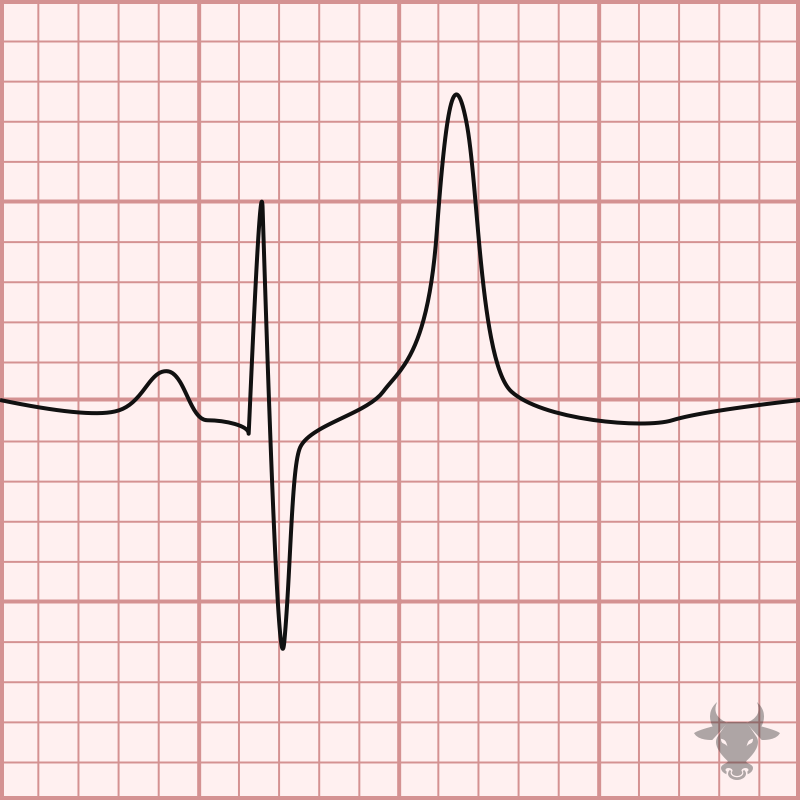
Electrocardiographic findings of hyperkalemia tend to follow a progression as toxicity progresses. Often, the earliest finding is narrow-based, peaked T waves, and at the extreme end of the hyperkalemia spectrum,...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death among individuals under 40 years of age, and a cause of outflow obstruction. A systolic murmur along the left...
Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia can all cause a prolongation of the QT interval. While hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia both delay the repolarization phase (phase 3) of the of the cardiac action...
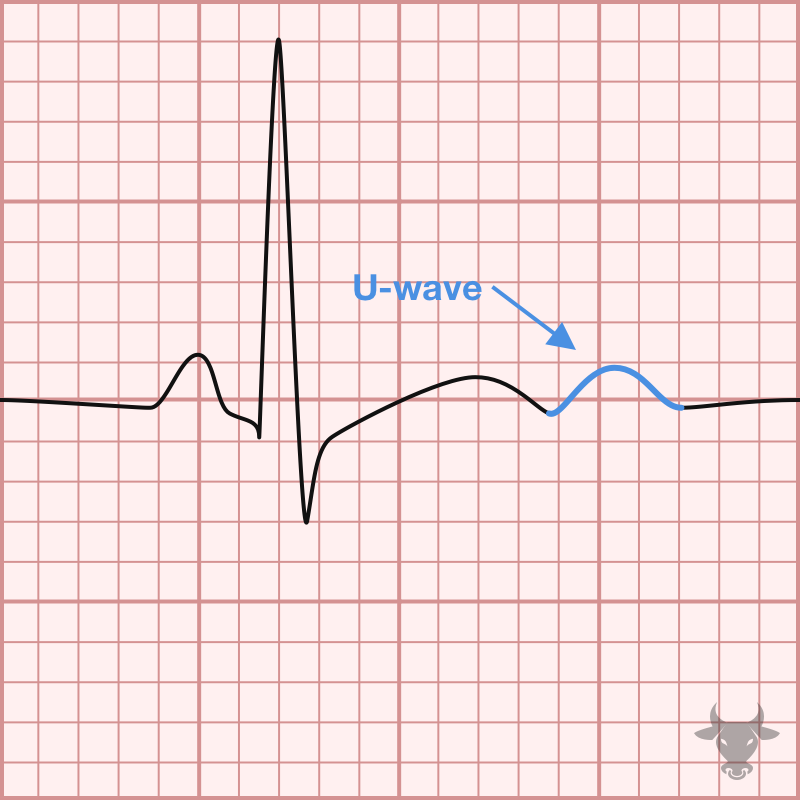
Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia can all cause a prolongation of the QT interval. While hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia both delay the repolarization phase (phase 3) of the of the cardiac action...
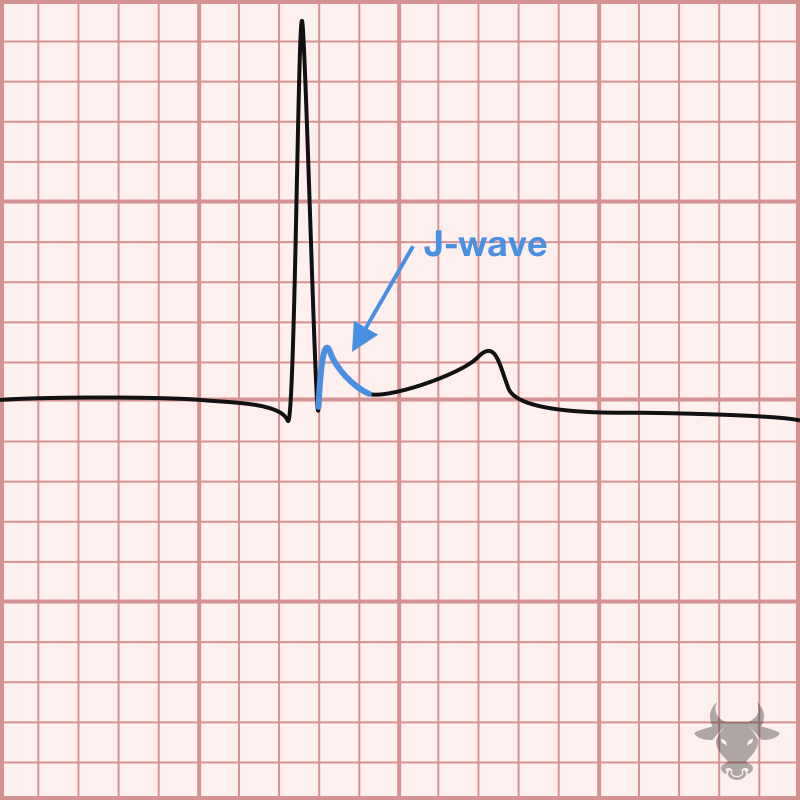
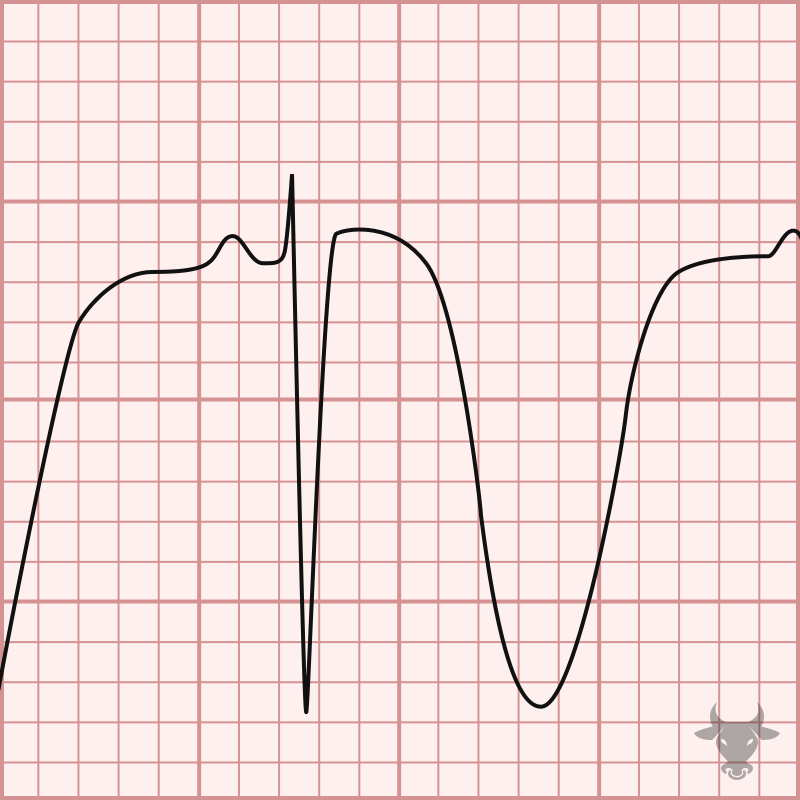
Hypothermia can cause J waves, or Osborn waves, bradycardia, a prolonged QT, and motion artifact from shivering.
The normal infranodal conduction system divides into the right and left bundles, the latter is further subdivided into anterior and posterior divisions or “fascicles.” Disruption of both fascicles produces the...
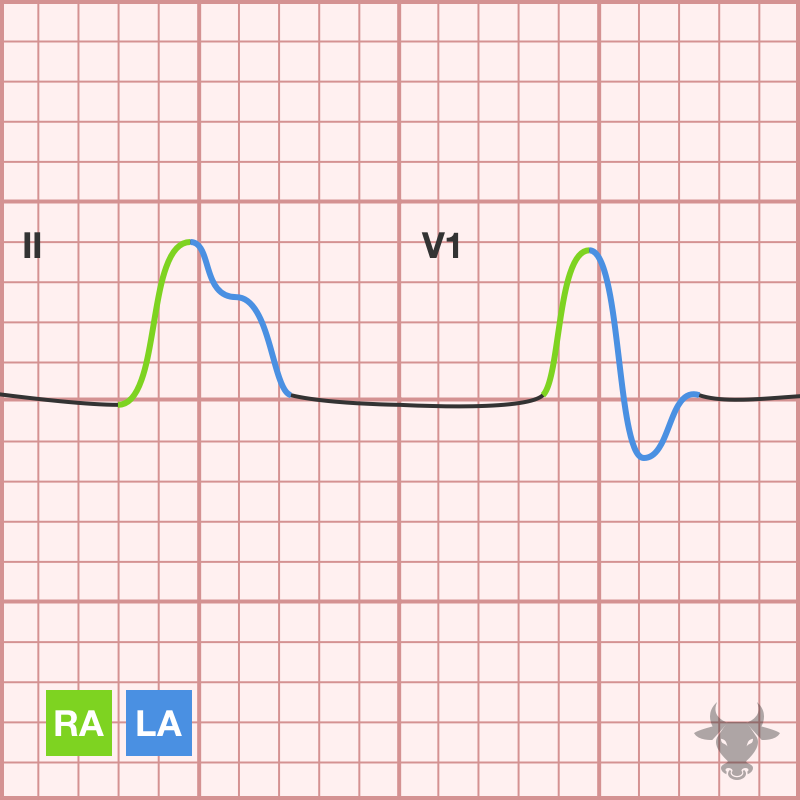
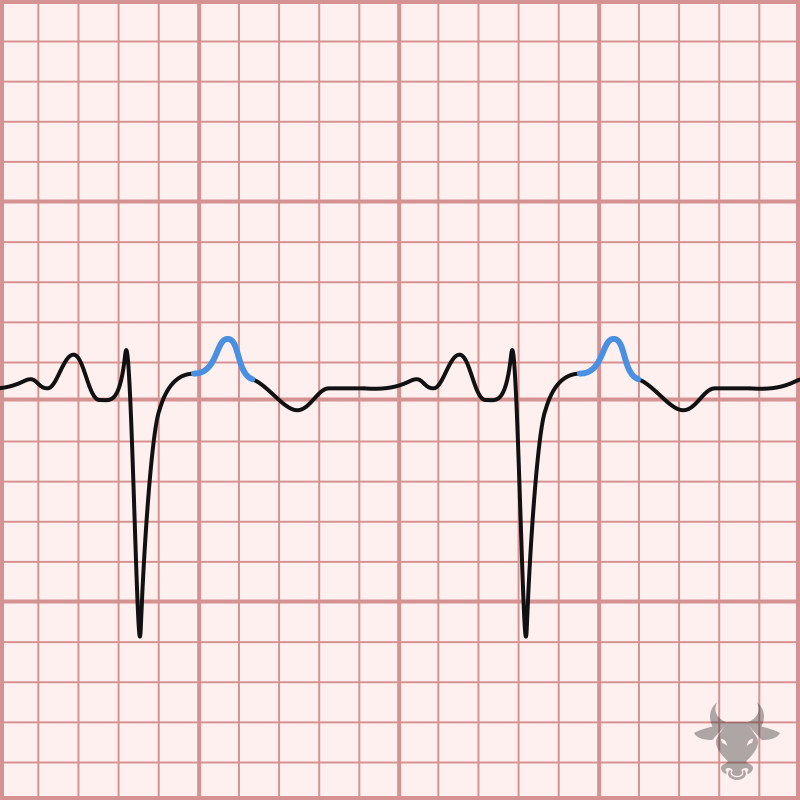
Atrial enlargement can be determined by analyzing the P waves in leads II and V1. The first half of the P wave represents right atrial depolarization, while the second half...
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) occurs when the left bundle no longer conducts, and the signal must pass to the left ventricle via myocyte-to-myocyte conduction. This pattern of conduction is...
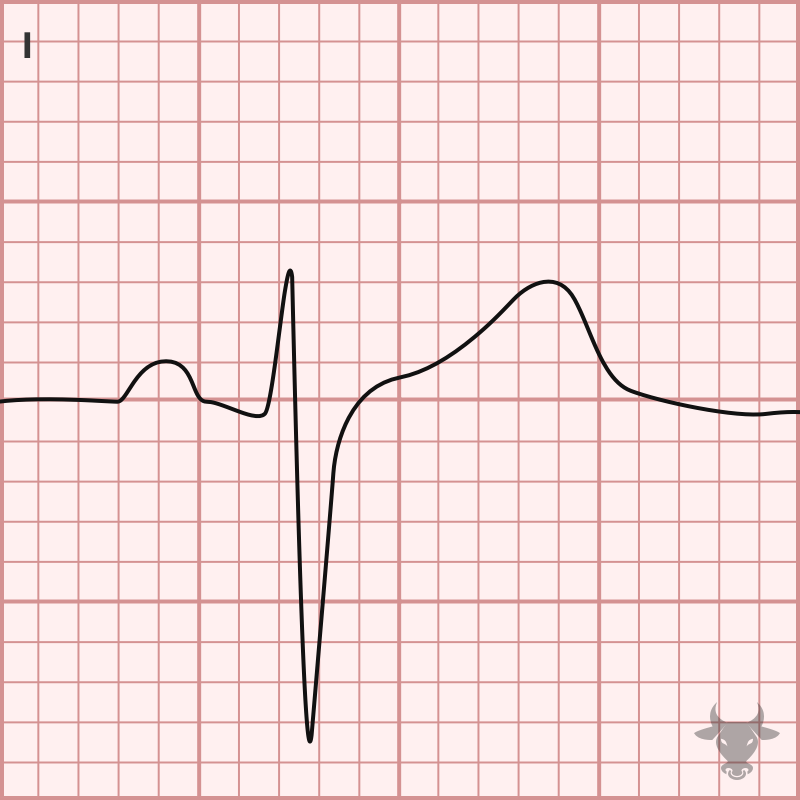
The normal infranodal conduction system divides into the right and left bundles, the latter is further subdivided into anterior and posterior divisions or “fascicles.” Disruption of both fascicles produces the...
In the age of reperfusion, left ventricular aneurysms have become quite rare, but in the absence of reperfusion, it is a common structural complication of acute myocardial infarction, occurring in...
There are several criteria out there for left ventricular hypertrophy, and none of them are particularly sensitive. They’re all less than 50% sensitive, but they’re usually quite specific - 85...
The Lewis lead describe a different positioning of the limb leads in order to better visualize atrial activity. The Lewis lead can help better visualize atrial activity. Lead placement...
Between 0.4 and 4% of ECG’s obtained in various settings demonstrate features of lead misplacement. Lead misplacement may either obscure important findings or simulate the appearance of ectopic rhythms, conduction...
The traditional definition of low voltage is QRS amplitudes less than 5 mm in all limb leads or less than 10 mm in all precordial leads. The differential for low...
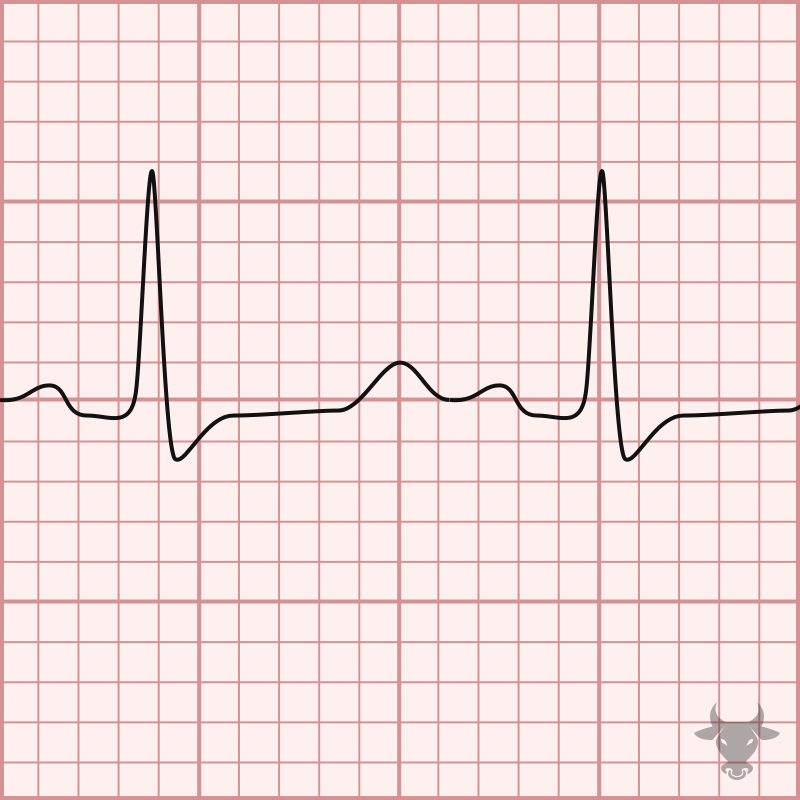
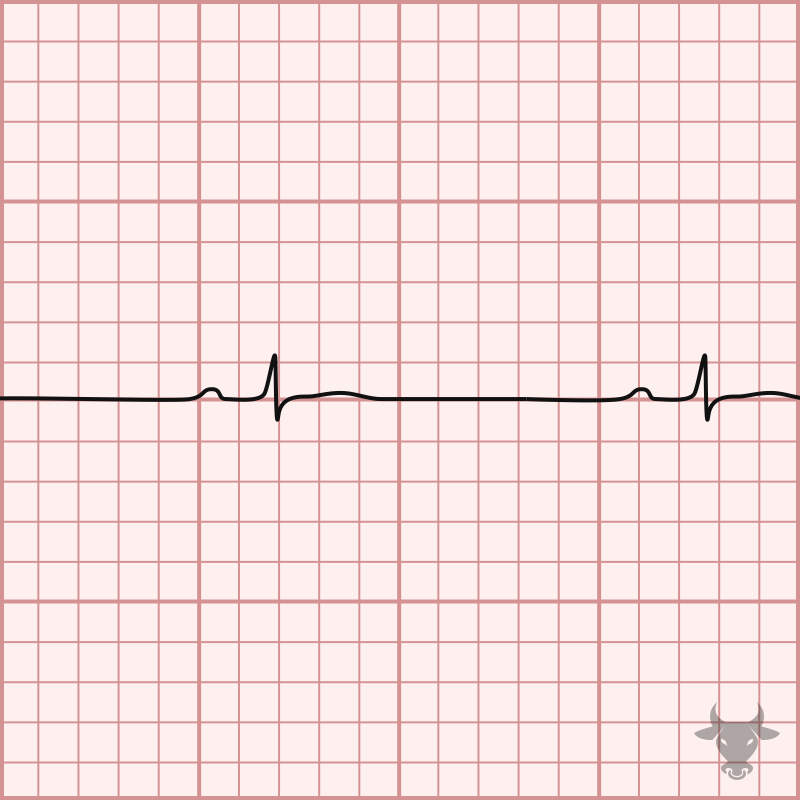
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is an irregularly irregular rhythm, typically between 100-150 beats per minute, that arises from multiple ectopic foci within the atria. It is a rare condition that...
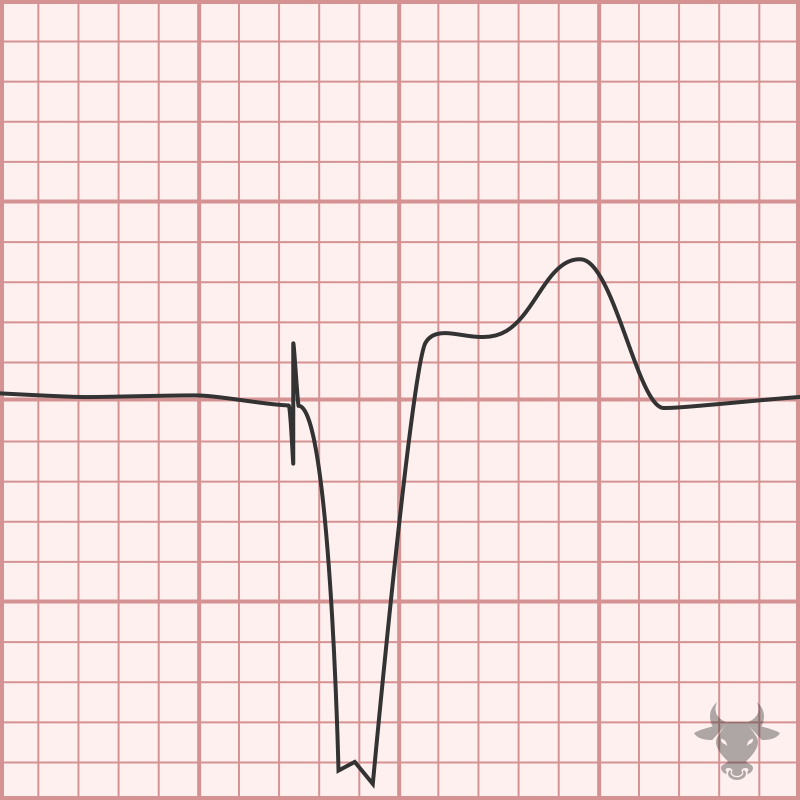
Pacemakers are programmed with five variables, the first three are relevant to emergency physicians. Pacemaker codes....
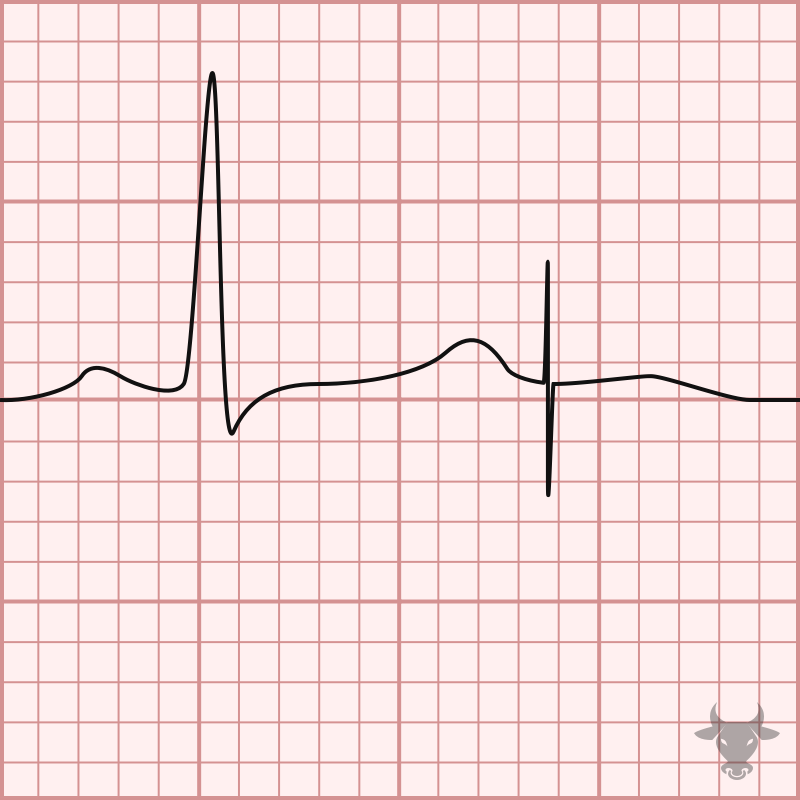
Failure to pace occurs when the paced stimulus is not generated when expected. Pacemaker spikes are decreased or absent. It is usually caused by oversensing but can also be caused...
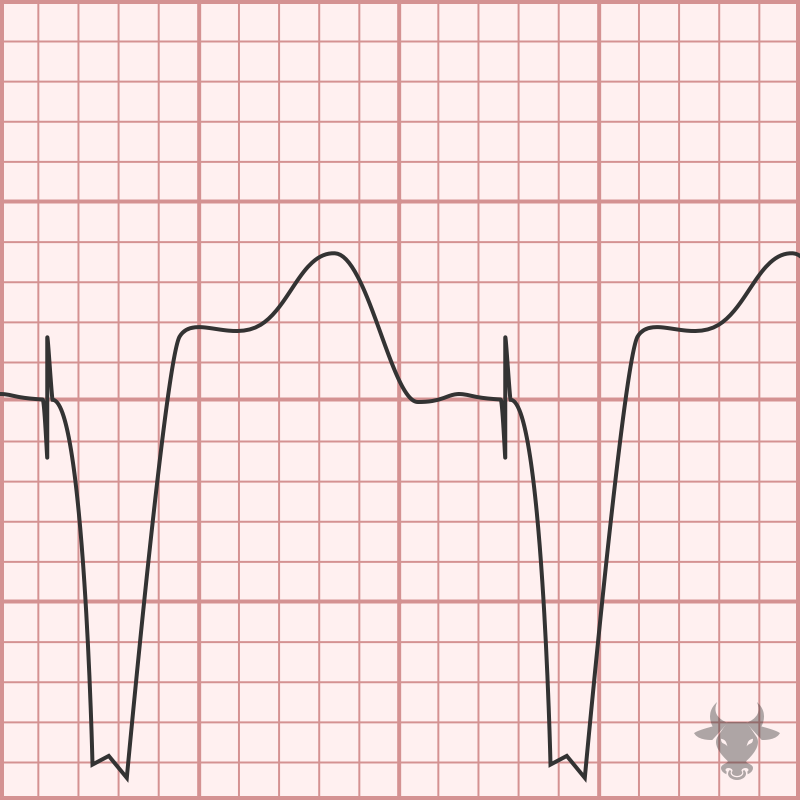
Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia (PMT), or endless loop tachycardia, is a reentrant tachycardia in which the pacemaker forms the anterograde pathway and the atrioventricular node forms the retrograde pathway, leading to a...
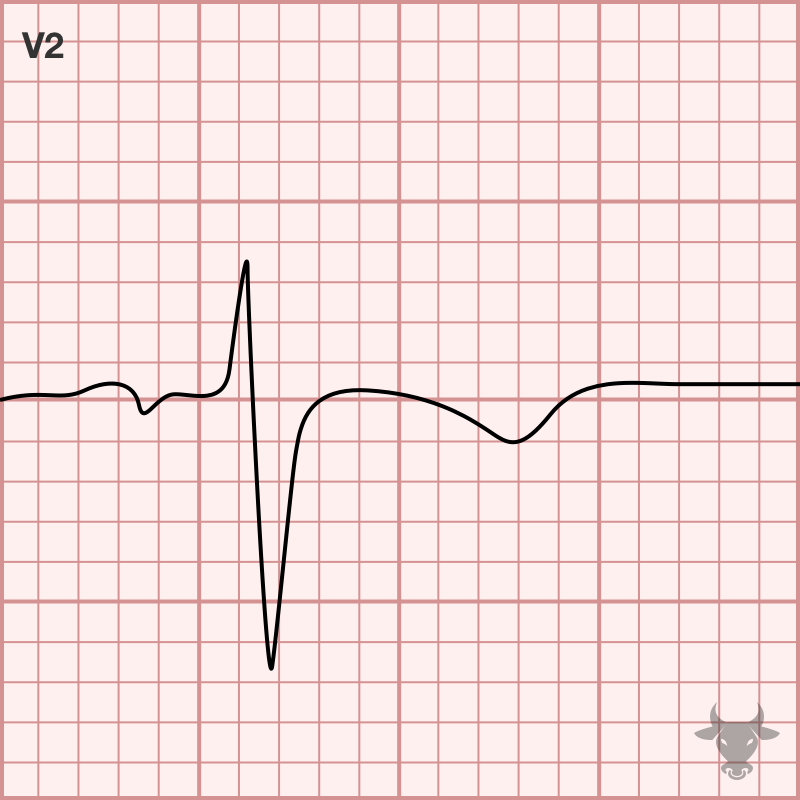
Inverted T-waves in V1-3 are a normal finding in children – the result of right ventricular dominance. While in utero, the neonate’s right ventricle strengthens as it pushes against the...
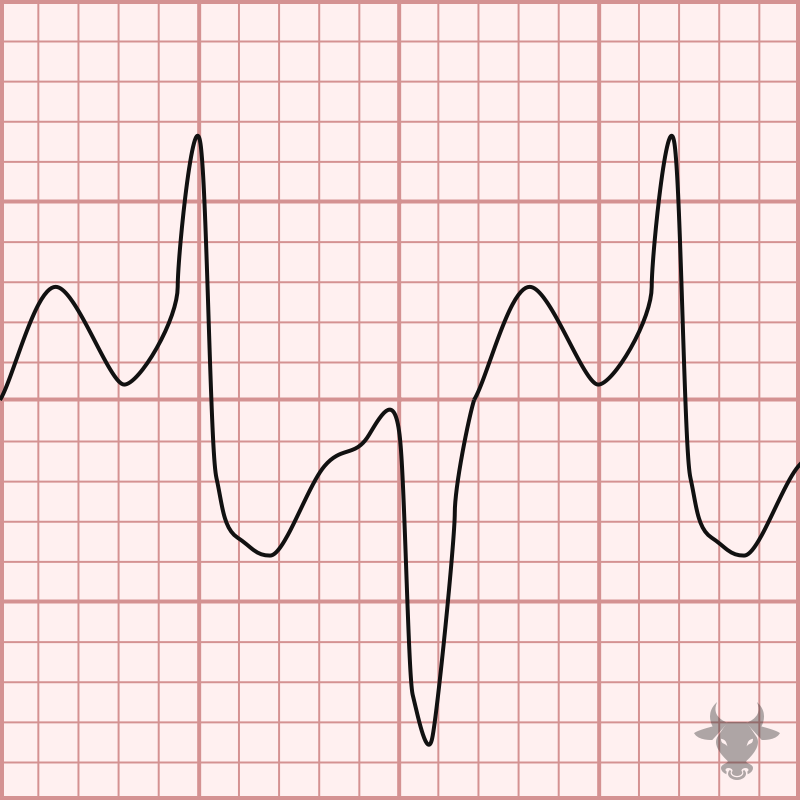
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (PVT) is a form of ventricular tachycardia in which there are multiple ventricular foci with the resultant QRS complex varying in amplitude, axis, and duration. The most...
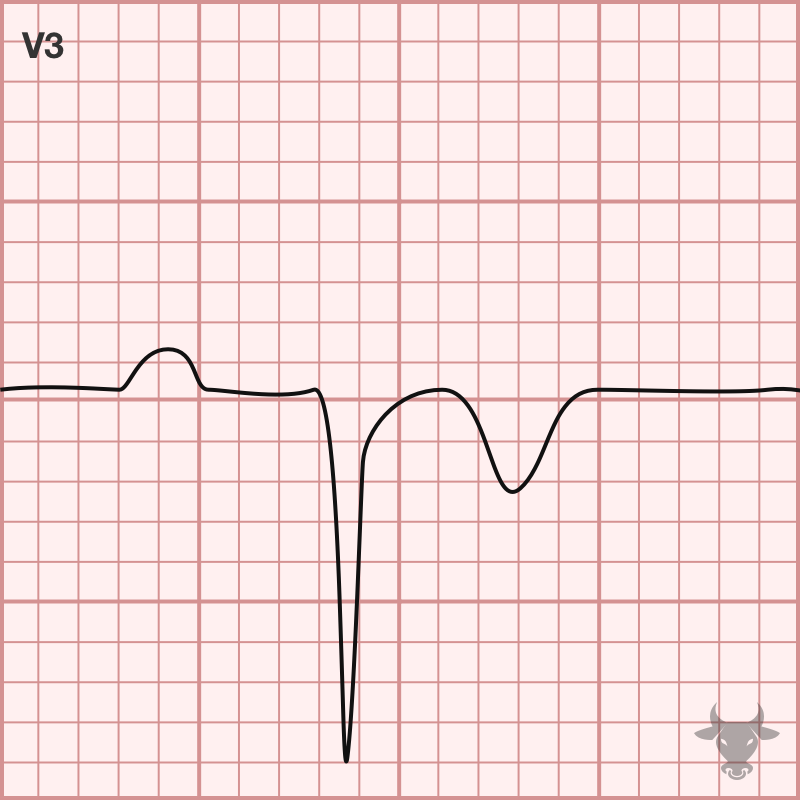
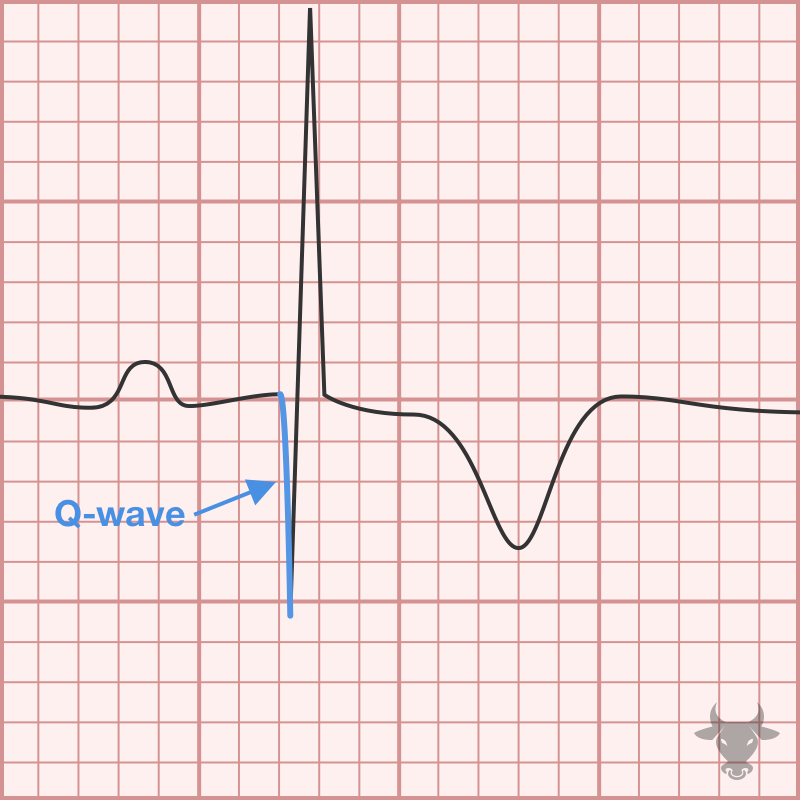
Poor R wave progression is a non-specific finding that is suggestive of prior anterior myocardial infarction. It is a poorly defined term that implies diminished amplitude of the R wave...
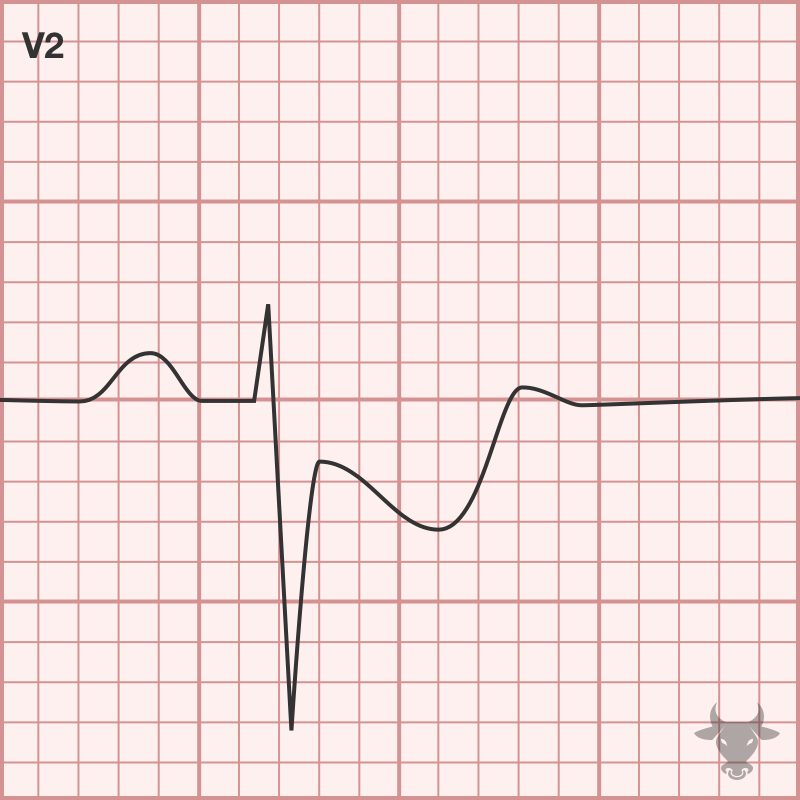
Posterior myocardial infarction is commonly confused with anterior subendocardial ischemia; however, the T waves are expected to be negatively deflected with anterior subendocardial ischemia (unless early on when they can...
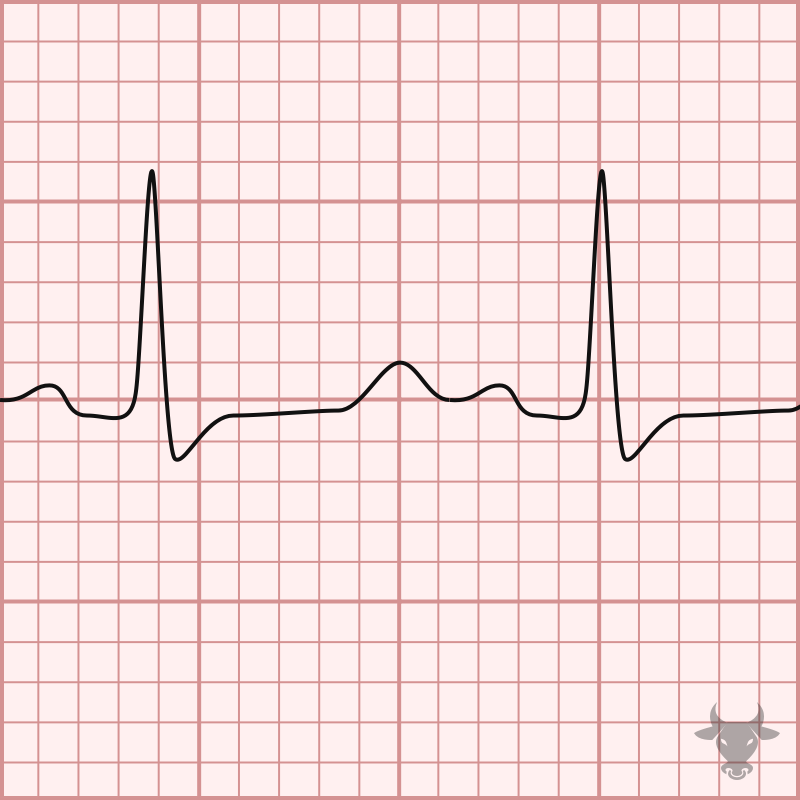
Measuring the QT can be challenging, and many different methods exist. One simple method is the “half the RR” rule – the QT interval is prolonged if it occupies more...
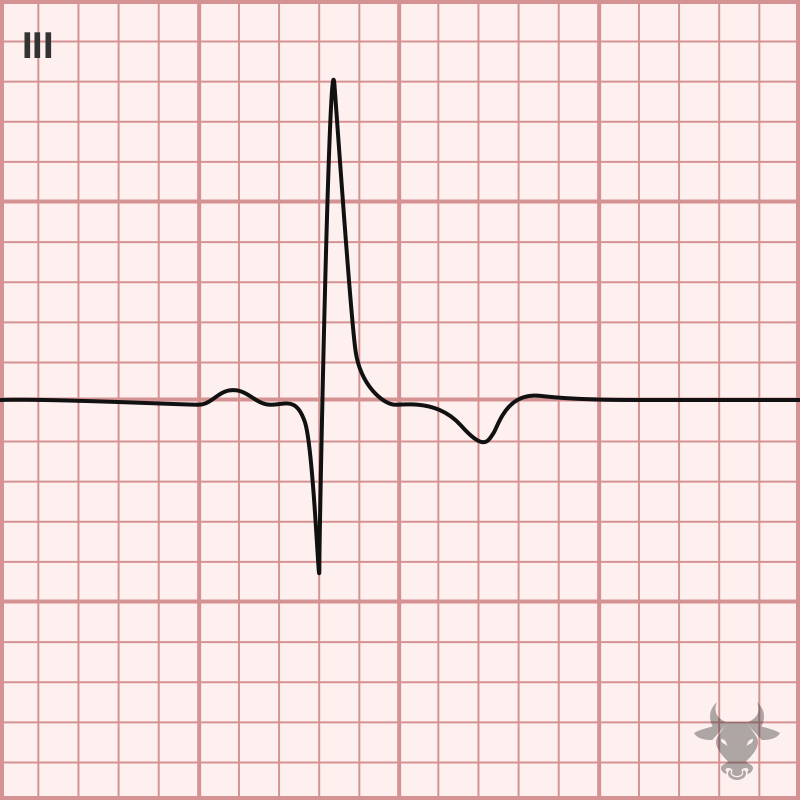
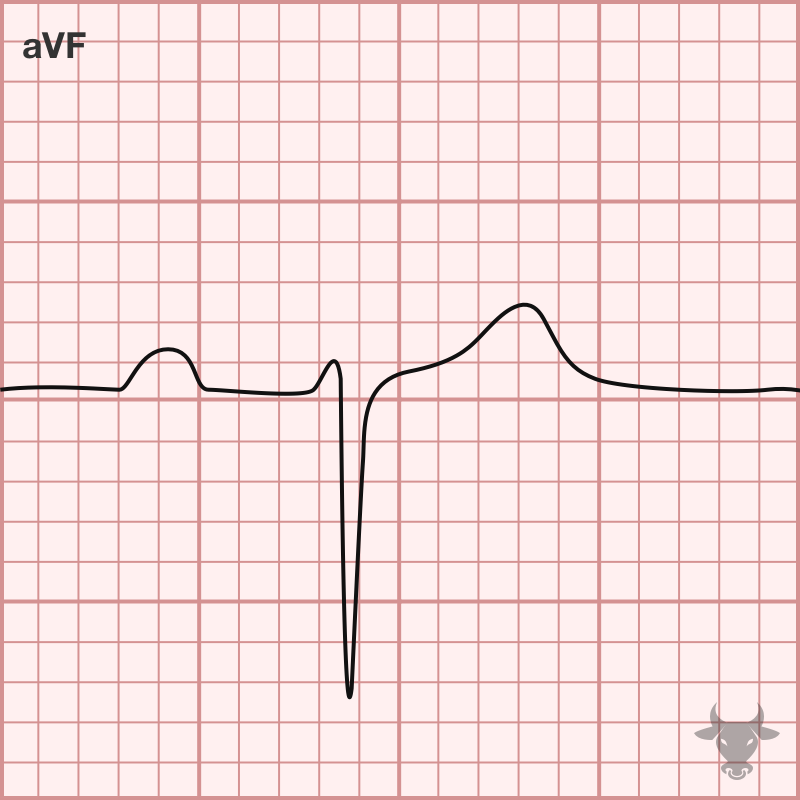
Tachycardia, S1Q3T3, tall P wave in II, ST elevation in right-sided leads (aVR, V1, III), right axis deviation, new right bundle branch block, new incomplete right bundle branch block, and...
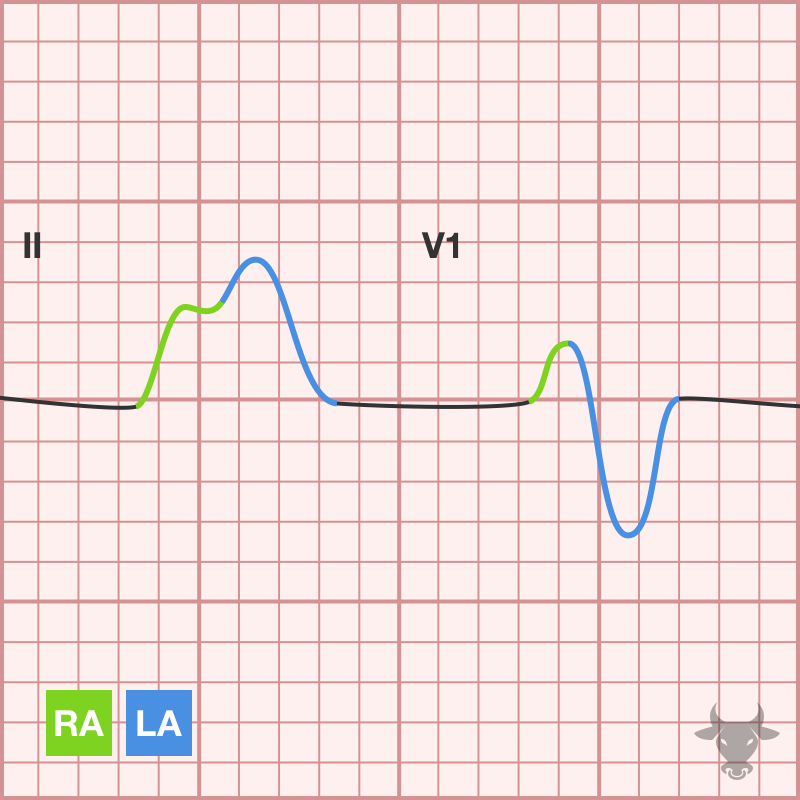
Atrial enlargement can be determined by analyzing the P waves in leads II and V1. The first half of the P wave represents right atrial depolarization, while the second half...
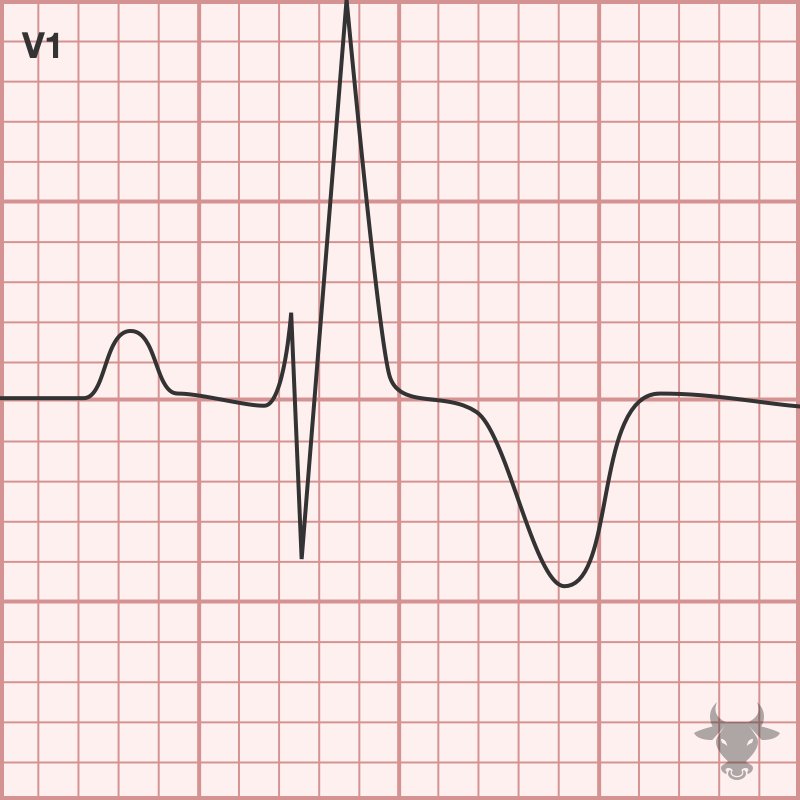
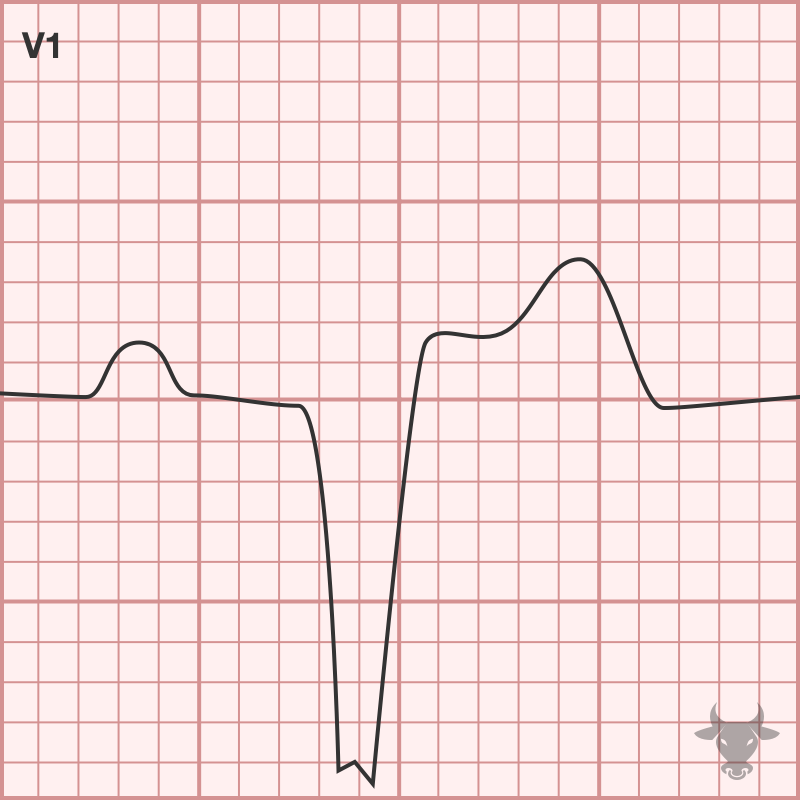
Right bundle branch block (RBBB) occurs when the right bundle no longer conducts, and the signal must pass to the right ventricle via myocyte-to-myocyte conduction. This pattern of conduction is...
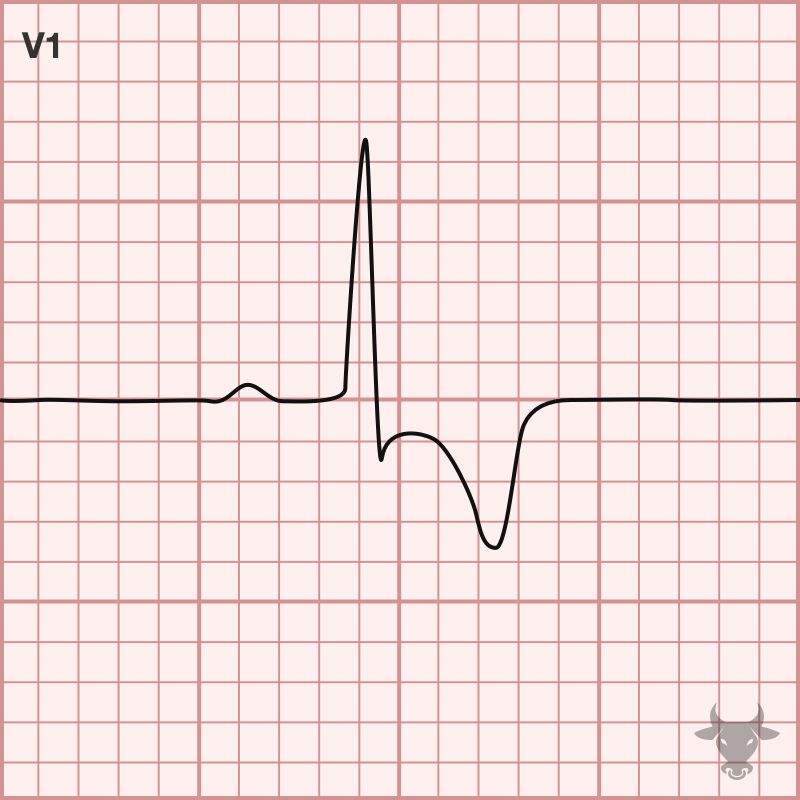
Tachycardia, S1Q3T3, tall P wave in II, ST elevation in right-sided leads (aVR, V1, III), right axis deviation, new right bundle branch block, new incomplete right bundle branch block, and...
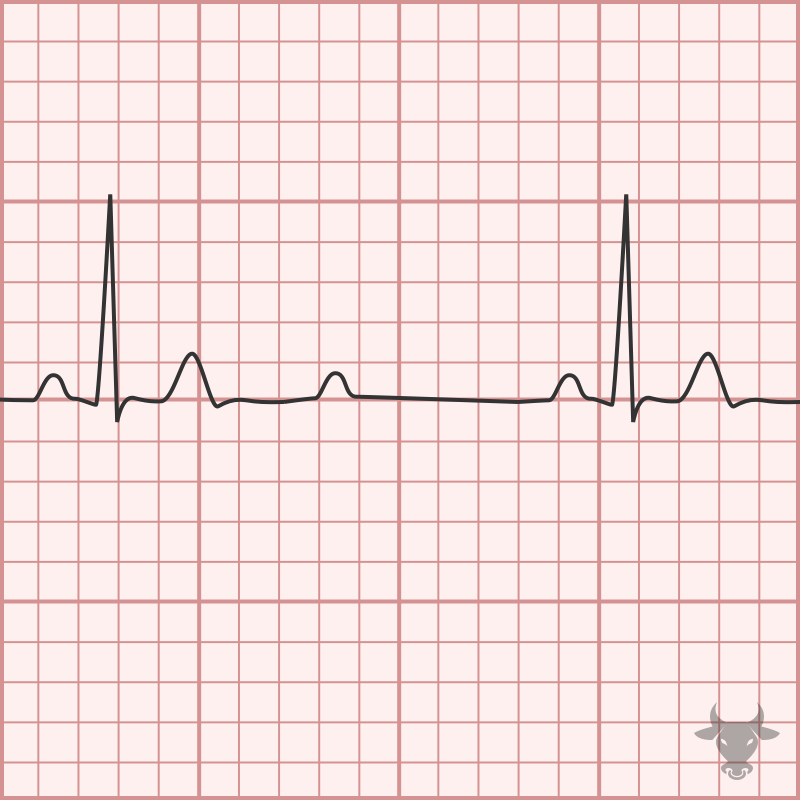
With 2:1 atrioventricular block, it is impossible to know whether it is Mobitz I (nodal) or Mobitz II (infranodal) based on the surface ECG; therefore, 2:1 AV block is simply...
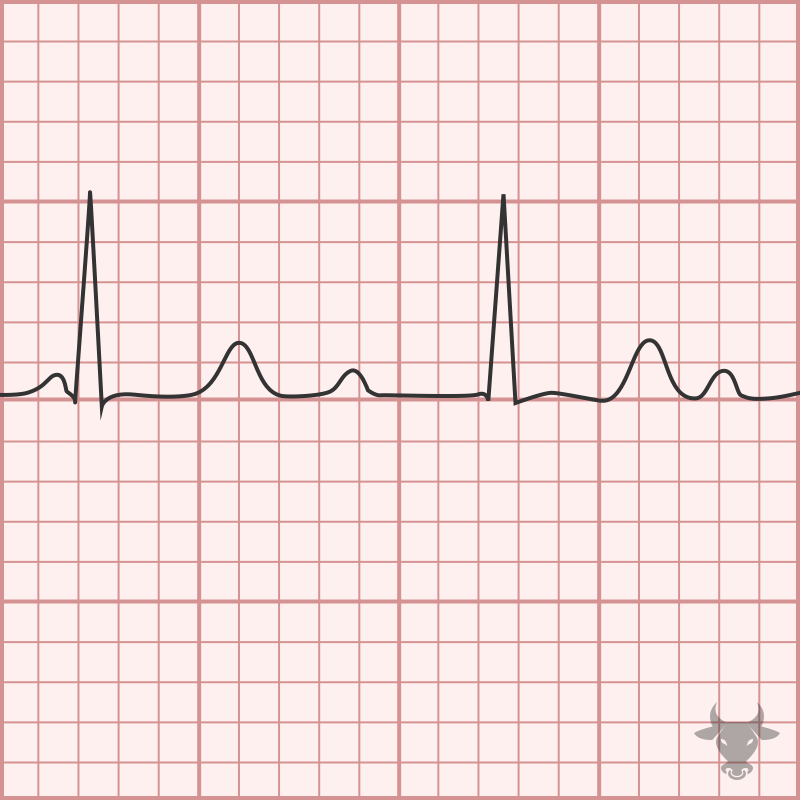
Mobitz I occurs when conduction is progressively delayed through the AV node and eventually fails. It is represented by progressively prolonging PR intervals followed by a “dropped” P wave. It...
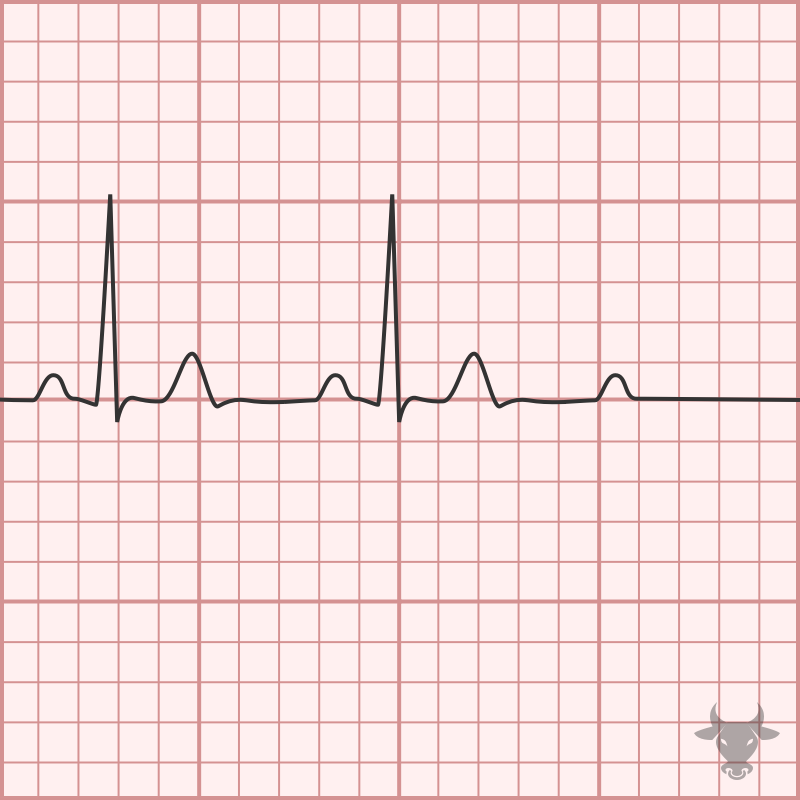
Mobitz II occurs when the infranodal conduction system intermittently fails, resulting in intermittently “dropped” P waves but consistent PR intervals when conducted. Mobitz II usually occurs with preexisting conduction disease...
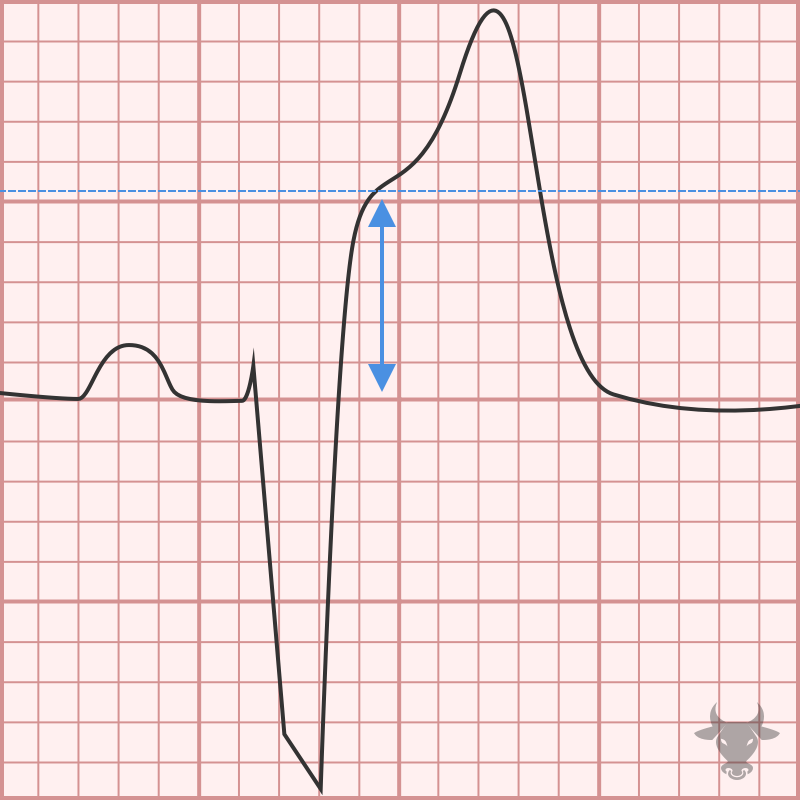
With left bundle branch block, expected ST/T changes include discordant ST depression and T wave inversion in the lateral leads (I, aVL, V5, V6). Discordance describe ST deviation in the...
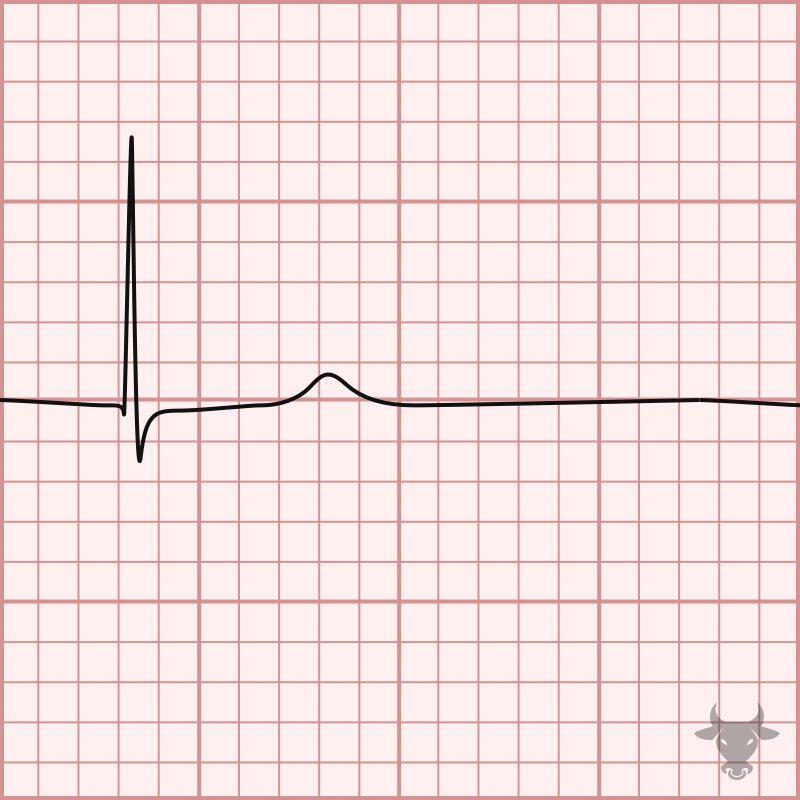
Sinus node dysfunction is historically referred to as sick sinus syndrome. It is due to age-related fibrotic degeneration of the sinus node resulting in impaired signal generation and propagation which...
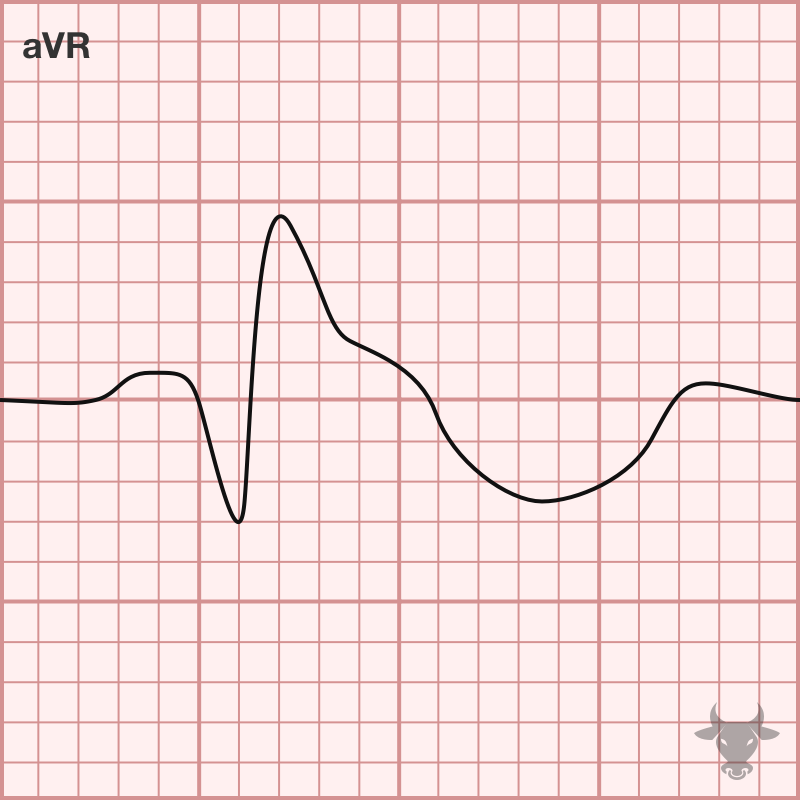
Classily, sodium channel toxicity was described in tricyclic overdoses,96 but many drugs can cause toxic sodium channel effects including antiarrhythmics (e.g., lidocaine, phenytoin, propafenone, flecainide, amiodarone, sotalol), antiepileptic medications (e.g.,...

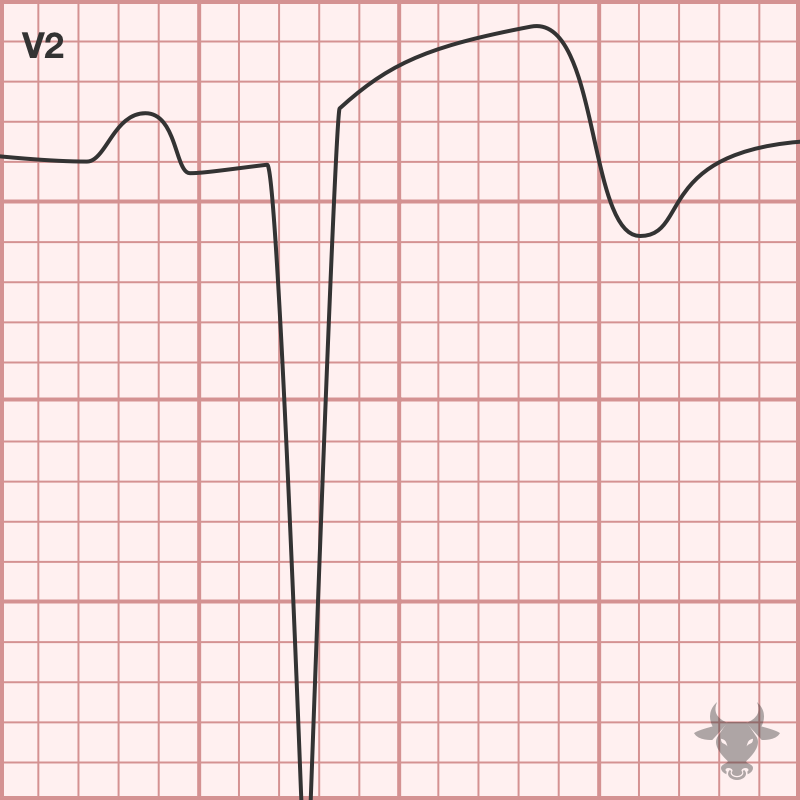
ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a term used to describe a transmural myocardial infarction that benefits from immediate percutaneous intervention. According to the fourth universal definition, STEMI is defined as...
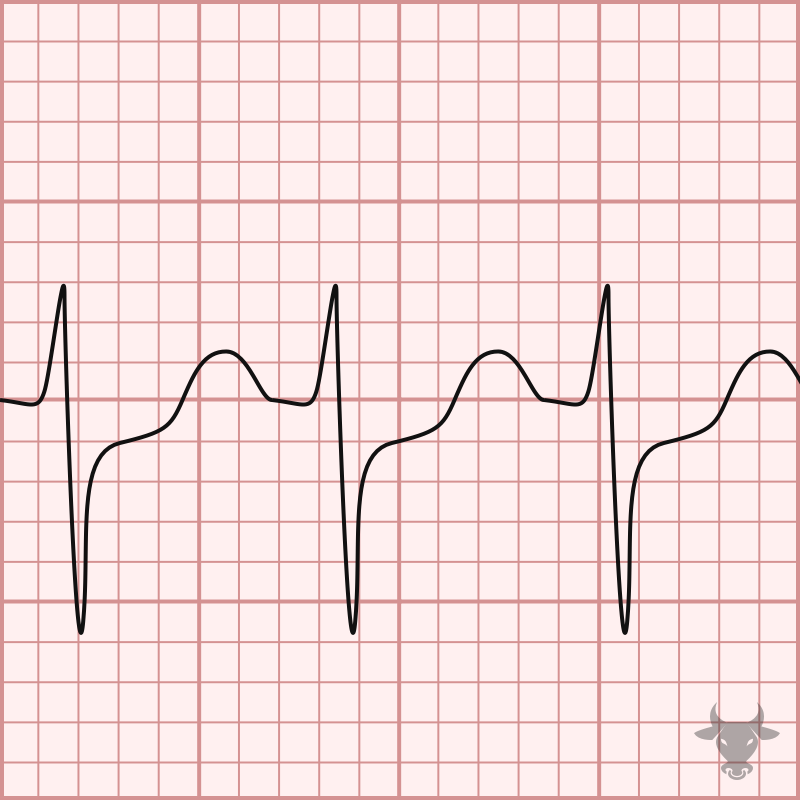
In the setting of regular, narrow complex tachycardia, P waves can aid the diagnosis but are often absent. At faster rates, sinus tachycardia can be obscured when P waves are...
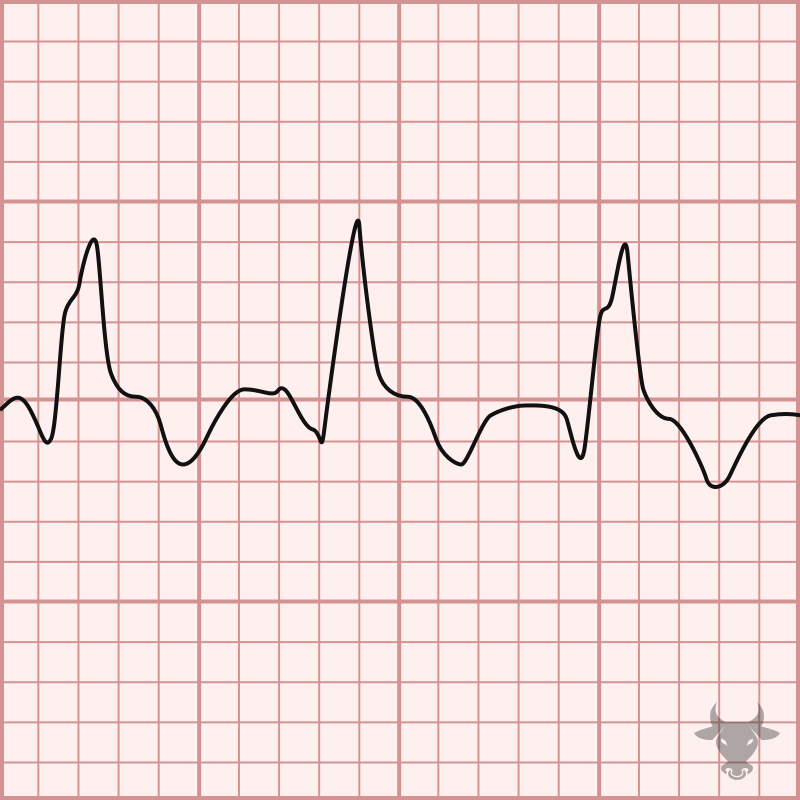
The differential for wide complex tachycardia includes ventricular tachycardia (VT), supraventricular tachycardia (SVT, e.g., atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, or atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia) with aberrancy (i.e., bundle branch block), antidromic...
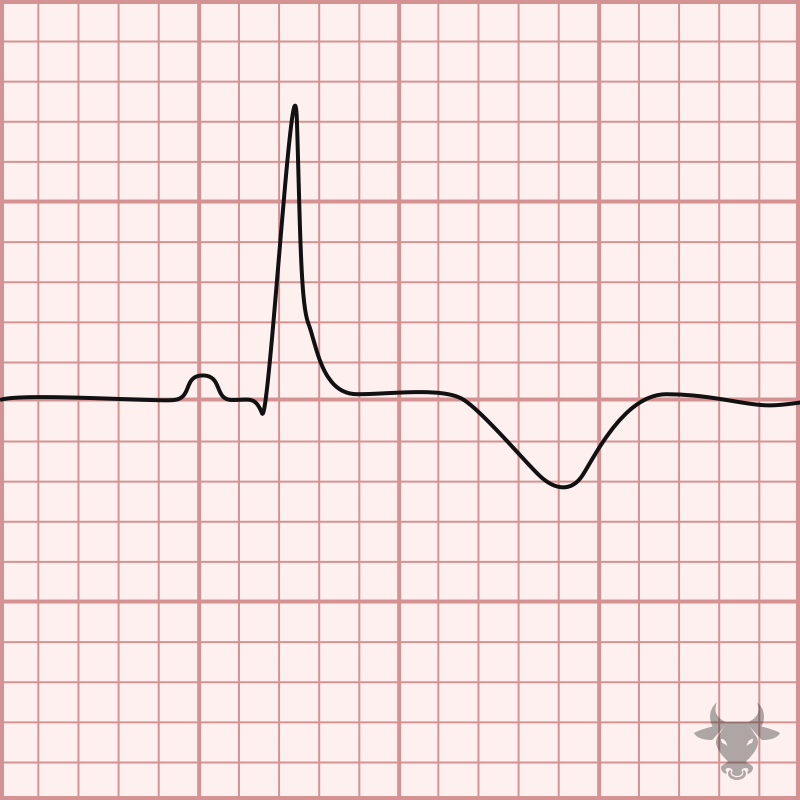
The differential diagnosis for T-wave inversions is broad and includes, but is not limited to: ischemia, hypertrophy, bundle branch blocks, early repolarization variants, persistent juvenille T wave pattern, cardiac memory,...
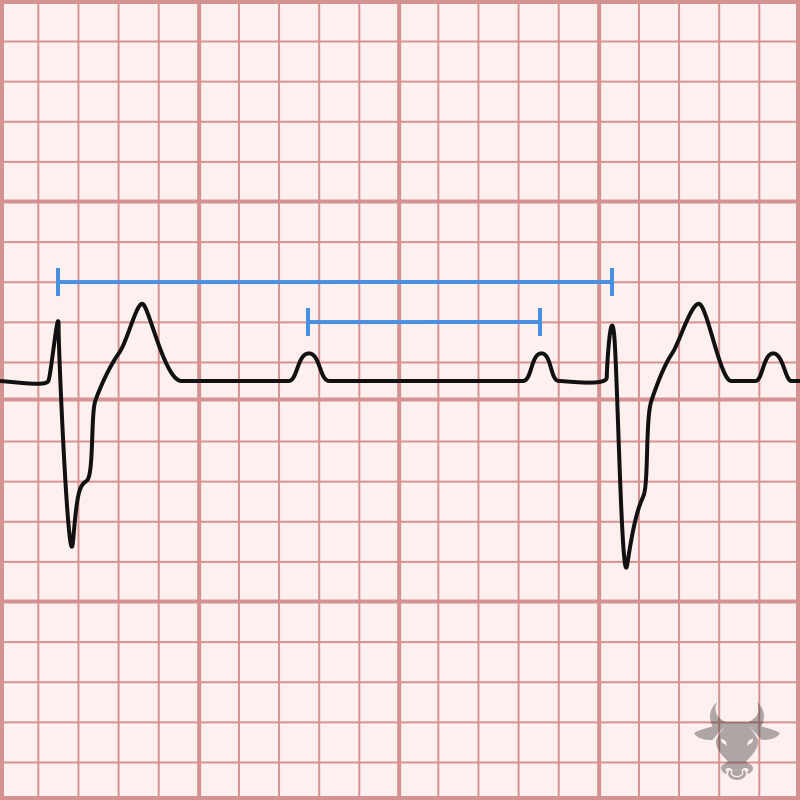
Third degree, or complete, heart block is characterized by atrioventricular dissociation - atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles and, therefore, the atria and ventricles act independently of each...
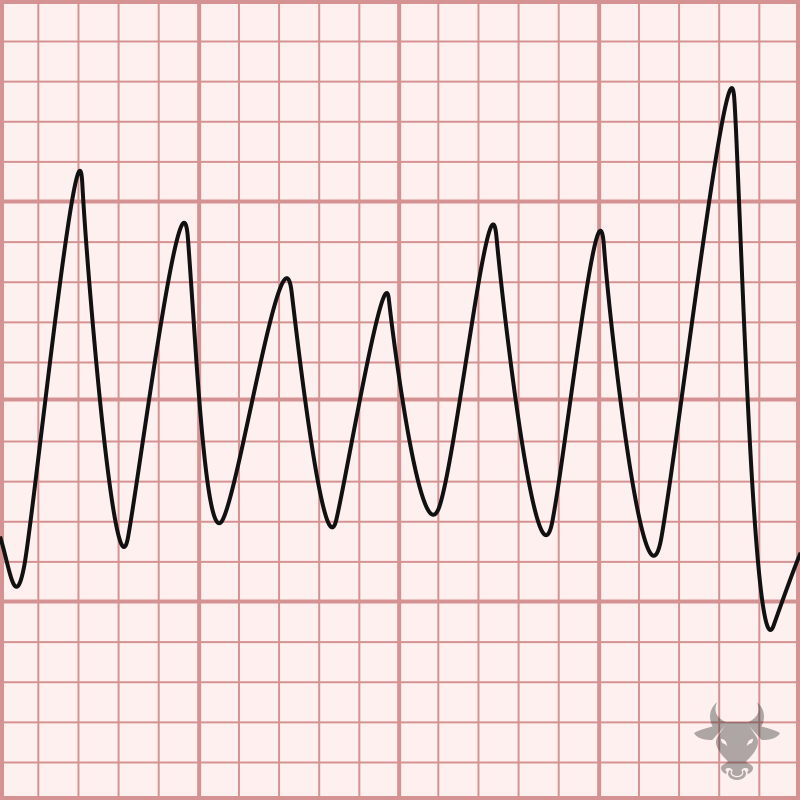
Torsades de pointes (TdP) is a specific form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia occurring in the context of QT prolongation — it has a characteristic morphology in which the QRS complexes...
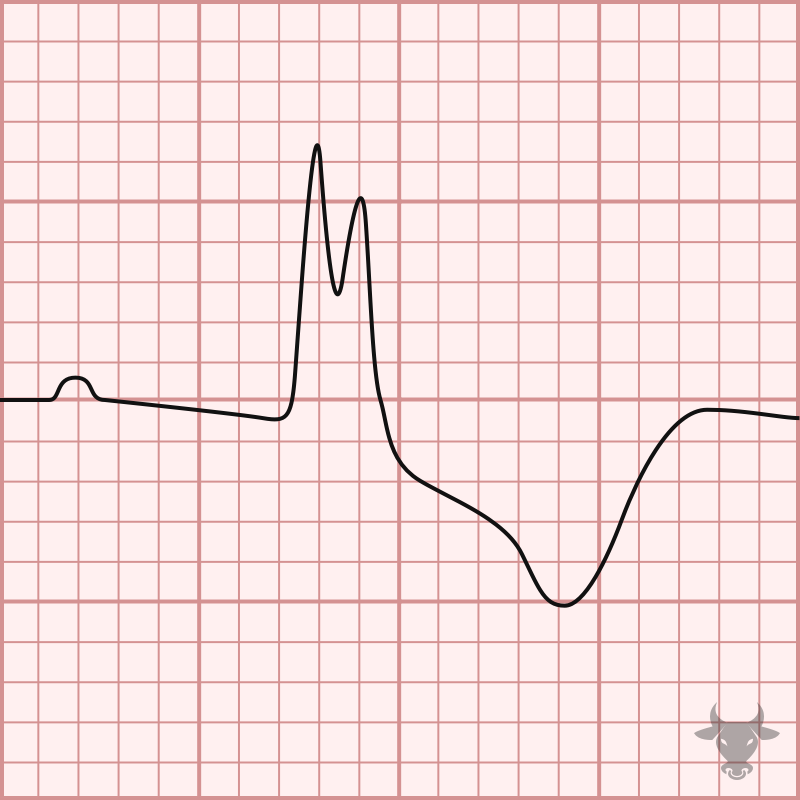
The term “trifascicular block” is a misnomer as a true block of all three fascicles (the right bundle branch, left anterior fascicle and left posterior fascicle) would result in complete...
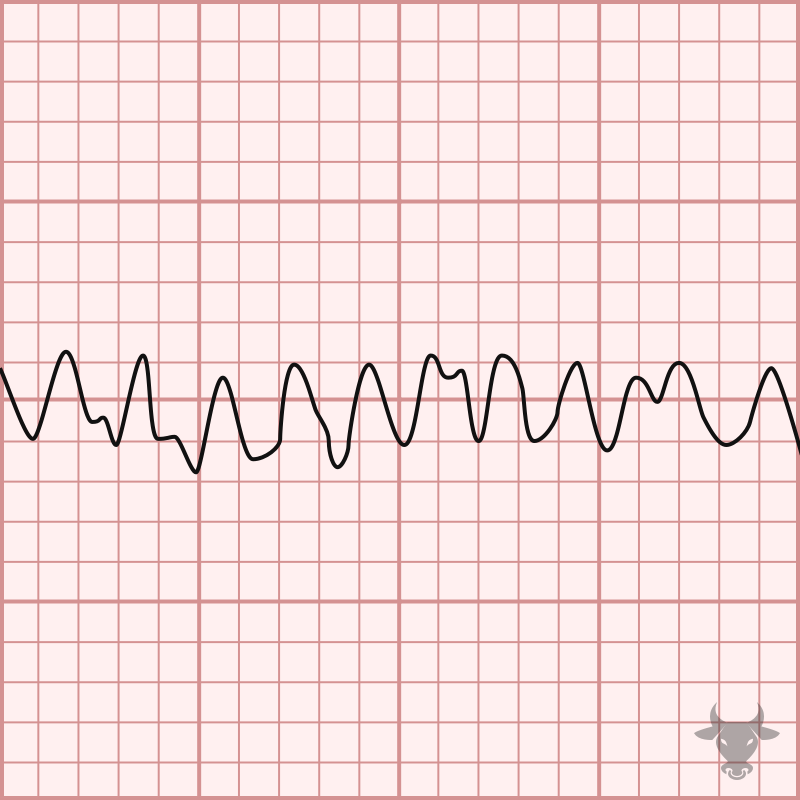
Ventricular fibrillation is a chaotic, disorganized rhythm in which the ventricles rapidly and asynchronously quiver. It is fatal and warrants immediate electrical cardioversion; otherwise, asystole is imminent. Mechanisms of ventricular...
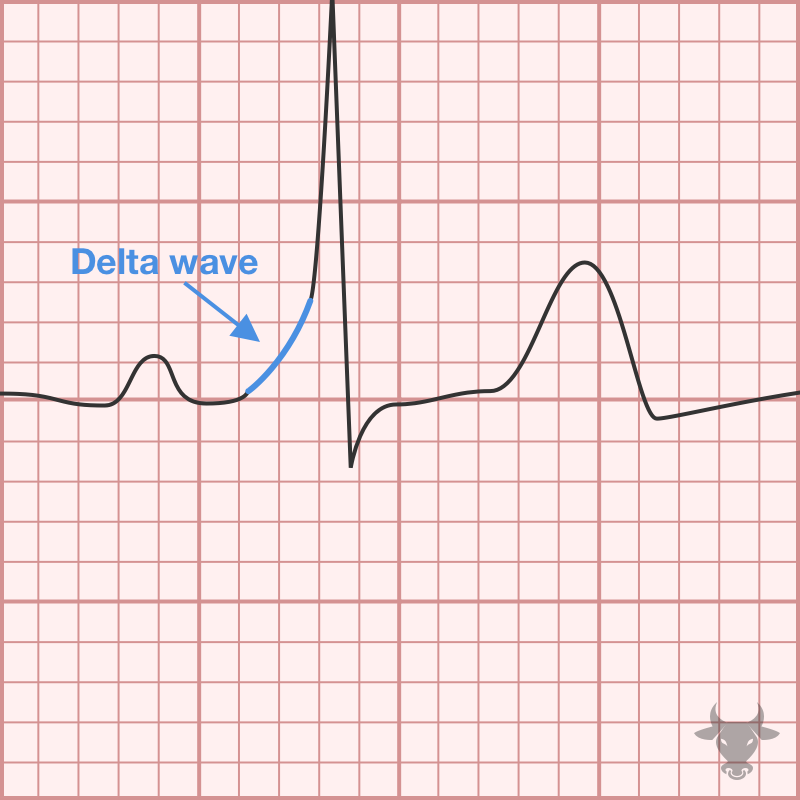
Pre-excitation is a condition in which an accessory pathway exists between the atria and the ventricles, often referred to as the bundle of Kent. When the accessory pathway conducts in...
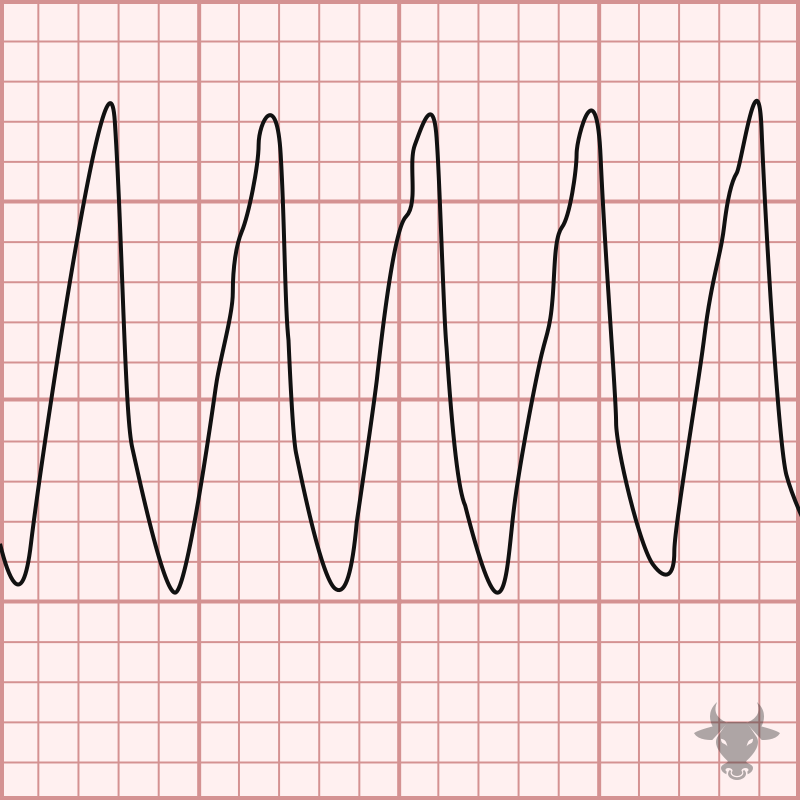
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) can be difficult to differentiate from supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy. When in doubt, it is safest to treat most wide complex tachycardia as VT. Up to 80%...
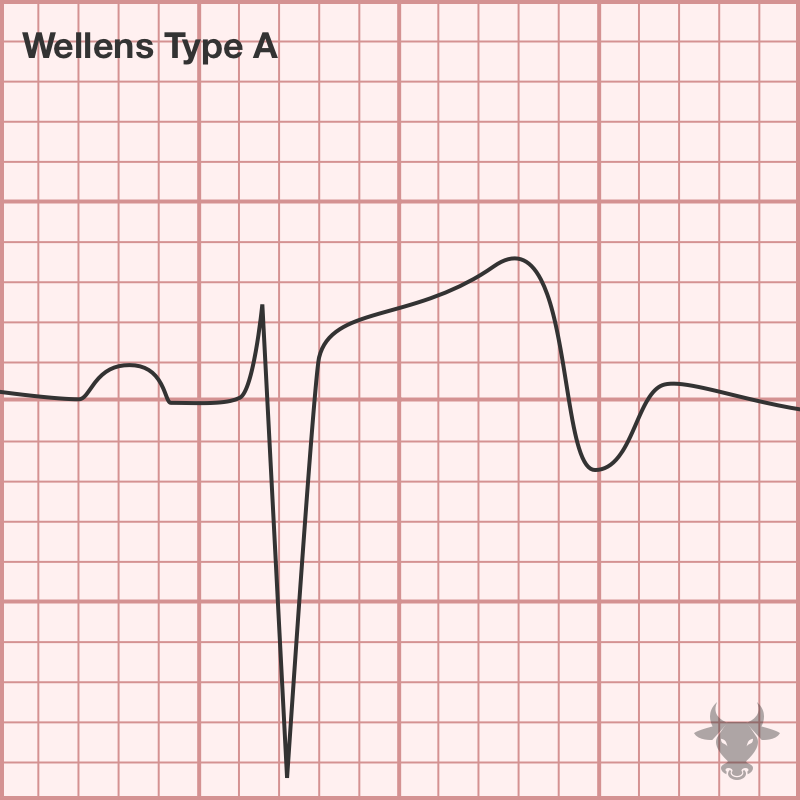
Wellens syndrome comes in two electrocardiographic varieties – biphasic T waves (up then down, type A) or deeply inverted and symmetric T waves in the anterior precordial leads V1-V3 (type...
